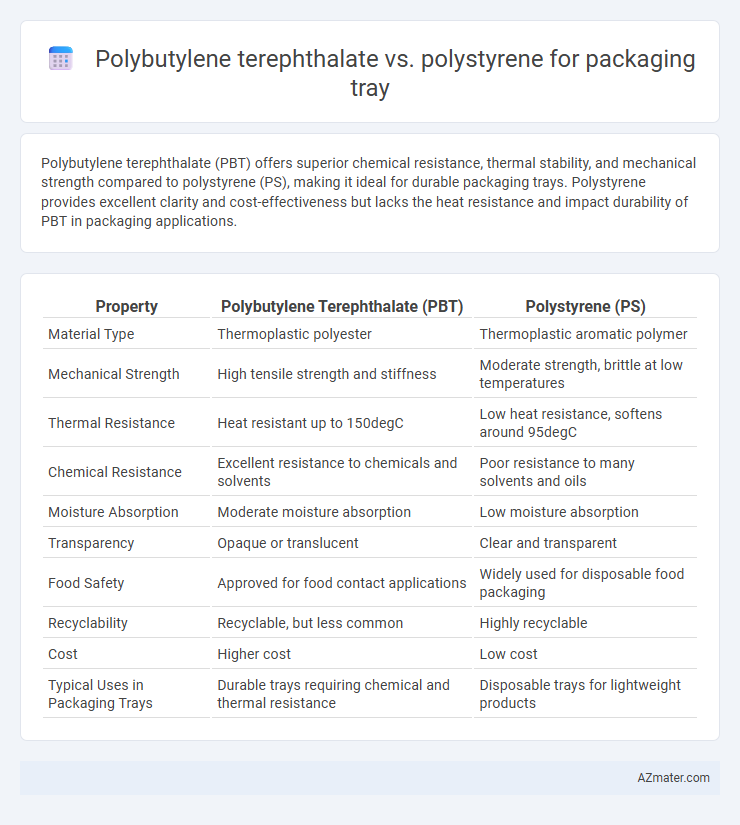
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength compared to polystyrene (PS), making it ideal for durable packaging trays. Polystyrene provides excellent clarity and cost-effectiveness but lacks the heat resistance and impact durability of PBT in packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Thermoplastic aromatic polymer |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate strength, brittle at low temperatures |
| Thermal Resistance | Heat resistant up to 150degC | Low heat resistance, softens around 95degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and solvents | Poor resistance to many solvents and oils |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate moisture absorption | Low moisture absorption |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Food Safety | Approved for food contact applications | Widely used for disposable food packaging |
| Recyclability | Recyclable, but less common | Highly recyclable |
| Cost | Higher cost | Low cost |
| Typical Uses in Packaging Trays | Durable trays requiring chemical and thermal resistance | Disposable trays for lightweight products |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate and Polystyrene
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its high mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it suitable for durable packaging trays. Polystyrene (PS) is a versatile polymer characterized by its rigidity, clarity, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in disposable packaging applications. The distinct physical and chemical properties of PBT and polystyrene influence their performance and suitability in various packaging tray designs.
Material Composition and Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polyester known for its high mechanical strength, excellent chemical resistance, and good thermal stability, making it suitable for reusable and heat-resistant packaging trays. Polystyrene (PS), an amorphous thermoplastic, offers rigidity and clarity with low moisture absorption but is more brittle and less heat-resistant compared to PBT. The material composition of PBT, consisting of repeating units of butylene terephthalate, provides enhanced durability and impact resistance, whereas PS's styrene monomers confer ease of processing and cost-effectiveness but with lower mechanical toughness and thermal performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Analysis
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to polystyrene (PS), making it more suitable for packaging trays requiring durability and repeated use. PBT's enhanced thermal stability and excellent resistance to chemical and moisture degradation contribute to its long-term structural integrity, outperforming the brittle and less heat-resistant nature of polystyrene. The combination of PBT's toughness and resilience under mechanical stress ensures optimal performance in demanding packaging applications, where PS may fail due to cracking or deformation.
Thermal Resistance: PBT vs PS
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to polystyrene (PS), with a heat deflection temperature typically around 140-160degC, making it suitable for high-temperature packaging applications. Polystyrene generally withstands temperatures up to approximately 70-100degC before deforming, limiting its use in scenarios requiring heat stability. The higher melting point and thermal stability of PBT enhance its durability and performance in packaging trays subjected to elevated heat conditions.
Chemical Resistance in Packaging Applications
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polystyrene (PS), making it more suitable for packaging trays exposed to various solvents, oils, and acidic substances. PBT maintains structural integrity and resists degradation under harsh chemical environments, ensuring product safety and longevity during storage and transportation. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, is more prone to chemical attack and deformation, limiting its use in packaging applications requiring robust chemical resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior environmental performance compared to polystyrene (PS) in packaging trays due to its higher recyclability and lower carbon footprint during production. PBT is derived from more sustainable raw materials and can be more efficiently recycled, reducing plastic waste and environmental pollution. In contrast, polystyrene generates significant greenhouse gas emissions and poses challenges in recycling, contributing to long-term environmental harm and landfill accumulation.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it cost-efficient for high-performance packaging trays despite a higher raw material price than polystyrene (PS). Polystyrene remains more widely available and affordable, dominating mass-market packaging due to its low production costs and ease of thermoforming. Market trends reveal polystyrene's extensive global distribution, while PBT is preferred for specialized applications requiring enhanced durability and heat resistance.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior food safety due to its high resistance to chemical migration and compliance with FDA and EU food contact regulations, making it ideal for packaging trays. Polystyrene (PS), while commonly used, poses challenges with potential styrene monomer migration and stricter regulatory scrutiny in food applications. PBT's thermal stability and minimal leachable substances ensure greater regulatory compliance and reduced health risks in food packaging compared to polystyrene.
Manufacturing Processes and Versatility
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is favored for packaging trays due to its excellent thermal stability and ease of injection molding, allowing precise, high-speed production suitable for complex shapes. Polystyrene (PS) offers versatility through various manufacturing techniques like thermoforming and extrusion, providing cost-effective solutions with good stiffness and clarity for simpler designs. PBT's superior resistance to chemicals and heat makes it ideal for durable packaging, while PS excels in applications requiring lightweight, rigid trays with excellent dimensional accuracy.
Final Recommendation: Choosing the Right Material for Packaging Trays
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength compared to polystyrene (PS), making it ideal for packaging trays requiring durability and high-temperature tolerance. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, is more brittle and less heat-resistant, limiting its use in heavy-duty or microwaveable packaging applications. For packaging trays demanding robustness, heat resistance, and longevity, PBT is the recommended material, whereas PS suits disposable or low-cost packaging needs.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polystyrene for Packaging tray
 azmater.com
azmater.com