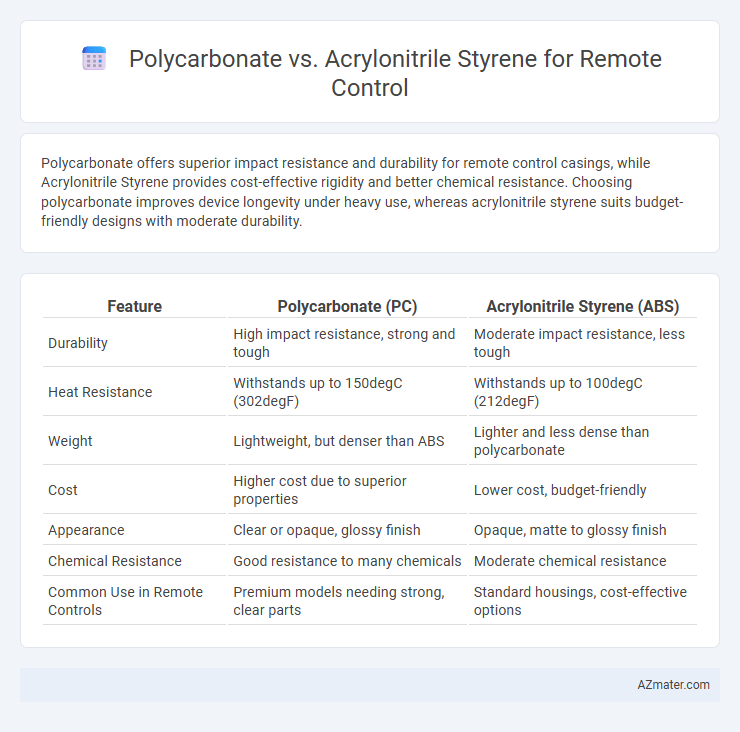
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and durability for remote control casings, while Acrylonitrile Styrene provides cost-effective rigidity and better chemical resistance. Choosing polycarbonate improves device longevity under heavy use, whereas acrylonitrile styrene suits budget-friendly designs with moderate durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polycarbonate (PC) | Acrylonitrile Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High impact resistance, strong and tough | Moderate impact resistance, less tough |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands up to 150degC (302degF) | Withstands up to 100degC (212degF) |
| Weight | Lightweight, but denser than ABS | Lighter and less dense than polycarbonate |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior properties | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Appearance | Clear or opaque, glossy finish | Opaque, matte to glossy finish |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to many chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Common Use in Remote Controls | Premium models needing strong, clear parts | Standard housings, cost-effective options |
Introduction to Remote Control Material Selection
Remote control devices demand materials that offer durability, impact resistance, and lightweight properties, making polycarbonate an ideal choice due to its high strength and transparency. Acrylonitrile styrene provides excellent rigidity and chemical resistance but generally falls short in impact resistance compared to polycarbonate. Selecting between polycarbonate and acrylonitrile styrene depends on balancing factors such as mechanical performance, weight, and cost-effectiveness in remote control applications.
Understanding Polycarbonate: Properties and Uses
Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance, high transparency, and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for remote control housings that require durability and clarity. Its lightweight yet robust nature ensures protection against drops and mechanical stress, extending the lifespan of electronic components inside. Polycarbonate's resistance to UV radiation and chemical exposure also supports remote controls used in diverse environments, enhancing overall performance and reliability.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Styrene: Characteristics and Applications
Acrylonitrile Styrene, commonly known as ABS, is a thermoplastic polymer renowned for its high impact resistance, toughness, and ease of processing, making it ideal for remote control housings. ABS offers excellent dimensional stability and good resistance to chemical corrosion and heat, ensuring durability in various environmental conditions. Its widespread use in remote controls stems from its ability to provide a balance between strength, lightweight construction, and cost-effectiveness.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Styrene, making it ideal for rugged remote control housings that require durability under repeated drops and stress. Acrylonitrile Styrene offers good stiffness and surface finish but lacks the high tensile strength and impact toughness of Polycarbonate, limiting its use in high-demand mechanical applications. Remote controls crafted from Polycarbonate benefit from enhanced resistance to cracking and deformation, ensuring longer lifespan and better performance in harsh environments.
Impact Resistance in Remote Control Housings
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Styrene in remote control housings, making it more durable against drops and collisions. Its high toughness and ability to absorb shock reduce the risk of cracking or breaking, ensuring longer-lasting protection for internal electronics. Acrylonitrile Styrene provides moderate impact resistance but is more prone to brittle failure under high-stress impacts, limiting its use in rugged remote control applications.
Heat and Chemical Resistance: Which Material Prevails?
Polycarbonate exhibits superior heat resistance, with a glass transition temperature around 147degC, making it more suitable for remote control components exposed to high temperatures. Acrylonitrile styrene, typically heat resistant up to about 100degC, tends to deform under prolonged thermal stress. Chemical resistance in polycarbonate is moderate, with vulnerability to solvents like acetone, while acrylonitrile styrene offers better resistance to oils and alkalis, influencing material choice based on the remote control's operating environment.
Weight and Ergonomics for User Experience
Polycarbonate offers a lightweight yet robust solution for remote control devices, enhancing user comfort during extended use through its exceptional impact resistance and flexibility. Acrylonitrile Styrene, while slightly heavier, provides a rigid structure that contributes to durability but may reduce ergonomic ease over long periods. Choosing polycarbonate typically results in a superior balance of weight and ergonomic handling, improving overall user experience in remote control applications.
Cost-Effectiveness in Manufacturing
Polycarbonate offers higher impact resistance and durability compared to Acrylonitrile Styrene, making it ideal for rugged remote control housings but at a significantly higher material cost. Acrylonitrile Styrene provides a more cost-effective solution with easier processing and faster cycle times, reducing overall manufacturing expenses. Manufacturers balance performance requirements against budget constraints, often choosing Acrylonitrile Styrene for cost-sensitive remote control models.
Durability and Lifespan in Real-World Use
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to Acrylonitrile Styrene (ABS), making it ideal for remote control housings exposed to drops and rough handling. Its high tensile strength and resistance to cracking ensure a longer lifespan in demanding environments, whereas ABS is more prone to wear and deformation over time. Real-world use demonstrates that polycarbonate maintains structural integrity and performance, significantly extending the functional lifespan of remote control devices.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Material for Remote Controls
Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for durable remote controls that withstand drops and daily use. Acrylonitrile Styrene, while less impact-resistant, provides a cost-effective and lightweight solution with good rigidity and ease of molding. For remote control applications requiring high durability and long-term performance, polycarbonate is the preferred choice, whereas Acrylonitrile Styrene suits budget-friendly designs with moderate durability needs.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Acrylonitrile Styrene for Remote Control
 azmater.com
azmater.com