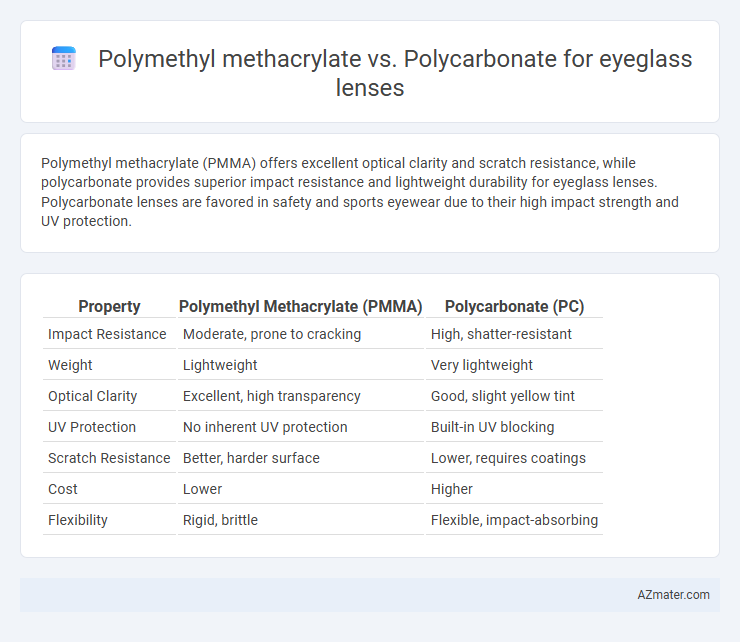
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent optical clarity and scratch resistance, while polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and lightweight durability for eyeglass lenses. Polycarbonate lenses are favored in safety and sports eyewear due to their high impact strength and UV protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, shatter-resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent, high transparency | Good, slight yellow tint |
| UV Protection | No inherent UV protection | Built-in UV blocking |
| Scratch Resistance | Better, harder surface | Lower, requires coatings |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Flexibility | Rigid, brittle | Flexible, impact-absorbing |
Introduction to Eyeglass Lens Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polycarbonate are two common materials used in eyeglass lenses, each offering unique optical and physical properties. PMMA lenses deliver excellent clarity and scratch resistance but are more brittle and heavier compared to polycarbonate lenses, which provide superior impact resistance and lightweight comfort ideal for active users and children. Advances in lens technology have enhanced polycarbonate's UV protection and durability, making it a popular choice in safety and sports eyewear.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a lightweight, transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent optical clarity and high scratch resistance, making it a popular choice for eyeglass lenses. Compared to polycarbonate, PMMA offers superior abrasion resistance but is more brittle and less impact-resistant, which can affect durability in active lifestyles. PMMA lenses typically provide sharper vision due to their higher refractive index, but they lack the inherent UV protection and flexibility found in polycarbonate lenses.
Key Properties of Polycarbonate Lenses
Polycarbonate lenses are highly favored for eyeglasses due to their exceptional impact resistance, making them ideal for safety glasses and children's eyewear. These lenses offer superior UV protection by naturally blocking 100% of harmful ultraviolet rays, which helps prevent eye damage. Although polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) lenses provide excellent optical clarity and scratch resistance, polycarbonate lenses are significantly lighter and more flexible, enhancing overall comfort and durability.
Optical Clarity Comparison: PMMA vs. Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior impact resistance but have slightly lower optical clarity compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which provides sharper vision due to its higher optical purity and minimal light distortion. PMMA lenses feature a refractive index of approximately 1.49, resulting in clearer and crisper images, while polycarbonate's refractive index of about 1.58 can cause minor chromatic aberrations. Despite this, polycarbonate is favored in safety eyewear for its durability, though PMMA remains the preferred choice for users prioritizing optimal optical clarity.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers high scratch resistance but lower impact resistance compared to polycarbonate, which is renowned for its superior impact strength, making it ideal for safety and sports eyewear. Polycarbonate lenses exhibit excellent durability under physical stress due to their ability to absorb and disperse impact forces, reducing the likelihood of lens breakage. While PMMA lenses maintain clarity and resist yellowing over time, polycarbonate provides greater overall protection in high-impact environments, enhancing wearer safety.
Weight and Comfort Factors
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) lenses are significantly lighter than polycarbonate lenses, offering enhanced comfort for extended wear but are more prone to shattering. Polycarbonate lenses provide superior impact resistance and durability, making them ideal for active lifestyles despite being slightly heavier than PMMA. Both materials balance weight and comfort differently, with polycarbonate favored for safety and PMMA for ultra-lightweight ease.
Scratch Resistance and Surface Hardness
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent scratch resistance due to its high surface hardness, making it a durable choice for eyeglass lenses. Polycarbonate lenses, while impact-resistant and lightweight, have lower surface hardness than PMMA, which makes them more prone to scratches unless coated with a protective layer. The inherent hardness difference means PMMA lenses maintain clarity longer under abrasive conditions, whereas polycarbonate requires additional treatments to achieve comparable scratch resistance.
UV Protection and Safety Considerations
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) lenses provide excellent UV protection by blocking nearly 100% of harmful ultraviolet rays, making them a safe choice for eye health. Polycarbonate lenses not only offer superior impact resistance but also inherently filter out 100% of UVA and UVB rays, enhancing safety during high-impact activities. Safety considerations favor polycarbonate for its shatterproof qualities, while PMMA lenses deliver clarity with UV defense but are more prone to cracking under stress.
Cost Analysis: PMMA vs. Polycarbonate
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) eyeglass lenses typically cost less than polycarbonate lenses, making them a budget-friendly choice for basic vision correction. Polycarbonate lenses, although pricier, offer superior impact resistance and are favored for safety and durability, often justifying the higher investment. The price difference varies by manufacturer and coating options, with polycarbonate lenses generally costing 30-50% more than PMMA lenses.
Best Use Cases and Recommendations
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity and scratch resistance, making it ideal for fashion eyewear and situations where lens quality is paramount. Polycarbonate lenses provide exceptional impact resistance and lightweight comfort, recommended for sports, safety glasses, and children's eyewear due to their durability and shatterproof properties. Choosing between PMMA and polycarbonate depends on the balance between optical quality and impact resistance required for specific activities and user needs.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com