Polyurethane offers superior elasticity and water resistance for textiles, while polyamide provides exceptional strength and abrasion resistance. Choosing between polyurethane and polyamide depends on the desired balance of flexibility and durability in fabric performance.
Table of Comparison
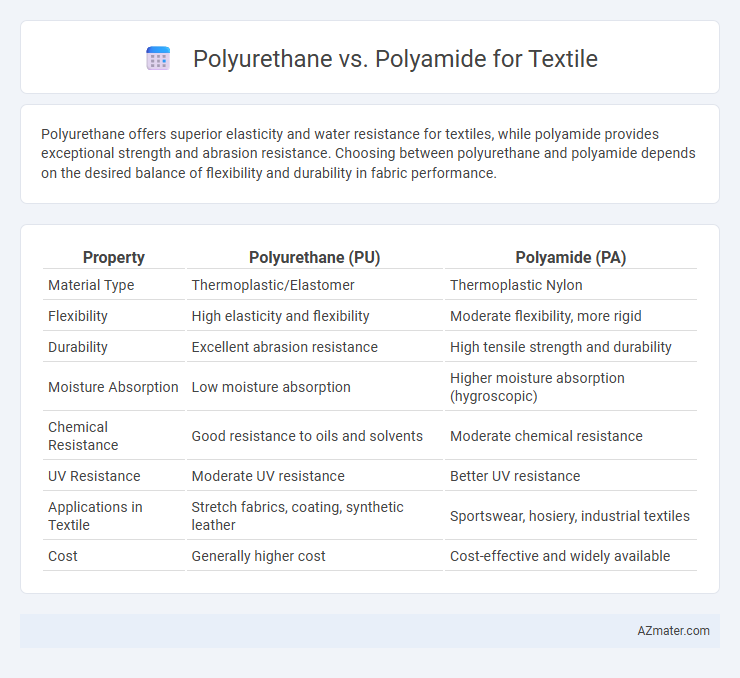
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polyamide (PA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic/Elastomer | Thermoplastic Nylon |
| Flexibility | High elasticity and flexibility | Moderate flexibility, more rigid |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance | High tensile strength and durability |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Higher moisture absorption (hygroscopic) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Moderate chemical resistance |
| UV Resistance | Moderate UV resistance | Better UV resistance |
| Applications in Textile | Stretch fabrics, coating, synthetic leather | Sportswear, hosiery, industrial textiles |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Cost-effective and widely available |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polyamide
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer widely used in textiles for its elasticity, durability, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals, making it ideal for stretch fabrics and coatings. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, offers high tensile strength, excellent elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties, which enhance fabric performance in activewear and outdoor gear. Both materials contribute unique advantages to textile applications, with polyurethane providing flexible comfort and polyamide delivering durability and resilience.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyurethane consists of repeating urethane linkages formed by the reaction of diisocyanates and polyols, offering high flexibility and elasticity ideal for stretchable textiles. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is composed of repeating amide groups derived from diamines and dicarboxylic acids, providing strong hydrogen bonding that enhances durability and abrasion resistance in fabrics. The chemical structure of polyurethane delivers superior moisture resistance, while polyamide fibers exhibit excellent tensile strength and thermal stability due to their tightly packed molecular chains.
Manufacturing Processes
Polyurethane and polyamide differ significantly in textile manufacturing processes, with polyurethane typically produced through a chemical reaction between diisocyanates and polyols, allowing for flexible film and coating applications. Polyamide fibers, commonly known as nylon, are synthesized via polycondensation or ring-opening polymerization, forming strong, durable fibers suited for spinning and weaving. Manufacturing polyurethane often involves casting or coating techniques, whereas polyamide processing relies on melt spinning to create continuous filaments for fabric construction.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Polyurethane exhibits superior elasticity and abrasion resistance, making it highly durable for textiles exposed to frequent stretching and friction. Polyamide fibers offer excellent tensile strength and moisture resistance, contributing to long-lasting fabric performance under heavy wear conditions. Comparing both materials, polyurethane excels in flexibility and impact resistance, while polyamide stands out for its strong structural integrity and resilience against environmental degradation.
Flexibility and Comfort in Textiles
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and stretchability, making it ideal for activewear and garments that require dynamic movement. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, provides excellent durability and moisture-wicking properties but tends to be less elastic, which may limit comfort in tight-fitting applications. Combining polyurethane's elasticity with polyamide's strength can enhance both comfort and flexibility in advanced textile blends.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
Polyurethane offers superior moisture resistance due to its dense, non-porous structure that prevents water penetration, making it ideal for waterproof textile applications. Polyamide, while less water-resistant, excels in breathability because of its fibrous, porous nature that facilitates moisture vapor transmission, enhancing wearer comfort. Selecting between polyurethane and polyamide depends on the balance required between waterproofing and breathability in textile performance.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Polyurethane and polyamide are widely used in the textile industry for their unique properties and versatility. Polyurethane offers exceptional elasticity, abrasion resistance, and moisture-wicking capabilities, making it ideal for sportswear, swimwear, and stretch fabrics. Polyamide provides high tensile strength, durability, and lightweight characteristics, which are crucial for outdoor gear, lingerie, and performance apparel.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is derived from petrochemicals and involves energy-intensive production processes with significant greenhouse gas emissions, whereas polyurethane can be produced with bio-based polyols, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Polyamide fibers are less biodegradable and persist longer in the environment, contributing to microplastic pollution, while certain formulations of polyurethane, especially water-based dispersions, offer improved biodegradability and recyclability. Sustainable textile innovations favor bio-based polyurethane for lower carbon footprints and enhanced lifecycle management compared to conventional polyamide, promoting circular economy principles in fabric manufacturing.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Polyurethane fabrics generally offer a lower initial cost compared to polyamide, making them attractive for budget-conscious textile manufacturers. Market trends indicate rising demand for polyamide due to its superior durability and abrasion resistance, which justifies its higher price point in performance-focused applications. Cost analysis reveals that while polyurethane provides affordability, polyamide's lifecycle cost-effectiveness is driving increased adoption in high-end activewear and technical textiles.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Textile Needs
Polyurethane offers excellent flexibility, water resistance, and durability, making it ideal for activewear and outdoor textiles requiring stretch and weather protection. Polyamide, known for its strength, abrasion resistance, and lightweight nature, performs well in high-performance sportswear and industrial fabrics that demand durability and quick-drying properties. Selecting between polyurethane and polyamide depends on the specific textile application, balancing factors like elasticity, moisture management, and wear resistance to optimize performance and comfort.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyamide for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com