Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and resilience for packaging sensitive items, while polystyrene foam provides lightweight, rigid protection with excellent impact resistance. Polyurethane is preferred for delicate electronics, whereas polystyrene is commonly used for insulating and structural packaging applications.
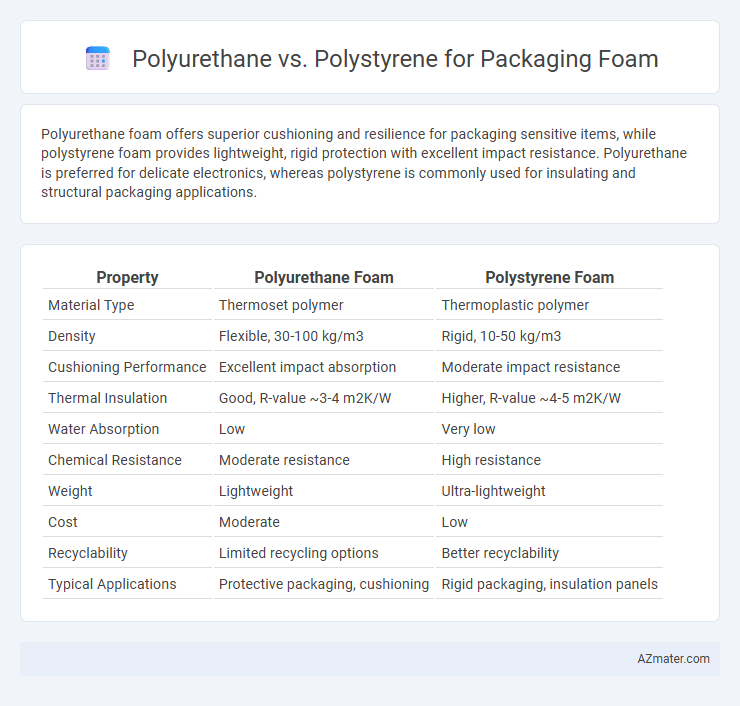
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoset polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | Flexible, 30-100 kg/m3 | Rigid, 10-50 kg/m3 |
| Cushioning Performance | Excellent impact absorption | Moderate impact resistance |
| Thermal Insulation | Good, R-value ~3-4 m2K/W | Higher, R-value ~4-5 m2K/W |
| Water Absorption | Low | Very low |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | High resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra-lightweight |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options | Better recyclability |
| Typical Applications | Protective packaging, cushioning | Rigid packaging, insulation panels |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Packaging foams such as polyurethane and polystyrene serve critical roles in protecting goods during transit by providing cushioning and shock absorption. Polyurethane foam, known for its elasticity and durability, offers superior impact resistance and thermal insulation, making it ideal for fragile or temperature-sensitive items. Polystyrene foam, recognized for its lightweight and rigid structure, excels in cost-effective packaging solutions and is widely used for protecting electronics and food packaging.
Overview of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam is a versatile packaging material known for its excellent cushioning properties and high impact resistance, making it ideal for protecting fragile items during shipping. It offers superior flexibility and durability compared to polystyrene, allowing it to absorb shocks effectively while maintaining its shape under pressure. Its ability to be molded into custom shapes ensures optimal product protection and efficient space utilization in packaging applications.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam is a lightweight, rigid material widely used in packaging for its excellent cushioning and insulating properties. It is composed of expanded beads that create a closed-cell structure, providing impact resistance and moisture barrier capabilities. Polystyrene foam is favored for cost-effectiveness, ease of molding, and its ability to protect fragile items during shipping.
Key Differences: Polyurethane vs Polystyrene
Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and cushioning compared to polystyrene, which is rigid and brittle, making polyurethane ideal for delicate or irregular-shaped items. Polystyrene excels in lightweight, cost-effective packaging with excellent thermal insulation, whereas polyurethane provides better durability and resistance to compression. The chemical composition of polyurethane, derived from polyols and isocyanates, results in a more resilient foam structure than the styrene monomer-based polystyrene.
Cushioning Performance Comparison
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning performance compared to polystyrene due to its higher resilience and energy absorption capabilities, making it ideal for protecting fragile items during transit. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, provides less shock absorption and is more prone to cracking under pressure. The enhanced elasticity and durability of polyurethane result in better impact resistance and long-term protection in packaging applications.
Insulation Properties for Packaging
Polyurethane foam offers superior insulation properties compared to polystyrene, with a higher R-value per inch, making it more effective for temperature-sensitive packaging. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, provides lower thermal resistance and is less efficient at maintaining consistent temperatures during transit. The denser cell structure of polyurethane enhances its ability to protect products from thermal fluctuations, crucial for pharmaceuticals and perishable goods packaging.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning properties but poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and reliance on petroleum-based chemicals. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, contributes heavily to plastic pollution and is difficult to recycle, often ending up in landfills or oceans. Emerging bio-based alternatives and advances in recyclable formulations for both materials aim to reduce ecological footprints and enhance sustainability in packaging applications.
Cost Considerations for Businesses
Polyurethane foam typically costs more than polystyrene due to its superior durability and cushioning properties, making it a preferred choice for packaging fragile items despite the higher expense. Polystyrene is more budget-friendly and widely used for cost-sensitive applications, offering adequate protection for less delicate products. Businesses must balance initial material costs with long-term benefits such as damage reduction and product safety when choosing between polyurethane and polystyrene packaging foams.
Common Applications and Industries
Polyurethane foam is widely used in automotive seating, furniture cushioning, and thermal insulation in refrigeration due to its high flexibility and durability. Polystyrene foam finds common applications in food packaging, disposable cups, and electronic product cushioning because of its lightweight and excellent shock absorption properties. Both materials serve critical roles in packaging industries, with polyurethane preferred for heavy-duty protection and polystyrene favored for cost-effective, lightweight solutions.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Polyurethane offers superior cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for packaging fragile items requiring shock absorption, while polystyrene excels in rigid, lightweight protection for less delicate goods. Evaluate factors such as impact resistance, insulation properties, and environmental conditions to determine the best foam material for your specific product protection. Cost-effectiveness and recyclability also play a crucial role in selecting between polyurethane and polystyrene packaging foam.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polystyrene for Packaging Foam
 azmater.com
azmater.com