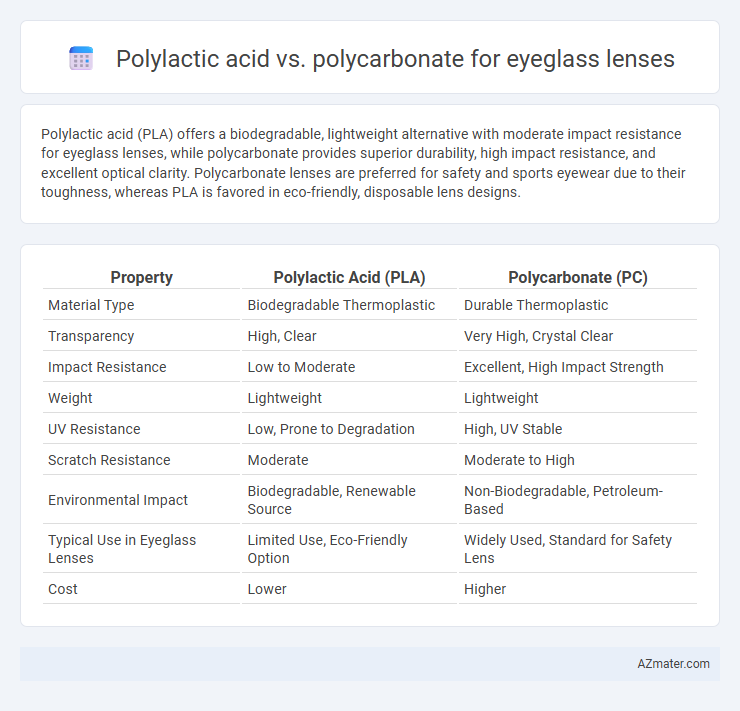
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers a biodegradable, lightweight alternative with moderate impact resistance for eyeglass lenses, while polycarbonate provides superior durability, high impact resistance, and excellent optical clarity. Polycarbonate lenses are preferred for safety and sports eyewear due to their toughness, whereas PLA is favored in eco-friendly, disposable lens designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable Thermoplastic | Durable Thermoplastic |
| Transparency | High, Clear | Very High, Crystal Clear |
| Impact Resistance | Low to Moderate | Excellent, High Impact Strength |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| UV Resistance | Low, Prone to Degradation | High, UV Stable |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, Renewable Source | Non-Biodegradable, Petroleum-Based |
| Typical Use in Eyeglass Lenses | Limited Use, Eco-Friendly Option | Widely Used, Standard for Safety Lens |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polylactic Acid and Polycarbonate Eyeglass Lenses
Polylactic acid (PLA) eyeglass lenses are biodegradable and derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials. Polycarbonate lenses are known for their high impact resistance, lightweight nature, and UV protection, making them durable and suitable for active lifestyles. Both materials provide unique benefits, with PLA focusing on sustainability and polycarbonate prioritizing strength and safety.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch, featuring a semi-crystalline structure that offers moderate rigidity and transparency for eyeglass lenses. Polycarbonate (PC), a synthetic polymer made from bisphenol A and phosgene, possesses an amorphous structure with exceptional impact resistance, high optical clarity, and superior durability compared to PLA. The structural differences between PLA's semi-crystalline arrangement and PC's amorphous matrix result in varying mechanical properties, with PC lenses providing enhanced shatter resistance and longevity over PLA alternatives.
Optical Clarity and Visual Performance
Polylactic acid (PLA) lenses offer excellent optical clarity with high light transmittance around 92-94%, providing sharp and vibrant visual performance suitable for everyday use. Polycarbonate lenses, known for impact resistance, maintain optical clarity with light transmittance approximately 88-90%, slightly lower than PLA but superior in safety and durability. The choice between PLA and polycarbonate involves balancing PLA's superior optical clarity against polycarbonate's enhanced impact resistance for eyeglass lenses.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polylactic acid (PLA) eyeglass lenses offer moderate impact resistance but tend to be less durable compared to polycarbonate lenses, which exhibit superior impact strength and high resistance to shattering. Polycarbonate is favored in eyewear for its ability to withstand significant impact without cracking, making it ideal for safety glasses and children's eyewear. While PLA is biodegradable and environmentally friendly, its lower durability and impact resistance limit its use in high-performance eyeglass lenses.
Weight and Comfort on Wear
Polylactic acid (PLA) eyeglass lenses offer significantly lighter weight compared to polycarbonate lenses, enhancing overall comfort during extended wear by reducing pressure on the nose and ears. PLA's bioplastic composition allows it to be more breathable and flexible, contributing to less fatigue and irritation. In contrast, polycarbonate lenses, though impact-resistant, tend to be denser and heavier, which may cause discomfort for prolonged use.
Environmental Sustainability and Biodegradability
Polylactic acid (PLA) eyeglass lenses offer superior environmental sustainability through their derivation from renewable resources such as corn starch and their ability to biodegrade under industrial composting conditions within months. In contrast, polycarbonate lenses are made from petroleum-based plastics that persist in the environment and require centuries to decompose, contributing to long-term plastic pollution. The biodegradable nature of PLA makes it a more eco-friendly choice for eyeglass lenses, reducing plastic waste and carbon footprint compared to the conventional polycarbonate material.
UV Protection and Safety Performance
Polylactic acid (PLA) lenses offer moderate UV protection by blocking approximately 85-90% of UV radiation, while polycarbonate lenses provide superior UV blocking, filtering nearly 100% of UVA and UVB rays, making them ideal for eye safety. Polycarbonate's high impact resistance and shatterproof nature significantly enhance safety performance compared to PLA, which is more prone to cracking under stress. For eyeglass lenses requiring robust UV protection and impact durability, polycarbonate remains the preferred material in optical applications.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polylactic acid (PLA) eyeglass lenses offer cost efficiency due to their lower raw material and production expenses compared to polycarbonate lenses, making them a budget-friendly option for eco-conscious consumers. While polycarbonate lenses dominate market availability owing to their widespread adoption in protective eyewear and advanced optical clarity, PLA lenses are emerging in niche markets driven by sustainability trends. The balance between PLA's affordability and growing presence versus polycarbonate's established market share and performance highlights key considerations for manufacturers and consumers prioritizing cost-effective, accessible eyewear materials.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers excellent customization possibilities due to its biodegradable nature and compatibility with 3D printing technologies, enabling intricate and personalized eyeglass lens designs. Polycarbonate provides superior design flexibility through its high impact resistance and ability to be easily molded into various shapes, making it ideal for durable, versatile lenses. Both materials support tailored lens production, but PLA excels in eco-friendly, innovative designs, while polycarbonate ensures robust, adaptable eyewear solutions.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Eyeglass Lenses
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers a biodegradable and lightweight option for eyeglass lenses, emphasizing environmental sustainability and comfort, while polycarbonate lenses provide superior impact resistance and scratch protection ideal for active lifestyles. Polycarbonate is highly preferred for safety eyewear and sports glasses due to its toughness and UV protection, whereas PLA suits those prioritizing eco-friendly materials with moderate optical clarity. Choosing the best material depends on balancing durability requirements, environmental impact, and optical performance specific to daily use and lifestyle needs.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com