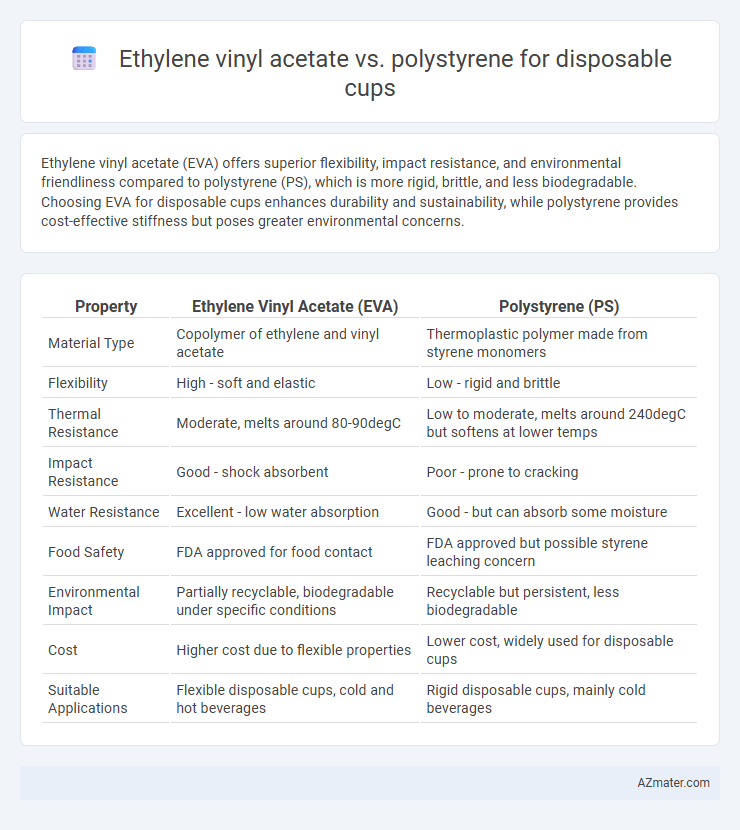
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and environmental friendliness compared to polystyrene (PS), which is more rigid, brittle, and less biodegradable. Choosing EVA for disposable cups enhances durability and sustainability, while polystyrene provides cost-effective stiffness but poses greater environmental concerns.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Thermoplastic polymer made from styrene monomers |
| Flexibility | High - soft and elastic | Low - rigid and brittle |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, melts around 80-90degC | Low to moderate, melts around 240degC but softens at lower temps |
| Impact Resistance | Good - shock absorbent | Poor - prone to cracking |
| Water Resistance | Excellent - low water absorption | Good - but can absorb some moisture |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved but possible styrene leaching concern |
| Environmental Impact | Partially recyclable, biodegradable under specific conditions | Recyclable but persistent, less biodegradable |
| Cost | Higher cost due to flexible properties | Lower cost, widely used for disposable cups |
| Suitable Applications | Flexible disposable cups, cold and hot beverages | Rigid disposable cups, mainly cold beverages |
Introduction to Disposable Cup Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polystyrene (PS) are widely used materials in disposable cup manufacturing due to their distinct properties. EVA offers flexibility, durability, and resistance to cracking, making it suitable for both hot and cold beverages, while polystyrene provides rigidity, excellent insulation, and cost-effectiveness, commonly found in foam cups for temperature retention. Selection between EVA and polystyrene depends on factors such as beverage temperature, environmental impact considerations, and the desired cup performance.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a flexible, rubber-like polymer widely used in disposable cups due to its excellent clarity, toughness, and resistance to impact and stress cracking. EVA offers superior moisture and chemical resistance compared to Polystyrene, making it more suitable for hot and cold beverages while enhancing user safety and environmental compliance. Its lightweight nature and excellent sealing properties contribute to the growing preference for EVA in food packaging applications over traditional Polystyrene.
Understanding Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its rigidity, clarity, and ease of molding, making it a popular choice for disposable cups. Its low cost and excellent insulating properties help maintain beverage temperature while providing structural stability. However, PS is brittle and less environmentally friendly compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), which offers greater flexibility and biodegradability advantages in disposable cup applications.
Manufacturing Processes of EVA and Polystyrene Cups
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) disposable cups are typically manufactured using injection molding or extrusion processes, which allow for flexibility and durability in the final product due to EVA's elastomeric properties. Polystyrene cups are produced mainly through thermoforming or injection molding, where heated polystyrene sheets are shaped into cups; this process is faster but results in more rigid and brittle cups compared to EVA. Manufacturing EVA cups demands precise temperature control to maintain material elasticity, while polystyrene cup production emphasizes rapid cooling to retain structural integrity and reduce cycle times.
Physical Properties Comparison: EVA vs Polystyrene
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) exhibits superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polystyrene, which is more rigid and brittle. EVA has a lower density (0.93-0.96 g/cm3) than polystyrene (1.04-1.06 g/cm3), contributing to lighter disposable cups with effective cushioning properties. Thermal resistance also favors EVA, offering better heat tolerance up to 90degC, whereas polystyrene cups typically soften around 70degC, affecting their performance in hot beverage applications.
Insulation and Heat Resistance Performance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior insulation and heat resistance compared to polystyrene, making it more effective for disposable cups used with hot beverages. EVA's flexible molecular structure provides enhanced thermal stability and prevents heat transfer, maintaining beverage temperature longer while protecting users' hands from heat. Polystyrene, while lightweight and cost-effective, has lower heat resistance and insulation properties, often resulting in quicker heat loss and potential discomfort when holding hot drinks.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers better flexibility and biodegradability compared to polystyrene (PS), which is widely criticized for its long decomposition time and environmental persistence. EVA's partial biodegradability contributes to reduced landfill accumulation, while polystyrene's dense molecular structure hinders recycling efforts and often results in contamination of recycling streams. Consumers and manufacturers favor EVA cups for their improved environmental footprint, although widespread recycling infrastructure for both materials remains limited, necessitating advancements in waste management technologies.
Cost Analysis: EVA vs Polystyrene Cups
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) cups generally have higher raw material costs compared to polystyrene cups, impacting overall production expenses. Polystyrene cups benefit from lower material prices and established mass production techniques, making them a cost-effective choice for disposable applications. However, EVA offers enhanced flexibility and durability, which can justify the initially higher investment in specific use cases requiring improved cup strength.
Consumer Safety and Food Contact Suitability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and chemical resistance, making it less likely to leach harmful substances into beverages compared to polystyrene, which can release styrene monomers when in contact with hot liquids, raising consumer safety concerns. EVA is FDA-approved for food contact applications, exhibiting excellent thermal stability and minimal odor, whereas polystyrene, while commonly used, has limited heat resistance and potential risks associated with styrene migration during prolonged exposure to heat. Selecting EVA for disposable cups enhances food safety compliance and reduces the risk of toxic compound exposure, aligning with stringent consumer protection standards.
Conclusion: Which Material is Better for Disposable Cups?
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and environmental friendliness compared to polystyrene, which is rigid and prone to brittle fracture. EVA's biodegradability and lower toxicity make it a more sustainable choice for disposable cups, reducing ecological footprint and health risks. Polystyrene remains cost-effective but falls short in durability and environmental impact, positioning EVA as the better overall material for disposable cup applications.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polystyrene for Disposable Cup
 azmater.com
azmater.com