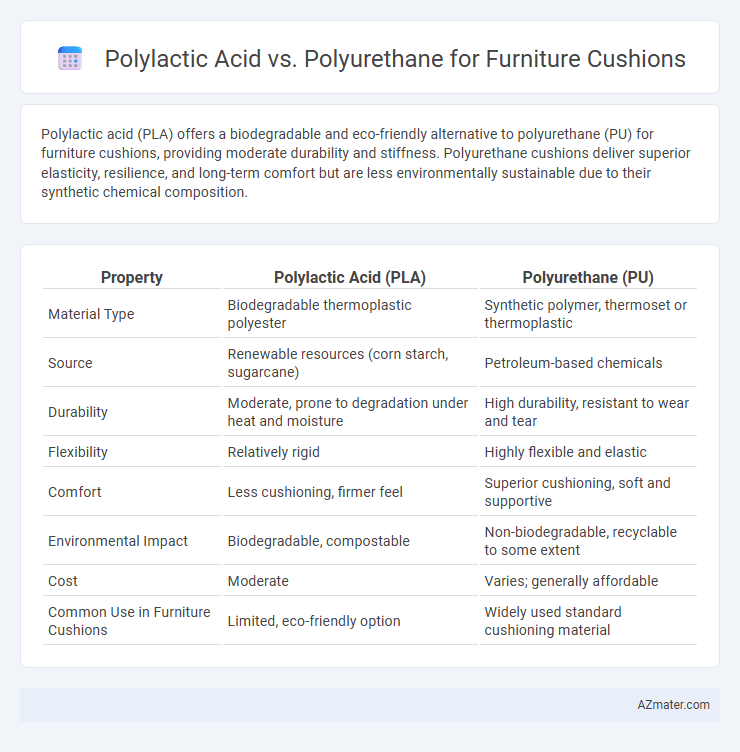
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to polyurethane (PU) for furniture cushions, providing moderate durability and stiffness. Polyurethane cushions deliver superior elasticity, resilience, and long-term comfort but are less environmentally sustainable due to their synthetic chemical composition.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable thermoplastic polyester | Synthetic polymer, thermoset or thermoplastic |
| Source | Renewable resources (corn starch, sugarcane) | Petroleum-based chemicals |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to degradation under heat and moisture | High durability, resistant to wear and tear |
| Flexibility | Relatively rigid | Highly flexible and elastic |
| Comfort | Less cushioning, firmer feel | Superior cushioning, soft and supportive |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable to some extent |
| Cost | Moderate | Varies; generally affordable |
| Common Use in Furniture Cushions | Limited, eco-friendly option | Widely used standard cushioning material |
Introduction to Polylactic Acid and Polyurethane
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, known for its eco-friendly properties and ability to decompose under industrial composting conditions. Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile synthetic polymer widely used in furniture cushions for its excellent durability, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion and moisture. PLA offers an environmentally sustainable alternative to conventional polyurethane, but PU remains preferred for high-performance cushioning due to its superior comfort and longevity.
Material Composition and Sourcing
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived primarily from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, offering an eco-friendly alternative for furniture cushion foams by reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Polyurethane (PU), composed of synthetic polymers formed from petrochemical-based polyols and isocyanates, is widely used for its durability and flexibility but involves non-renewable resource extraction and complex chemical processing. Sourcing PLA supports sustainable agriculture and closed-loop recycling systems, whereas polyurethane production depends on industrial-scale petroleum refining with higher environmental impact.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers a biodegradable alternative to traditional polyurethane foam, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions during production. Polyurethane, commonly used in furniture cushions, is petroleum-based, non-biodegradable, and contributes to environmental pollution through toxic chemical release and challenges in recycling. Choosing PLA cushions enhances sustainability by promoting compostability and reducing landfill waste, supporting a circular economy in the furniture industry.
Durability and Longevity in Furniture Use
Polylactic acid (PLA) cushions offer moderate durability with natural biodegradability but tend to degrade faster under prolonged stress and moisture compared to polyurethane, which provides superior resilience and long-lasting comfort in furniture applications. Polyurethane foam is highly resistant to wear, compression, and environmental factors, ensuring extended cushioning performance and structural integrity over years of regular use. Choosing polyurethane enhances furniture longevity, while PLA suits eco-friendly designs prioritizing sustainability over extended durability.
Comfort and Support Properties
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers moderate firmness and breathability, making it suitable for cushions requiring eco-friendly, lightweight comfort but less ideal for prolonged support. Polyurethane foam excels in durability and high resilience, providing superior comfort and consistent support, essential for long-term use in furniture cushions. The choice between PLA and polyurethane depends on prioritizing sustainable materials versus enhanced cushioning performance.
Manufacturing Process and Scalability
Polylactic acid (PLA) is derived from renewable resources through fermentation and polymerization, enabling eco-friendly manufacturing but facing challenges in scalability due to slower production rates and higher material costs. Polyurethane (PU) is produced via chemical reactions between polyols and isocyanates, allowing fast, highly scalable manufacturing with versatile formulations suited for mass production of furniture cushions. While PLA offers biocompatibility and biodegradability, PU excels in process efficiency and large-scale adaptability within the furniture industry.
Cost Comparison for Furniture Applications
Polylactic acid (PLA) cushions generally have a higher upfront cost compared to polyurethane (PU) foam due to the bio-based raw materials and sustainable production processes. Polyurethane remains more cost-effective for large-scale furniture applications, offering lower material and manufacturing expenses. However, PLA's price gap is narrowing as demand for eco-friendly furniture materials grows and production technologies advance.
Health and Safety Considerations
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam offers superior health benefits for furniture cushions due to its biodegradable, non-toxic composition derived from renewable resources, reducing exposure to harmful chemicals and off-gassing compared to traditional polyurethane foam. Polyurethane cushions often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and flame retardants that can contribute to indoor air pollution and potential respiratory issues. Choosing PLA cushions supports hypoallergenic environments and lowers the risk of chemical sensitivities, making it a safer option for health-conscious consumers.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Polylactic acid (PLA) cushions require gentle cleaning with mild soap and cold water to prevent degradation, as they are biodegradable and prone to damage from heat and harsh chemicals. Polyurethane cushions offer more durability with easier maintenance, tolerating spot cleaning, exposure to higher temperatures, and common household cleaners without losing integrity. Choosing between PLA and polyurethane for furniture cushions depends on balancing eco-friendliness with practicality in routine care and longevity.
Future Trends in Furniture Cushion Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) is gaining traction in furniture cushions due to its biodegradability and renewable sourcing, aligning with growing environmental sustainability trends. Polyurethane remains popular for its durability and superior comfort but faces challenges from increasing regulatory pressure on petrochemical-based foams. Future trends indicate a shift towards bio-based, compostable materials like PLA composites enhanced for resilience, aiming to balance comfort, environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness in furniture cushioning.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Polyurethane for Furniture Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com