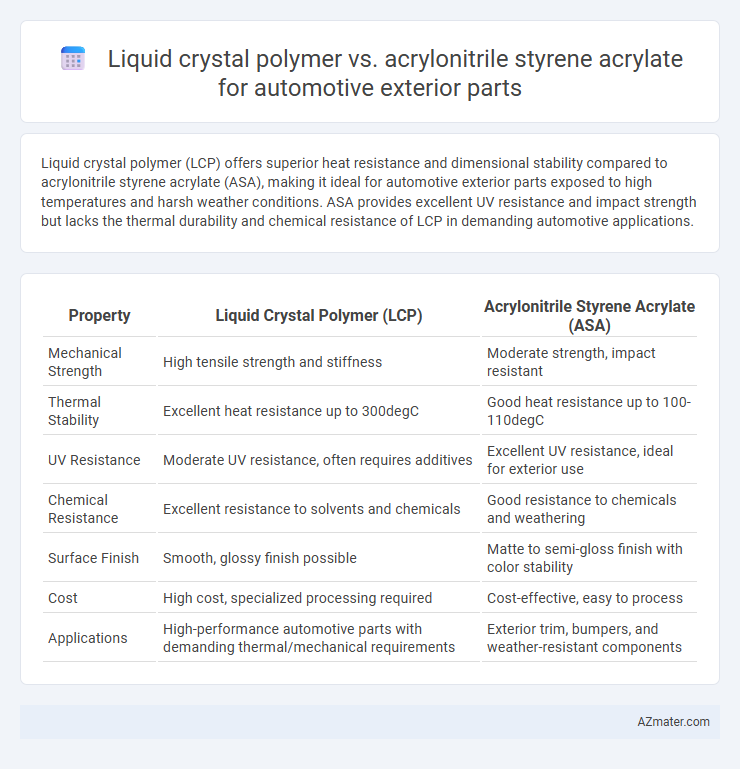
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior heat resistance and dimensional stability compared to acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA), making it ideal for automotive exterior parts exposed to high temperatures and harsh weather conditions. ASA provides excellent UV resistance and impact strength but lacks the thermal durability and chemical resistance of LCP in demanding automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate strength, impact resistant |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent heat resistance up to 300degC | Good heat resistance up to 100-110degC |
| UV Resistance | Moderate UV resistance, often requires additives | Excellent UV resistance, ideal for exterior use |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents and chemicals | Good resistance to chemicals and weathering |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, glossy finish possible | Matte to semi-gloss finish with color stability |
| Cost | High cost, specialized processing required | Cost-effective, easy to process |
| Applications | High-performance automotive parts with demanding thermal/mechanical requirements | Exterior trim, bumpers, and weather-resistant components |
Introduction to Liquid Crystal Polymer and Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding automotive exterior parts exposed to harsh environments. Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA) offers superior weatherability, UV resistance, and impact toughness, which ensures durable and aesthetically pleasing automotive exterior components. Both materials serve critical roles in automotive design, with LCP favored for precision parts requiring high strength and ASA preferred for robust, long-lasting exterior panels.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability compared to acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA), making it ideal for automotive exterior parts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. ASA offers excellent UV resistance and impact strength, ensuring durability against weathering and physical stress, but lacks the high-temperature resilience of LCP. The choice between LCP and ASA depends on the specific performance requirements, with LCP favored for high-performance, heat-resistant components and ASA preferred for cost-effective, weather-resistant applications.
Mechanical Performance in Automotive Applications
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior mechanical performance in automotive exterior applications due to its exceptional tensile strength, high stiffness, and excellent dimensional stability under thermal stress. Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) offers good impact resistance and weatherability but lacks the high modulus and thermal endurance that LCP provides, making it less suitable for parts exposed to extreme conditions. LCP's outstanding fatigue resistance and chemical resistance ensure longer service life and reliability in demanding automotive exterior components.
Weather and UV Resistance Differences
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior weather and UV resistance compared to acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) in automotive exterior parts, maintaining structural integrity and color stability under prolonged sun exposure. LCP's molecular alignment provides enhanced thermal stability and minimal degradation when subjected to harsh environmental conditions, outperforming ASA which tends to yellow and embrittle over time. This makes LCP especially suitable for exterior components requiring long-term durability against ultraviolet radiation and fluctuating weather elements.
Chemical and Environmental Stability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior chemical resistance and environmental stability compared to acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) in automotive exterior applications, with enhanced resistance to UV radiation, solvents, and high temperatures. LCP's molecular structure provides excellent dimensional stability and resistance to hydrolysis, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions and prolonged exposure to automotive chemicals. ASA offers good weatherability and impact resistance but generally falls short of LCP's long-term chemical inertness and thermal performance in aggressive outdoor environments.
Processing and Moldability for Exterior Parts
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers exceptional flow properties and high dimensional stability, enabling precise injection molding of complex automotive exterior parts with tight tolerances. Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) provides excellent weather resistance and UV stability but requires optimized molding parameters due to higher melt viscosity compared to LCP. LCP's superior processability reduces cycle times and shrinkage, making it ideal for intricate exterior components, while ASA balances moldability with outdoor durability for robust vehicle surfaces.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance for automotive exterior parts but comes at a higher raw material and processing cost compared to acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA). ASA provides a cost-effective alternative with good weatherability and impact resistance, making it economically viable for large-scale production and budget-conscious automotive applications. The choice between LCP and ASA depends on the balance between performance requirements and cost constraints, with ASA favored for budget-sensitive projects and LCP for high-performance, specialized components.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior design flexibility for automotive exterior parts due to its high dimensional stability, allowing for intricate shapes and detailed features without compromising structural integrity. Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) provides enhanced aesthetic options with excellent UV resistance and color retention, ensuring vibrant and durable finishes suitable for long-term outdoor exposure. Combining LCP's precision molding capabilities with ASA's weatherability addresses both complex design and extended visual appeal in automotive exteriors.
Case Studies: LCP vs. ASA in Automotive Exteriors
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) demonstrates superior dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and heat tolerance in automotive exterior components compared to acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA), which offers better paintability and UV resistance. Case studies reveal LCP's advantage in high-performance applications such as under-the-hood trim and connectors subject to harsh environments, while ASA is favored for visible exterior parts requiring aesthetic durability. The selection largely depends on part function priorities, with LCP excelling in mechanical and thermal demands and ASA providing cost-effective, weather-resistant finishes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Polymer for Automotive Exterior Parts
Liquid crystal polymers (LCPs) offer exceptional dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and high-temperature performance, making them ideal for automotive exterior parts exposed to harsh environments. Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) provides superior weatherability, UV resistance, and impact strength, ensuring durability and aesthetic retention for exterior applications. Selecting LCPs ensures maximum engineering performance in demanding conditions, while ASA is preferred for cost-effective, visually appealing parts requiring long-term exposure to the elements.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate for Automotive exterior part
 azmater.com
azmater.com