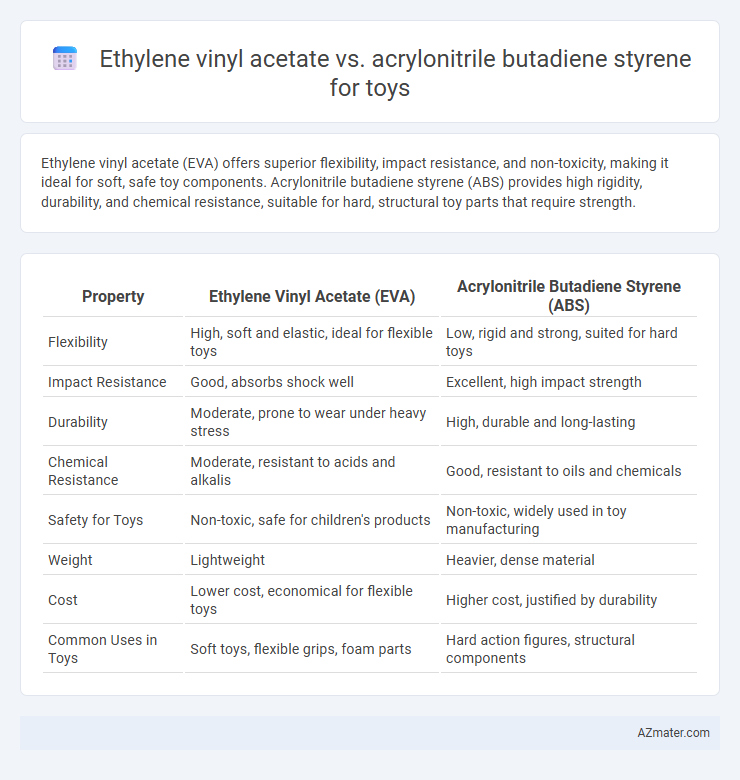
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and non-toxicity, making it ideal for soft, safe toy components. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides high rigidity, durability, and chemical resistance, suitable for hard, structural toy parts that require strength.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High, soft and elastic, ideal for flexible toys | Low, rigid and strong, suited for hard toys |
| Impact Resistance | Good, absorbs shock well | Excellent, high impact strength |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear under heavy stress | High, durable and long-lasting |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, resistant to acids and alkalis | Good, resistant to oils and chemicals |
| Safety for Toys | Non-toxic, safe for children's products | Non-toxic, widely used in toy manufacturing |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier, dense material |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical for flexible toys | Higher cost, justified by durability |
| Common Uses in Toys | Soft toys, flexible grips, foam parts | Hard action figures, structural components |
Introduction to Toy Materials: EVA vs ABS
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, shock absorption, and softness, making it ideal for toy components requiring cushioning and safe play. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides high impact resistance, rigidity, and durability, suitable for structural toy parts demanding strength and detailed molding. Choosing between EVA and ABS depends on desired toy features, balancing safety, comfort, and sturdiness in product design.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer composed of ethylene and vinyl acetate units, characterized by its flexible, rubber-like structure and low crystallinity, which provides excellent softness and impact resistance in toys. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a terpolymer consisting of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering a rigid, tough structure with high impact strength and heat resistance, ideal for durable toy components. EVA's chemical composition emphasizes elasticity and cushioning, while ABS's structure prioritizes rigidity and structural integrity, influencing their specific applications in toy manufacturing.
Safety and Non-Toxicity in Children's Toys
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is widely favored for children's toys due to its non-toxic, hypoallergenic properties and excellent resistance to cracking, making it safer for prolonged contact and chewing. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), while durable and impact-resistant, can release toxic substances if degraded or burned, posing potential health risks in toys exposed to harsh conditions. Regulatory standards such as EN71 and ASTM F963 often recognize EVA as a safer material option compared to ABS for direct contact toys intended for young children.
Physical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for soft, pliable toy components that require cushioning and durability. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides higher tensile strength and rigidity, resulting in sturdy, hard toys with superior structural integrity and resistance to breakage. EVA's elasticity outperforms ABS in bending and compression, while ABS excels in maintaining form under stress, suiting different toy design requirements based on strength and flexibility needs.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is manufactured through a polymerization process that blends ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers, resulting in a soft, flexible material commonly used in toys requiring cushioning and impact absorption. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) production involves polymerizing acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene to create a rigid, durable thermoplastic favored for structurally demanding toy components. The EVA manufacturing process typically allows for easier molding and coloring, while ABS requires precise temperature control and injection molding to achieve its high strength and toughness.
Durability and Longevity of Toys
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for toys requiring cushioning and shock absorption, enhancing overall durability. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides higher rigidity and toughness, ensuring structural strength and long-term longevity for toys subjected to rough handling. ABS's resistance to wear and environmental factors typically results in toys with prolonged lifespan compared to EVA-based counterparts.
Colorability and Surface Finish
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior colorability with vibrant, translucent hues ideal for toys requiring bright, eye-catching appearances, while acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent surface finish with a smooth, glossy texture that enhances durability and aesthetic appeal. EVA's flexibility allows for easy pigmentation, resulting in consistent, rich color distribution, whereas ABS maintains its rigidity and resists discoloration, preserving the integrity of surface details over time. Both materials support high-quality toy manufacturing, but EVA excels in color vibrancy and softness, whereas ABS is preferred for its polished finish and structural strength.
Cost-Effectiveness for Toy Production
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior cost-effectiveness for toy production due to its lower raw material and processing expenses compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). EVA's flexibility and impact resistance reduce the need for additional reinforcement, lowering manufacturing costs while maintaining safety standards. ABS provides higher structural strength but often incurs greater expenses in material and molding, making EVA a more economical choice for lightweight, durable toys.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior environmental benefits over acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) in toy manufacturing due to its lower toxicity and better biodegradability, reducing harmful waste accumulation. ABS, a petroleum-based plastic, presents significant challenges in recyclability and contributes more to landfill pollution and microplastic generation. Choosing EVA for toys aligns with sustainability goals by enabling easier recycling processes and minimizing long-term environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Material: EVA or ABS for Toys
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and cushioning, making it ideal for soft, safe toy components and items requiring shock absorption. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) excels in rigidity, durability, and surface finish, preferred for hard toys, structural parts, and toys requiring detailed molding. Selecting EVA or ABS depends on the desired toy properties: EVA for softness and safety, ABS for strength and precision.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com