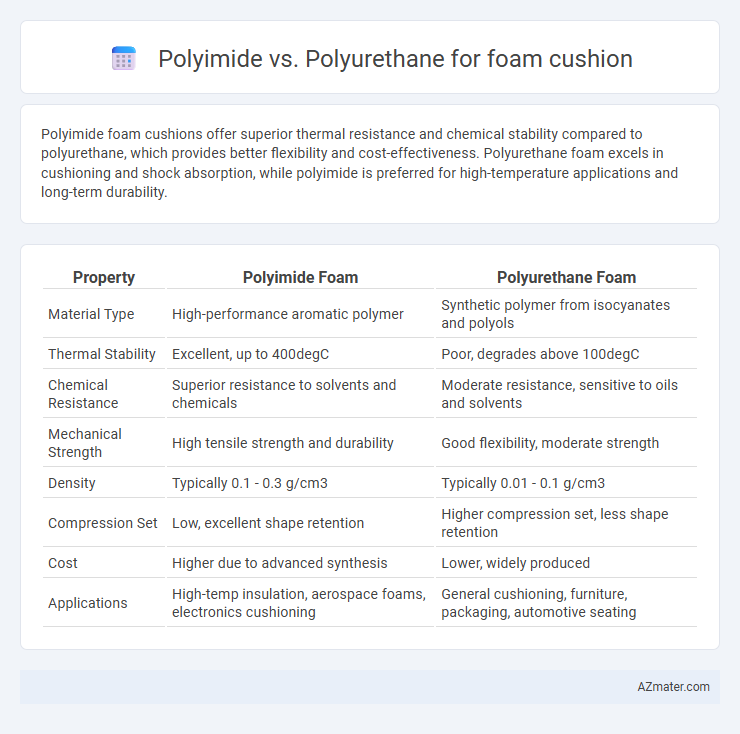
Polyimide foam cushions offer superior thermal resistance and chemical stability compared to polyurethane, which provides better flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Polyurethane foam excels in cushioning and shock absorption, while polyimide is preferred for high-temperature applications and long-term durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance aromatic polymer | Synthetic polymer from isocyanates and polyols |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, up to 400degC | Poor, degrades above 100degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to solvents and chemicals | Moderate resistance, sensitive to oils and solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Good flexibility, moderate strength |
| Density | Typically 0.1 - 0.3 g/cm3 | Typically 0.01 - 0.1 g/cm3 |
| Compression Set | Low, excellent shape retention | Higher compression set, less shape retention |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced synthesis | Lower, widely produced |
| Applications | High-temp insulation, aerospace foams, electronics cushioning | General cushioning, furniture, packaging, automotive seating |
Introduction to Foam Cushion Materials
Polyimide foam offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance cushioning in aerospace and electronics applications. Polyurethane foam is widely used due to its versatility, comfort, and cost-effectiveness, with excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties for everyday furniture and automotive seating. Both materials provide unique benefits, where polyimide excels in extreme environments and polyurethane dominates in commercial cushioning solutions.
What is Polyimide Foam?
Polyimide foam is a high-performance, lightweight material known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and flame retardance, making it ideal for demanding aerospace and electronics cushioning applications. Compared to polyurethane foam, polyimide foam exhibits superior temperature tolerance, maintaining structural integrity in environments exceeding 300degC, whereas polyurethane typically degrades at much lower temperatures. Its closed-cell structure also provides enhanced sound absorption and mechanical strength, offering critical protection for sensitive equipment and components.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile polymer widely used in foam cushions due to its excellent flexibility, durability, and cushioning properties. It consists of polymer chains formed by reacting polyols with diisocyanates, resulting in a lightweight material that offers superior resilience and support. Polyurethane foam's ability to conform to body shapes while maintaining structural integrity makes it a preferred choice for ergonomic and comfort applications in seating and bedding.
Key Properties: Polyimide vs Polyurethane
Polyimide foam exhibits exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature and harsh environment cushioning applications. Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility, cushioning comfort, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in everyday furniture and bedding products. The key properties comparison highlights polyimide's durability under extreme conditions versus polyurethane's versatility and softness for general comfort uses.
Performance Comparison in Cushioning
Polyimide foam cushions exhibit superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and compression set retention compared to polyurethane foams, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability and long-term cushioning. Polyurethane foams provide excellent initial softness and resilience with better energy absorption and flexibility, suitable for general comfort and everyday use. The choice between polyimide and polyurethane foam cushions hinges on balancing advanced mechanical properties versus cost-effectiveness and comfort needs.
Durability and Longevity
Polyimide foam cushions exhibit superior durability compared to polyurethane counterparts due to their high thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation, making them ideal for long-term use in harsh environments. Polyurethane foams, while offering excellent cushioning and flexibility, tend to degrade faster under UV exposure and moisture, reducing their lifespan significantly. For applications demanding extended longevity and performance under extreme conditions, polyimide foam is the preferred material due to its robust molecular structure and exceptional wear resistance.
Thermal and Fire Resistance
Polyimide foam cushions offer superior thermal stability with service temperatures exceeding 400degC, making them ideal for high-heat applications compared to polyurethane foams, which typically withstand up to 120degC. Polyimide exhibits excellent fire resistance, characterized by low flammability and self-extinguishing properties, while polyurethane cushions are more prone to combustion and produce toxic smoke during burning. The inherent aromatic backbone of polyimide provides enhanced char formation and thermal insulation, significantly outperforming polyurethane in fire safety and heat tolerance for cushioning solutions.
Application Areas and Industries
Polyimide foam cushions excel in aerospace and electronics industries due to their outstanding thermal resistance, chemical stability, and flame retardant properties, making them suitable for insulation and protective packaging. Polyurethane foam cushions dominate automotive, furniture, and bedding applications where flexibility, comfort, and cost-effectiveness are critical, providing superior cushioning and impact absorption. Both materials find specialized use in medical devices and sports equipment, with selection driven by specific performance requirements such as durability and environmental exposure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyimide foam cushions exhibit superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them highly durable and reducing the frequency of replacement, which contributes to lower environmental impact over time. Polyurethane foams, commonly used in cushions, often involve petrochemical-derived components and release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), posing challenges for sustainability and indoor air quality. Advances in bio-based polyurethane formulations aim to improve environmental profiles, but polyimide's inherent recyclability and longer lifecycle generally offer greater sustainability benefits in foam cushioning applications.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Cushion
Polyimide foam offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance cushion applications requiring durability and heat resistance. Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for everyday comfort and shock absorption in furniture and automotive seats. Choosing the right foam depends on the specific requirements for temperature tolerance, mechanical strength, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polyurethane for Foam cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com