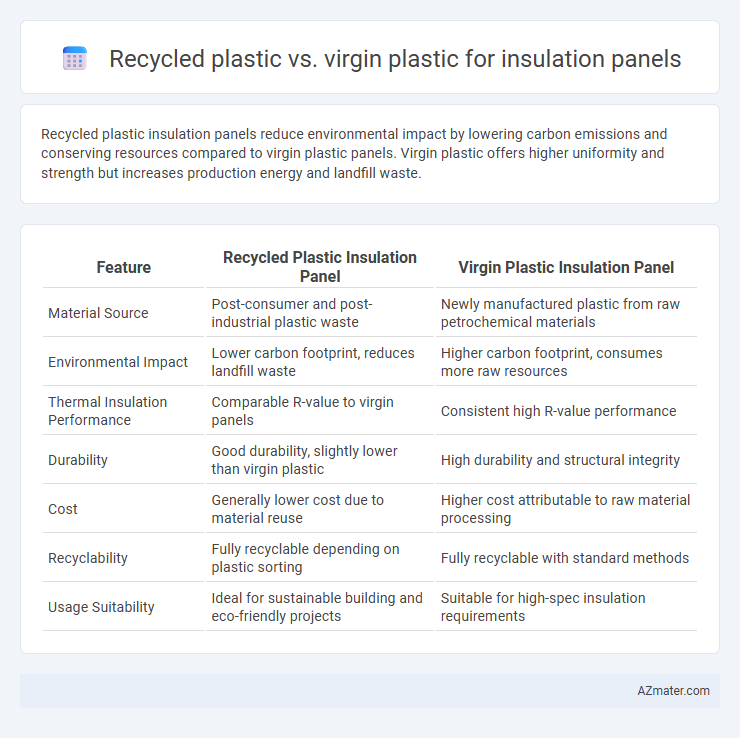
Recycled plastic insulation panels reduce environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions and conserving resources compared to virgin plastic panels. Virgin plastic offers higher uniformity and strength but increases production energy and landfill waste.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Plastic Insulation Panel | Virgin Plastic Insulation Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial plastic waste | Newly manufactured plastic from raw petrochemical materials |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Higher carbon footprint, consumes more raw resources |
| Thermal Insulation Performance | Comparable R-value to virgin panels | Consistent high R-value performance |
| Durability | Good durability, slightly lower than virgin plastic | High durability and structural integrity |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to material reuse | Higher cost attributable to raw material processing |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable depending on plastic sorting | Fully recyclable with standard methods |
| Usage Suitability | Ideal for sustainable building and eco-friendly projects | Suitable for high-spec insulation requirements |
Introduction to Insulation Panels: Materials Matter
Insulation panels significantly impact energy efficiency, with material choice playing a crucial role in performance and sustainability. Recycled plastic insulation panels utilize post-consumer waste, reducing landfill impact and conserving raw resources compared to virgin plastic panels made from newly extracted polymers. Selecting recycled plastic enhances environmental benefits without compromising thermal resistance and durability essential for effective insulation.
What Is Virgin Plastic? Properties and Uses in Insulation
Virgin plastic refers to plastic material that is made directly from petrochemical feedstocks without any prior use or recycling. It offers superior consistency, strength, and thermal insulation properties due to its uncontaminated molecular structure, making it ideal for manufacturing high-performance insulation panels. Common uses include rigid foam boards and spray foam insulation, where durability, moisture resistance, and long-term thermal efficiency are critical.
Recycled Plastic Explained: Sources and Processing
Recycled plastic insulation panels are primarily made from post-consumer and post-industrial plastic waste such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) containers, and polypropylene (PP) packaging. The recycling process involves collection, sorting, cleaning, shredding, and melting the plastic materials to form pellets that can be molded into insulation panels, significantly reducing environmental impact compared to virgin plastic production. Advanced techniques like chemical recycling and extrusion molding enhance the structural integrity and thermal performance of recycled plastic insulation panels, making them a sustainable alternative in building materials.
Comparing Thermal Performance: Recycled vs Virgin Plastic
Recycled plastic insulation panels exhibit comparable thermal conductivity values to virgin plastic panels, typically ranging between 0.030 to 0.040 W/m*K, ensuring effective thermal resistance in building applications. Virgin plastic panels often demonstrate slightly higher uniformity in thermal performance due to controlled material properties, while recycled plastics may contain variable additives affecting insulation consistency. Advances in recycling technologies have minimized these disparities, allowing recycled plastic panels to meet stringent thermal performance standards required for eco-friendly construction.
Environmental Impact: Carbon Footprint Analysis
Recycled plastic insulation panels exhibit a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to virgin plastic due to reduced energy consumption in raw material processing and minimized landfill waste. Life cycle assessments reveal up to a 60% reduction in CO2 emissions when using recycled content, contributing to sustainable building practices. Choosing recycled plastic supports circular economy principles by diverting plastic from landfills and lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with production.
Durability and Lifespan Considerations
Recycled plastic insulation panels exhibit strong durability with resistance to moisture, mold, and UV exposure, often comparable to virgin plastic panels. Virgin plastic panels typically offer a more uniform molecular structure, potentially enhancing long-term structural integrity and lifespan. Longevity of recycled plastic panels may vary due to material source and processing methods but remain a sustainable option without significant compromise in performance.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Lifecycle Expenses
Recycled plastic insulation panels typically offer lower upfront costs compared to virgin plastic panels due to reduced raw material expenses and manufacturing energy requirements. Lifecycle analysis shows recycled plastic panels can further reduce total costs by enhancing waste diversion and often requiring less energy-intensive production, yet durability and performance factors may influence long-term maintenance expenses. Cost efficiency depends on specific project parameters, availability of recycled materials, and potential savings from environmental incentives or reduced disposal fees.
Health and Safety: VOCs and Indoor Air Quality
Recycled plastic insulation panels often emit lower levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to virgin plastic, reducing the risk of indoor air pollution and associated health issues like respiratory irritation and headaches. Studies highlight that recycled materials can help maintain better indoor air quality by minimizing chemical off-gassing typically linked to virgin plastic production. Choosing recycled plastic for insulation supports healthier living spaces by decreasing exposure to harmful VOCs and enhancing overall indoor environmental safety.
Certifications and Industry Standards
Recycled plastic insulation panels often meet rigorous industry standards such as ASTM C578 and EN 13162, ensuring performance comparable to virgin plastic alternatives. Certifications like GREENGUARD and LEED recognition emphasize their environmental benefits without compromising thermal insulation quality. Compliance with fire safety standards, including UL 94 and Euroclass classifications, is critical for both recycled and virgin plastic panels used in construction.
Future Trends: Innovations in Sustainable Insulation
Recycled plastic insulation panels are increasingly favored for sustainable construction due to their lower environmental impact and reduced carbon footprint compared to virgin plastic counterparts. Innovations in biodegradable additives and enhanced recycling technologies are improving the thermal performance and durability of recycled plastic panels. Future trends emphasize circular economy principles, with manufacturers developing closed-loop systems to maximize material reuse and minimize waste in insulation production.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Virgin plastic for Insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com