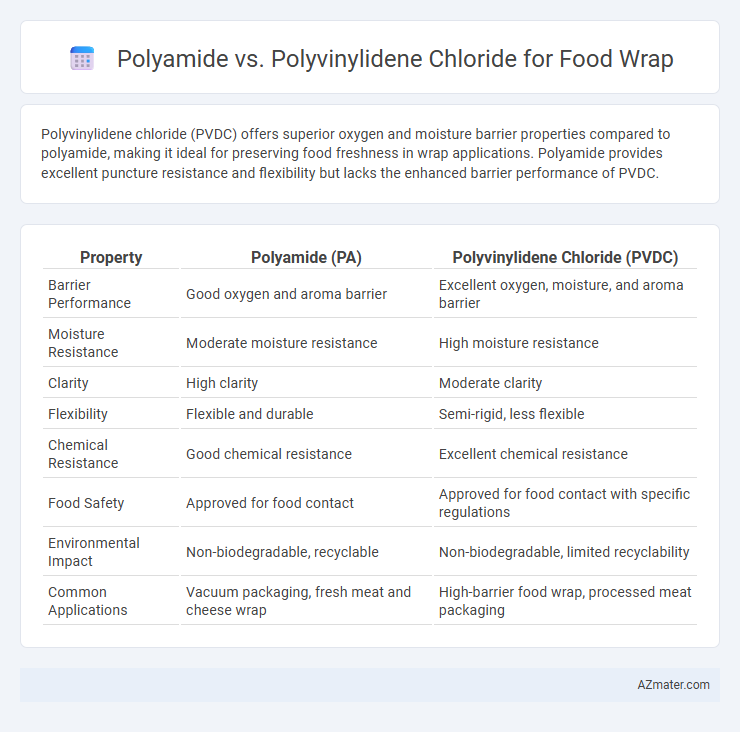
Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) offers superior oxygen and moisture barrier properties compared to polyamide, making it ideal for preserving food freshness in wrap applications. Polyamide provides excellent puncture resistance and flexibility but lacks the enhanced barrier performance of PVDC.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyamide (PA) | Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) |
|---|---|---|
| Barrier Performance | Good oxygen and aroma barrier | Excellent oxygen, moisture, and aroma barrier |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate moisture resistance | High moisture resistance |
| Clarity | High clarity | Moderate clarity |
| Flexibility | Flexible and durable | Semi-rigid, less flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Good chemical resistance | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Food Safety | Approved for food contact | Approved for food contact with specific regulations |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Non-biodegradable, limited recyclability |
| Common Applications | Vacuum packaging, fresh meat and cheese wrap | High-barrier food wrap, processed meat packaging |
Introduction to Food Wrap Materials
Polyamide and polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) are prominent materials used in food wraps due to their barrier properties that preserve freshness and prevent contamination. Polyamide offers high tensile strength and excellent puncture resistance, making it suitable for protecting delicate foods. PVDC provides superior moisture, oxygen, and odor barriers, which enhance shelf life by preventing spoilage and maintaining product quality in packaging applications.
What Is Polyamide?
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is a synthetic polymer characterized by strong, flexible fibers often used in food wraps due to its excellent mechanical strength and heat resistance. Its molecular structure allows for effective barrier properties, preventing moisture and aroma loss in packaged food. In comparison to Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC), polyamide offers superior puncture resistance, making it ideal for wrapping sharp or irregularly shaped food items.
What Is Polyvinylidene Chloride?
Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) is a high-barrier polymer renowned for its exceptional moisture, gas, and aroma resistance, making it ideal for food wrap applications. Compared to polyamide, PVDC offers superior protection against oxygen and water vapor transmission, significantly extending shelf life and preserving food freshness. PVDC's durability and chemical stability enable it to maintain packaging integrity even under varying temperature conditions.
Barrier Properties: Polyamide vs Polyvinylidene Chloride
Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) offers superior barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and odors compared to polyamide (PA), making it highly effective for food preservation and extending shelf life. Polyamide provides excellent mechanical strength and puncture resistance but has higher oxygen permeability than PVDC, which can compromise freshness over time. For applications requiring maximum protection from external contaminants and prolonged preservation, PVDC is the preferred choice due to its low gas permeability and moisture barrier capabilities.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility Comparison
Polyamide exhibits superior mechanical strength with high tensile resistance and excellent puncture toughness, making it ideal for durable food wrap applications. Polyvinylidene chloride offers enhanced flexibility and cling properties, allowing tighter seals around irregular shapes while maintaining moderate strength. The balance between polyamide's rigidity and polyvinylidene chloride's pliability influences their selection based on packaging requirements for protection versus conformity.
Food Safety and Chemical Resistance
Polyamide offers superior flexibility and puncture resistance but has moderate chemical resistance, making it suitable for packaging that requires durability and some barrier properties. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) provides excellent chemical resistance, oxygen barrier performance, and superior food safety by preventing contamination and extending shelf life. Choosing PVDC for food wrap ensures better protection against oils, acids, and moisture, enhancing food preservation and safety standards.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyamide (PA) films typically exhibit higher durability and heat resistance but present challenges in recycling due to limited collection streams and contamination risks. Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) is known for its superior barrier properties, yet its chlorine content raises environmental concerns related to harmful emissions during production and disposal. Both materials require specialized recycling processes, with polyamide offering slightly better recyclability options in environments equipped for polymer separation, making selection critical based on local waste management infrastructure and environmental priorities.
Cost-Effectiveness for Food Packaging
Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) offers superior barrier properties against moisture and oxygen compared to polyamide, enhancing food preservation and reducing waste. Although PVDC typically has a higher upfront cost, its extended shelf life and reduced spoilage make it more cost-effective for high-quality food packaging. Polyamide is generally less expensive but may require additional layers or coatings to achieve comparable barrier performance, potentially increasing overall packaging costs in the long term.
Common Applications in the Food Industry
Polyamide (PA) is widely used in food packaging for its excellent puncture resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for vacuum-sealed meats, cheese wrapping, and multi-layer films requiring durability. Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) excels in barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and odors, commonly applied in packaging for processed meats, cheese, and baked goods to extend shelf life. Both films are favored for preserving food quality but are selected based on specific barrier and mechanical requirements in the food industry.
Choosing the Right Material for Food Wraps
Polyamide offers excellent puncture resistance and high-temperature tolerance, making it ideal for wrapping cooked or hot foods, while polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) provides superior oxygen and moisture barrier properties, extending shelf life for perishable items. Selecting the right food wrap depends on the specific preservation needs: polyamide suits applications requiring durability and heat resistance, whereas PVDC excels in maintaining freshness by preventing oxidation and moisture loss. Understanding these material properties ensures optimal food protection and reduces spoilage during storage.
Infographic: Polyamide vs Polyvinylidene Chloride for Food Wrap
 azmater.com
azmater.com