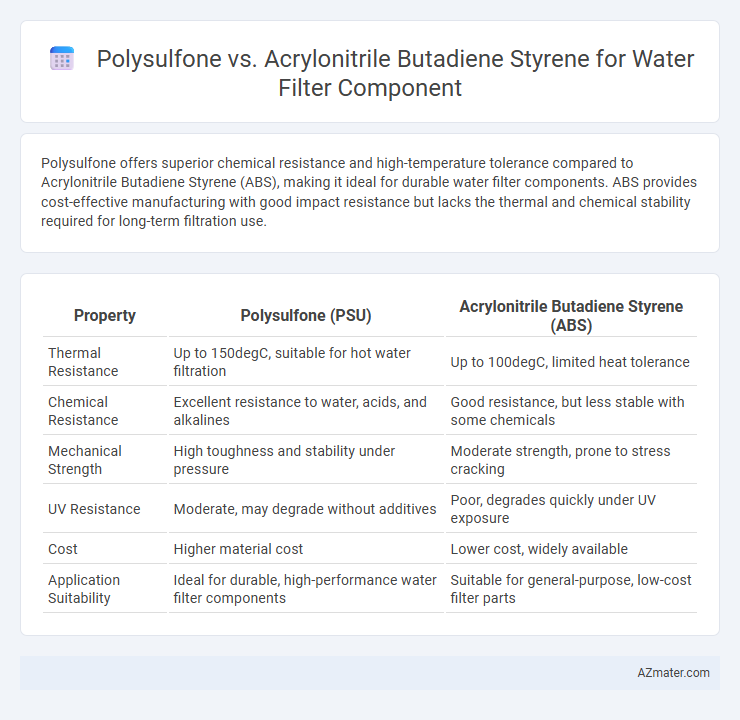
Polysulfone offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it ideal for durable water filter components. ABS provides cost-effective manufacturing with good impact resistance but lacks the thermal and chemical stability required for long-term filtration use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC, suitable for hot water filtration | Up to 100degC, limited heat tolerance |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to water, acids, and alkalines | Good resistance, but less stable with some chemicals |
| Mechanical Strength | High toughness and stability under pressure | Moderate strength, prone to stress cracking |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, may degrade without additives | Poor, degrades quickly under UV exposure |
| Cost | Higher material cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for durable, high-performance water filter components | Suitable for general-purpose, low-cost filter parts |
Introduction to Water Filter Component Materials
Polysulfone and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) are prominent materials used in water filter components due to their unique properties. Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and durability essential for high-performance filtration systems exposed to hot water and aggressive cleaning agents. ABS provides a cost-effective solution with excellent impact resistance and ease of molding, ideal for durable housings and structural parts in filtration units.
Overview of Polysulfone (PSU)
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for water filter components exposed to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. PSU maintains structural integrity in continuous use up to 160degC and resists hydrolysis, ensuring long-term durability in filtration systems. Its inherent toughness and transparency allow for reliable performance and easy inspection of water filters, outperforming many conventional plastics like Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) in critical filtration environments.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its toughness, impact resistance, and ease of fabrication, making it a popular choice for water filter components. Its chemical resistance against water and mild acids ensures durability in typical water filtration environments, though it may degrade under prolonged exposure to strong chemicals or UV light. Compared to Polysulfone, ABS offers cost-effectiveness and good mechanical properties, but it exhibits lower thermal stability and less resistance to high-temperature sterilization processes.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) in water filter components, offering higher tensile strength and better impact resistance under prolonged exposure to various water chemistries. ABS is more prone to stress cracking and degradation when subjected to chlorine and other disinfectants commonly found in treated water. Polysulfone's enhanced thermal stability and durability make it the preferred choice for critical water filtration applications requiring long-term structural integrity.
Chemical Resistance in Water Filtration Applications
Polysulfone exhibits superior chemical resistance in water filtration applications compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), particularly against chlorinated water, ozone, and acidic conditions. This thermoplastic polymer maintains structural integrity and performance under prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals commonly found in water treatment processes, ensuring durability and reliability. ABS components, while cost-effective, tend to degrade faster when exposed to these aggressive chemical environments, limiting their lifespan and effectiveness in filtration systems.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Rating
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability with a continuous use temperature up to 150degC, making it ideal for water filter components exposed to hot water or sterilization processes. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) has a lower temperature rating, typically around 80-100degC, which limits its use in high-temperature water filtration applications. The higher glass transition temperature of polysulfone ensures better performance and durability under thermal stress compared to ABS.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polysulfone exhibits superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it more suitable for water filter components that require prolonged exposure to hot water and disinfectants. Polysulfone complies with stringent NSF/ANSI 61 standards for drinking water system components, ensuring safety and low leaching of harmful substances, whereas ABS may struggle to meet these requirements under high-temperature conditions. Regulatory bodies favor polysulfone due to its proven performance in maintaining water purity and structural integrity, essential for health-safe water filtration applications.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polysulfone offers higher chemical resistance and thermal stability for water filter components but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides affordability and ease of manufacturing. ABS demonstrates sufficient durability for standard filtration applications, reducing overall production expenses while maintaining adequate performance. Cost-effectiveness analysis favors ABS for budget-conscious projects, whereas Polysulfone justifies its premium price in high-demand environments requiring extended lifespan and superior material integrity.
Lifespan and Durability of Filter Components
Polysulfone offers superior lifespan and durability for water filter components due to its high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and toughness under continuous exposure to water and disinfectants. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides good impact resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to water and UV light, which limits its longevity in filter applications. Polysulfone's resistance to hydrolysis and mechanical stress makes it the preferred choice for long-lasting, reliable water filter components.
Recommendations: Choosing Between PSU and ABS
Polysulfone (PSU) is recommended for water filter components requiring superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and long-term durability under hot water exposure, making it ideal for hot water filtration systems. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is suitable for cost-effective applications with moderate temperature exposure and where impact resistance is needed, but it may degrade faster in prolonged hot water environments. For optimal performance and lifespan in water filters, PSU is preferred when handling high-temperature conditions, whereas ABS fits well for less demanding, ambient temperature applications.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Water filter component
 azmater.com
azmater.com