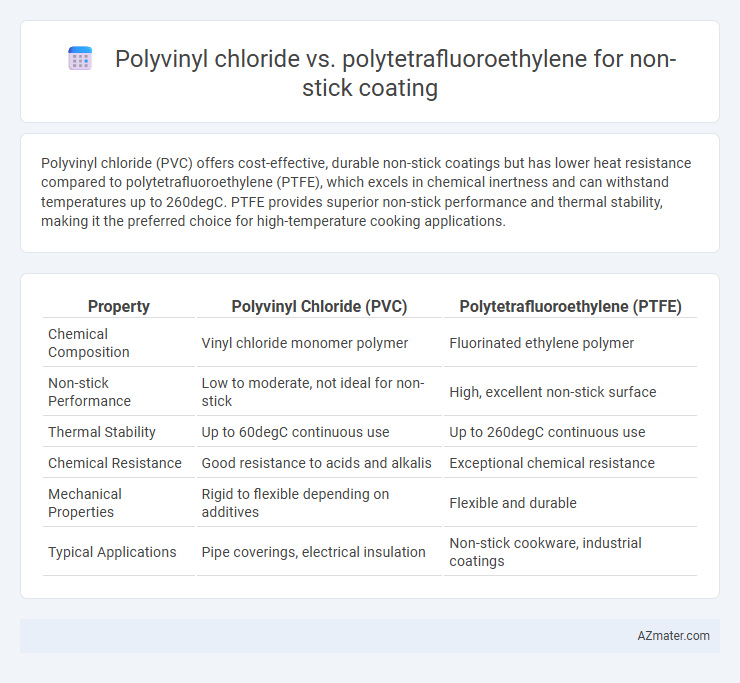
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers cost-effective, durable non-stick coatings but has lower heat resistance compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which excels in chemical inertness and can withstand temperatures up to 260degC. PTFE provides superior non-stick performance and thermal stability, making it the preferred choice for high-temperature cooking applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Vinyl chloride monomer polymer | Fluorinated ethylene polymer |
| Non-stick Performance | Low to moderate, not ideal for non-stick | High, excellent non-stick surface |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 60degC continuous use | Up to 260degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Exceptional chemical resistance |
| Mechanical Properties | Rigid to flexible depending on additives | Flexible and durable |
| Typical Applications | Pipe coverings, electrical insulation | Non-stick cookware, industrial coatings |
Introduction to Non-Stick Coatings
Non-stick coatings enhance cookware by preventing food adhesion and facilitating easy cleaning, with Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as common materials. PVC offers durability and affordability but lacks the superior non-stick and heat resistance properties of PTFE, which excels in high-temperature applications up to 260degC. PTFE's chemical inertness and low friction coefficient make it the preferred choice for premium non-stick cookware coatings.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Properties and Applications
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a versatile polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, durability, and affordability, making it widely used in various applications including non-stick coatings. Its rigidity and heat resistance are lower compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), but PVC's ease of processing and cost-effectiveness make it suitable for cookware coatings and other surface applications requiring moderate non-stick properties. Due to its chlorine content, PVC offers strong resistance to oils, acids, and environmental factors, enhancing the lifespan of coated products in domestic and industrial settings.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): Properties and Applications
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers exceptional non-stick properties, chemical resistance, and a high melting point around 327degC, making it ideal for cookware coatings. Unlike polyvinyl chloride (PVC), PTFE provides superior thermal stability and low friction, which prevents food from sticking and enhances durability. Its applications extend beyond kitchenware to include industrial uses such as gaskets, seals, and lubricants due to its non-reactive and hydrophobic nature.
Thermal Stability: PVC vs PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with a decomposition temperature above 500degC, making it ideal for high-temperature non-stick coatings. PVC begins to degrade at around 140degC to 160degC, releasing harmful gases, which limits its use in heat-exposed applications. The enhanced thermal resistance of PTFE ensures longer durability and consistent non-stick performance in cookware and industrial coatings.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) outperforms Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in chemical resistance, exhibiting exceptional stability against acids, bases, solvents, and high temperatures. PVC tends to degrade when exposed to strong chemicals, limiting its use in harsh environments. PTFE's superior resistance makes it the preferred non-stick coating in applications requiring durability and chemical inertness.
Non-Stick Performance and Surface Smoothness
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) outperforms polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in non-stick coating applications due to its ultra-low friction surface and exceptional chemical inertness, resulting in superior non-stick performance. PTFE's molecular structure creates an extremely smooth surface that resists adhesion and allows easy food release, whereas PVC's surface tends to be rougher and less resistant to sticking. The durability and heat resistance of PTFE also maintain surface smoothness longer under high-temperature cooking conditions, making it the preferred choice for high-quality non-stick coatings.
Durability and Lifespan Assessment
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers moderate durability for non-stick coatings but tends to degrade under high temperatures and prolonged use, resulting in a shorter lifespan compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). PTFE exhibits superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, maintaining its non-stick properties and structural integrity over extended periods even under frequent heating cycles. The lifespan of PTFE-coated cookware typically exceeds that of PVC, making it a preferred choice for long-term durability in non-stick applications.
Safety and Food Contact Considerations
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is widely preferred over polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for non-stick coatings due to its superior chemical inertness and high thermal stability, minimizing the risk of harmful compound release during cooking. PVC can release toxic plasticizers and dioxins when heated, posing significant safety concerns for food contact applications. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EFSA approve PTFE for cookware use, ensuring it meets stringent safety standards for food-grade materials.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers high cost efficiency due to its low production expense and widespread availability in global markets, making it a common choice for budget-friendly non-stick coatings. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), while more expensive because of its complex manufacturing process and superior chemical resistance, dominates premium non-stick applications due to its exceptional durability and performance. Market availability of PVC is extensive with numerous suppliers, whereas PTFE's specialized production limits its accessibility, impacting overall cost and supply dynamics.
Choosing the Right Material for Non-Stick Coatings
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness but lacks the high-temperature resistance and chemical inertness essential for non-stick coatings compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). PTFE provides superior non-stick properties, exceptional thermal stability up to 260degC, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for cookware and industrial applications. Selecting PTFE ensures durability and performance in non-stick surfaces, while PVC is better suited for less demanding applications where flexibility is prioritized.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Non-stick coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com