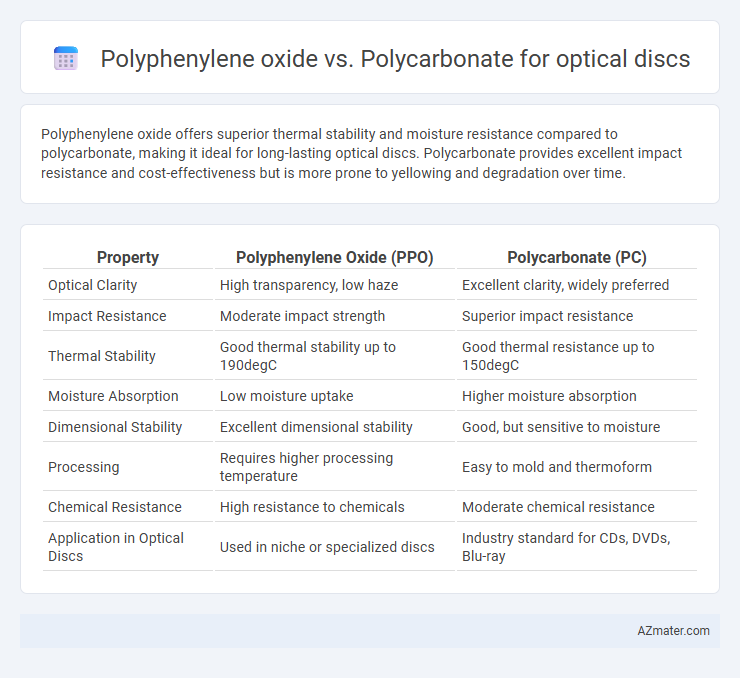
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior thermal stability and moisture resistance compared to polycarbonate, making it ideal for long-lasting optical discs. Polycarbonate provides excellent impact resistance and cost-effectiveness but is more prone to yellowing and degradation over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Clarity | High transparency, low haze | Excellent clarity, widely preferred |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate impact strength | Superior impact resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal stability up to 190degC | Good thermal resistance up to 150degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture uptake | Higher moisture absorption |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent dimensional stability | Good, but sensitive to moisture |
| Processing | Requires higher processing temperature | Easy to mold and thermoform |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Application in Optical Discs | Used in niche or specialized discs | Industry standard for CDs, DVDs, Blu-ray |
Introduction to Optical Disc Materials
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and polycarbonate (PC) are prominent polymers used in optical disc manufacturing due to their excellent optical clarity and dimensional stability. PC offers superior impact resistance and is widely favored for its ease of molding and reliable performance in high-density data storage discs like CDs, DVDs, and Blu-rays. PPO provides enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring prolonged durability in varying environmental conditions.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, high heat resistance, and superior moisture resistance, making it suitable for optical disc applications where durability and clarity are critical. Its inherent rigidity and transparency provide reliable optical properties, while PPO's low coefficient of thermal expansion helps maintain structural integrity under varying environmental conditions. Compared to polycarbonate, PPO offers improved chemical resistance and reduced susceptibility to stress cracking, enhancing the longevity and performance of optical discs.
Overview of Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a high-performance thermoplastic widely used in optical discs due to its excellent impact resistance, optical clarity, and dimensional stability. Its molecular structure provides superior light transmittance and scratch resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring precision and durability, such as CDs and DVDs. Compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), PC offers better moldability and cost efficiency for mass production while maintaining reliable performance in optical data storage.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent dimensional stability and impact resistance, making it suitable for optical discs requiring high mechanical durability and thermal resistance. Polycarbonate (PC) provides superior toughness and higher fracture resistance but can be more prone to stress cracking under prolonged mechanical stress. In optical disc applications, PPO's rigidity and resistance to deformation under load ensure better long-term performance, while PC's flexibility enhances impact absorption during handling and use.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior optical clarity and high transparency, making it ideal for optical discs requiring minimal light distortion and enhanced data readability. Polycarbonate (PC) is widely used in optical discs due to its excellent transparency, impact resistance, and dimensional stability, though it may exhibit slight yellowing over time affecting clarity. PPO provides better UV resistance and thermal stability, contributing to more consistent optical performance in demanding environments compared to polycarbonate.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability with a high glass transition temperature around 210degC, making it resistant to deformation under prolonged heat exposure during optical disc manufacturing. Polycarbonate (PC) exhibits good heat resistance but has a lower glass transition temperature near 150degC, which can lead to dimensional changes and reduced performance in high-temperature environments. PPO's enhanced heat resistance ensures greater durability and reliability for optical discs subjected to intense thermal processing or extended use under elevated temperatures.
Chemical Resistance in Optical Disc Applications
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polycarbonate, making it more suitable for optical disc applications exposed to cleaning solvents and environmental contaminants. PPO offers enhanced dimensional stability and resistance to hydrolysis, reducing the risk of disc warping or degradation over time. Polycarbonate, while commonly used, is more susceptible to chemical attack and surface crazing, potentially compromising data integrity in harsh conditions.
Durability and Environmental Impact
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior heat resistance and dimensional stability, enhancing the durability of optical discs compared to polycarbonate (PC), which can become brittle over time. PPO's resistance to moisture and UV degradation extends the lifespan of optical discs, making it a preferred choice for long-term data storage. From an environmental perspective, PPO's potential for recycling and lower emission production processes contribute to a reduced ecological footprint compared to conventional polycarbonate materials.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers lower raw material costs compared to polycarbonate, making it a cost-effective option for optical disc production. PPO's thermal stability and dimensional accuracy reduce manufacturing defects, enhancing yield rates during injection molding processes. Polycarbonate, while more expensive, provides superior impact resistance and clarity but demands higher processing temperatures and equipment maintenance, increasing overall manufacturing expenses.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Optical Disc Production
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior dimensional stability and excellent heat resistance, making it ideal for maintaining signal integrity in optical discs during high-speed reading. Polycarbonate (PC), known for its outstanding impact strength and optical clarity, remains the industry standard due to cost-effectiveness and ease of processing. For optical disc production, polycarbonate is the best choice when balancing optical performance, manufacturing efficiency, and economic feasibility.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polycarbonate for Optical disc
 azmater.com
azmater.com