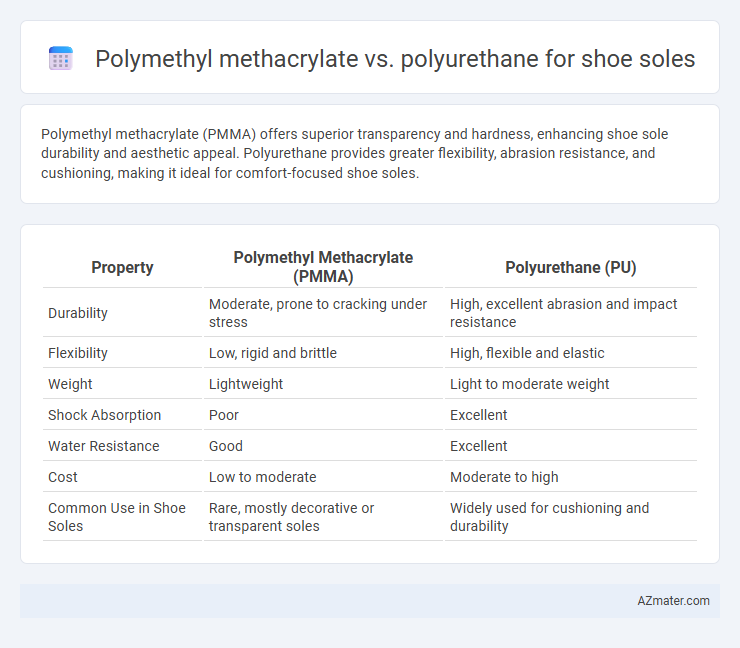
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior transparency and hardness, enhancing shoe sole durability and aesthetic appeal. Polyurethane provides greater flexibility, abrasion resistance, and cushioning, making it ideal for comfort-focused shoe soles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking under stress | High, excellent abrasion and impact resistance |
| Flexibility | Low, rigid and brittle | High, flexible and elastic |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to moderate weight |
| Shock Absorption | Poor | Excellent |
| Water Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Common Use in Shoe Soles | Rare, mostly decorative or transparent soles | Widely used for cushioning and durability |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyurethane (PU) are prominent materials used in shoe sole manufacturing, each offering distinct benefits in durability and flexibility. PMMA provides excellent transparency, rigidity, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for shoes that require a firm and stylish sole. Polyurethane excels in cushioning, abrasion resistance, and versatility, delivering superior shock absorption and comfort for various footwear applications.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic polymer known for its rigidity, excellent weather resistance, and high clarity, commonly used as a lightweight alternative to glass. In shoe sole applications, PMMA offers good abrasion resistance and durability but tends to be less flexible compared to polyurethane, which can affect comfort and shock absorption. Its chemical resistance and resistance to UV degradation make PMMA suitable for footwear exposed to various environmental conditions, although its brittleness limits impact resilience relative to softer sole materials.
Key Properties of PMMA for Shoe Soles
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent rigidity, transparency, and UV resistance, making it ideal for shoe soles that require durability and aesthetic appeal. Its high hardness and resistance to abrasion ensure long-lasting wear, while its lightweight nature contributes to overall comfort. PMMA's low water absorption and chemical resistance further enhance the sole's performance in various environmental conditions.
Overview of Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer widely used in shoe soles for its excellent elasticity, durability, and cushioning properties. It offers superior abrasion resistance and flexibility compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it suitable for high-performance footwear applications. PU soles provide enhanced shock absorption and lightweight comfort, contributing to long-lasting wear and improved foot support.
Key Properties of PU for Shoe Soles
Polyurethane (PU) offers exceptional flexibility, abrasion resistance, and excellent cushioning, making it a preferred material for shoe soles compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PU soles provide superior shock absorption and durability, enhancing comfort and longevity in footwear applications. The material's resistance to oils, solvents, and environmental factors further contributes to its widespread use in performance and casual shoes.
Durability: PMMA vs Polyurethane
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits high scratch resistance and rigidity, making it less prone to surface wear but more susceptible to cracking under heavy impact compared to polyurethane. Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and shock absorption, resulting in enhanced durability for shoe soles subjected to repeated stress and dynamic movements. When evaluating long-term wear performance, polyurethane generally outperforms PMMA in maintaining structural integrity and cushioning properties.
Comfort and Flexibility Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent durability and rigidity but tends to be less flexible and less comfortable for extended wear compared to polyurethane (PU). Polyurethane provides superior cushioning and elasticity, making it ideal for shoe soles that require enhanced comfort and flexibility during prolonged use. The material's ability to absorb impact and conform to foot movements significantly improves wearer comfort and reduces fatigue.
Weight and Cushioning Differences
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) shoe soles are generally lighter than polyurethane (PU) soles, making them ideal for lightweight footwear designs that prioritize speed and agility. However, polyurethane excels in cushioning, offering superior shock absorption and durability due to its elastic properties, which enhance comfort for prolonged use. The choice between PMMA and PU soles significantly impacts the balance between weight reduction and cushioning performance in athletic and casual shoes.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) shoe soles generally incur higher material costs and require precise molding techniques due to their rigidity and brittleness, impacting manufacturing scalability. Polyurethane (PU) offers more cost-effective production with versatile injection molding and cushioning properties that enhance durability and comfort, making it favorable for mass production. Manufacturers prioritize PU for lower expenses and ease of customization, while PMMA is selected for niche applications requiring transparency and hardness despite elevated costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyurethane (PU) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for shoe soles. PMMA is derived from petrochemicals but offers greater recyclability and durability, potentially reducing overall waste. Polyurethane soles, while providing superior flexibility and comfort, often rely on non-renewable resources and present challenges in biodegradability, contributing to long-term environmental concerns.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyurethane for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com