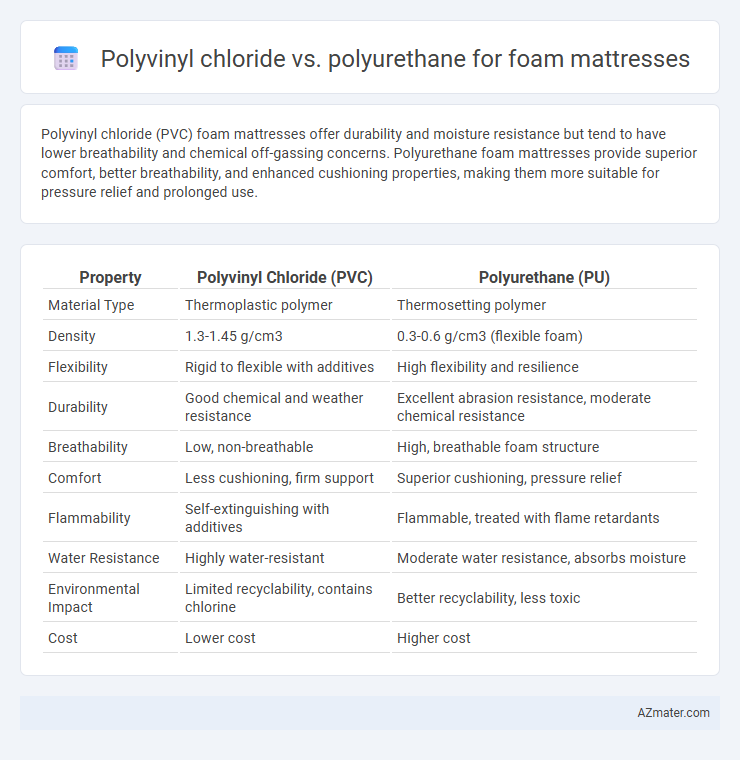
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses offer durability and moisture resistance but tend to have lower breathability and chemical off-gassing concerns. Polyurethane foam mattresses provide superior comfort, better breathability, and enhanced cushioning properties, making them more suitable for pressure relief and prolonged use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermosetting polymer |
| Density | 1.3-1.45 g/cm3 | 0.3-0.6 g/cm3 (flexible foam) |
| Flexibility | Rigid to flexible with additives | High flexibility and resilience |
| Durability | Good chemical and weather resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance, moderate chemical resistance |
| Breathability | Low, non-breathable | High, breathable foam structure |
| Comfort | Less cushioning, firm support | Superior cushioning, pressure relief |
| Flammability | Self-extinguishing with additives | Flammable, treated with flame retardants |
| Water Resistance | Highly water-resistant | Moderate water resistance, absorbs moisture |
| Environmental Impact | Limited recyclability, contains chlorine | Better recyclability, less toxic |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Mattress Materials: Polyvinyl Chloride and Polyurethane
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyurethane (PU) are two prominent materials used in foam mattresses, each offering distinct properties and benefits. PVC, known for its durability and water resistance, provides a firm support surface often utilized in mattress covers and protective layers. Polyurethane foam, renowned for its cushioning ability and flexibility, delivers superior comfort and pressure relief, making it a popular choice for the mattress core.
Chemical Structure Differences between PVC and PU
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) consists of repeating vinyl chloride monomers, characterized by a rigid carbon-chlorine bond that imparts durability and resistance to moisture and chemicals. Polyurethane (PU) features flexible urethane linkages formed from the reaction between polyols and isocyanates, resulting in a highly elastic, open-cell foam structure suited for cushioning. The fundamental chemical distinction lies in PVC's thermoplastic polymer chains with chlorine atoms compared to PU's elastomeric network created through urethane bonding, influencing their respective applications in foam mattresses.
Comfort and Support: How PVC and PU Affect Sleep Quality
Polyurethane (PU) foam mattresses offer superior comfort and support compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) options due to PU's enhanced elasticity and pressure-relieving properties, which promote spinal alignment and reduce sleep disturbances. PVC foam is generally firmer and less breathable, often resulting in heat retention and less contouring ability, which can negatively impact sleep quality. The breathable structure of PU foam improves airflow and temperature regulation, making it a preferred choice for overall sleep comfort and support.
Durability Comparison: Lifespan of PVC vs PU Foam Mattresses
Polyurethane foam mattresses generally offer a longer lifespan, typically lasting 7 to 10 years, due to their superior elasticity and resilience compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses. PVC foam tends to degrade faster, often showing signs of wear and tear within 3 to 5 years, as it is less flexible and more prone to cracking and brittleness over time. The durability of PU foam mattresses is enhanced by their ability to retain shape and resist compression, making them a preferred choice for extended use.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation in Mattresses
Polyurethane foam mattresses excel in breathability and temperature regulation due to their open-cell structure, allowing better air circulation and moisture dissipation compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, which tends to trap heat and retain humidity. PVC foam's denser composition limits airflow, often resulting in a warmer sleep surface and increased perspiration buildup. Selecting polyurethane foam enhances sleep comfort by maintaining a cooler, more ventilated environment throughout the night.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of PVC and PU Foams
Polyurethane (PU) foam in mattresses generally offers better environmental sustainability than polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam due to the lower toxicity in production and improved recyclability of PU materials. PVC foam manufacturing involves chlorine, which releases harmful dioxins contributing to pollution and persistent environmental damage. PU foams are increasingly produced with bio-based polyols, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and enhancing biodegradability compared to PVC foams, which are less eco-friendly and more challenging to dispose of safely.
Health and Safety: Allergens and VOC Emissions
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses often emit higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can trigger respiratory issues and allergic reactions in sensitive individuals, while polyurethane foam typically releases fewer VOCs, enhancing indoor air quality. PVC materials may contain additives like phthalates linked to hormone disruption and allergies, whereas polyurethane foam is generally formulated with fewer toxic chemicals, reducing allergen risks. Selecting polyurethane foam mattresses contributes to improved health and safety by minimizing exposure to allergens and harmful VOC emissions commonly associated with PVC-based foams.
Cost Analysis: Affordability of PVC vs PU Foam Mattresses
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to polyurethane (PU) foam mattresses, making them a more budget-friendly option for consumers. PU foam mattresses, while more expensive, provide enhanced durability and comfort, often justifying the higher price point through longer lifespan and superior performance. Cost analysis should also consider factors such as material density, manufacturing quality, and intended mattress use to determine overall value.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses require regular cleaning with mild soap and water to prevent dirt buildup and maintain their durability, as harsh chemicals can degrade the material. Polyurethane foam mattresses demand careful handling to avoid moisture absorption and mold growth, necessitating the use of protective covers and routine airing. Both materials benefit from avoiding direct sunlight exposure to prolong the mattress lifespan, but polyurethane's sensitivity to heat and humidity demands stricter environmental control.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam Material for Your Mattress
Polyurethane foam offers superior comfort and durability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, making it the preferred choice for mattress construction. PVC foam tends to be less breathable and may emit stronger odors, impacting sleep quality and indoor air. Selecting polyurethane foam enhances mattress longevity and provides better support, ideal for consumers prioritizing comfort and health.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polyurethane for Foam mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com