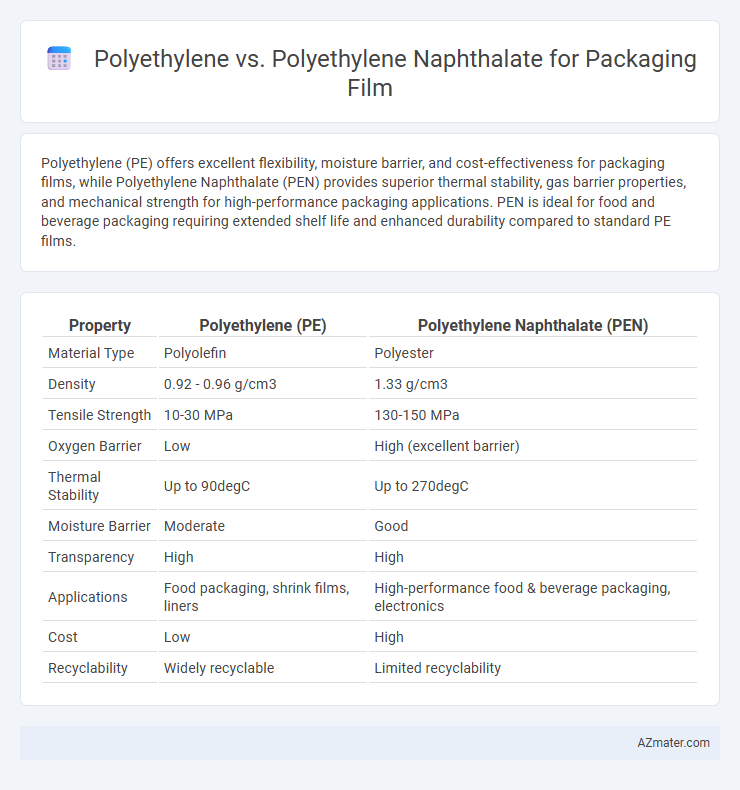
Polyethylene (PE) offers excellent flexibility, moisture barrier, and cost-effectiveness for packaging films, while Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) provides superior thermal stability, gas barrier properties, and mechanical strength for high-performance packaging applications. PEN is ideal for food and beverage packaging requiring extended shelf life and enhanced durability compared to standard PE films.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyolefin | Polyester |
| Density | 0.92 - 0.96 g/cm3 | 1.33 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 10-30 MPa | 130-150 MPa |
| Oxygen Barrier | Low | High (excellent barrier) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 90degC | Up to 270degC |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate | Good |
| Transparency | High | High |
| Applications | Food packaging, shrink films, liners | High-performance food & beverage packaging, electronics |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable | Limited recyclability |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polyethylene Naphthalate in Packaging
Polyethylene (PE) is a widely used polymer in packaging films known for its flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for food wraps and industrial packaging. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN), a copolymer of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), offers superior barrier properties, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, enhancing the shelf life of sensitive products. The choice between PE and PEN in packaging depends on the balance between economic efficiency and the need for advanced protection against oxygen, moisture, and UV degradation.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyethylene (PE) is a polymer composed of long chains of ethylene monomers with a simple, saturated hydrocarbon backbone, resulting in high chemical resistance, flexibility, and moisture barrier properties suitable for general packaging. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) features a rigid aromatic naphthalate ring in its backbone, providing superior thermal stability, mechanical strength, and excellent gas barrier performance compared to PE, making it ideal for high-performance packaging applications. The aromatic structure in PEN also enhances dimensional stability and resistance to UV degradation, distinguishing it chemically and functionally from the aliphatic PE.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to conventional Polyethylene (PE) in packaging film applications, offering enhanced tensile strength and improved resistance to deformation under stress. PEN's molecular structure provides higher dimensional stability and better barrier properties against moisture and gases, making it more suitable for durable and long-lasting packaging solutions. The improved crystallinity and thermal stability of PEN contribute to its robustness and extended lifespan in demanding environmental conditions.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Permeability
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) exhibits significantly superior barrier properties compared to standard Polyethylene (PE), with much lower moisture vapor transmission rates and enhanced resistance to oxygen and carbon dioxide permeability. PE, while widely used for flexible packaging due to its cost-effectiveness and flexibility, inherently allows higher moisture and gas permeation, limiting its suitability for products requiring extended shelf life. PEN's aromatic structure contributes to its dense molecular arrangement, making it an optimal choice for packaging applications demanding high-performance moisture and gas barrier properties.
Thermal Stability and Processing Temperatures
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to standard Polyethylene (PE), with a higher glass transition temperature around 120degC versus PE's approximately -80degC, enabling better performance in high-temperature packaging applications. PEN's enhanced thermal resistance allows processing temperatures between 270-300degC, significantly above polyethylene's typical range of 130-180degC, facilitating improved dimensional stability and durability in demanding environments. The elevated thermal properties of PEN contribute to greater barrier performance and extended shelf life in packaging films, especially in products requiring heat resistance.
Optical Clarity and Surface Appearance
Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) offers superior optical clarity compared to conventional Polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for packaging films that require excellent transparency and high gloss. PEN films exhibit enhanced surface smoothness and a more uniform appearance due to their higher crystallinity and molecular structure, which also contributes to better UV resistance and dimensional stability. In contrast, PE films often present lower clarity and a matte or less consistent surface finish, limiting their use in applications demanding premium visual aesthetics.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene (PE) is widely used in packaging films due to its high recyclability and lower environmental footprint, being easily processed in existing recycling streams and contributing less to greenhouse gas emissions during production. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN), although offering superior barrier properties and thermal stability, presents challenges in recyclability because it requires specialized processing and separation from other polymers, which limits its widespread recycling infrastructure. The environmental impact of PEN is higher due to its complex manufacturing process and limited recyclability, making PE a more sustainable option for packaging films in terms of circular economy and resource efficiency.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polyethylene (PE) offers significantly lower production costs compared to Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN), making PE the preferred choice for high-volume, cost-sensitive packaging films. Market availability of PE is vastly greater due to its widespread use and established manufacturing infrastructure, while PEN remains limited primarily to specialty applications with higher performance requirements and consequently higher price points. The cost differential and supply chain scale heavily favor PE in standard packaging markets, whereas PEN's niche applications justify its premium.
Common Applications in Packaging Films
Polyethylene (PE) is widely used in packaging films for its flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for food wrapping, shrink films, and grocery bags. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) offers superior barrier properties against gases and moisture, improved thermal stability, and enhanced mechanical strength, which suits high-performance packaging such as pharmaceutical blister packs, electronics packaging, and beverage bottles. Both materials serve distinct roles in packaging films, with PE dominating everyday applications and PEN preferred for specialized, high-barrier requirements.
Choosing the Right Material: Polyethylene vs Polyethylene Naphthalate
Polyethylene (PE) offers excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and low cost, making it ideal for general packaging films such as food wraps and bags. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) provides superior thermal stability, gas barrier properties, and durability, suitable for high-performance applications requiring extended shelf life and resistance to heat and pressure. Selecting the right material depends on specific packaging requirements like barrier protection, mechanical strength, and budget constraints to optimize performance and cost efficiency.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polyethylene Naphthalate for Packaging Film
 azmater.com
azmater.com