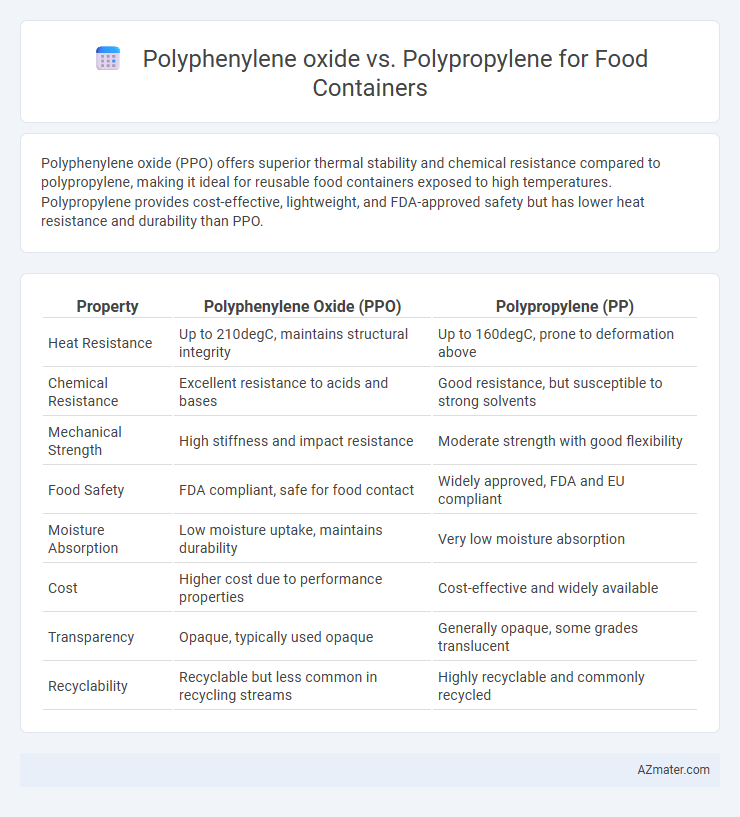
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for reusable food containers exposed to high temperatures. Polypropylene provides cost-effective, lightweight, and FDA-approved safety but has lower heat resistance and durability than PPO.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 210degC, maintains structural integrity | Up to 160degC, prone to deformation above |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and bases | Good resistance, but susceptible to strong solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness and impact resistance | Moderate strength with good flexibility |
| Food Safety | FDA compliant, safe for food contact | Widely approved, FDA and EU compliant |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture uptake, maintains durability | Very low moisture absorption |
| Cost | Higher cost due to performance properties | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Transparency | Opaque, typically used opaque | Generally opaque, some grades translucent |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but less common in recycling streams | Highly recyclable and commonly recycled |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide and Polypropylene
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for durable, reusable food containers. Polypropylene (PP) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer recognized for its lightweight, low cost, and good chemical resistance, commonly used in disposable and microwave-safe food packaging. When comparing PPO and PP for food containers, PPO offers superior heat resistance and structural integrity, whereas PP provides economic efficiency and ease of manufacturing.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic backbone with ether linkages, providing excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance ideal for food containers requiring durability against heat and solvents. In contrast, polypropylene (PP) has a semi-crystalline aliphatic hydrocarbon structure that offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and a lower melting point, making it suitable for lightweight, disposable food packaging. PPO's higher glass transition temperature and resistance to oxidation improve shelf life and safety for hot food storage, whereas PP's cost-effectiveness and moisture barrier properties dominate everyday cold and dry food applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polypropylene (PP), offering enhanced rigidity and impact resistance ideal for food container applications requiring durability. PPO's inherent thermal stability allows it to withstand higher temperatures without deformation, making it more durable during repeated heating cycles. In contrast, polypropylene provides good chemical resistance and flexibility but may suffer from creep and reduced mechanical integrity under prolonged stress and elevated temperatures.
Thermal Resistance Capabilities
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 180degC, while polypropylene typically withstands heat up to 120degC. This enhanced thermal stability of PPO makes it ideal for food containers intended for high-temperature applications such as microwave reheating or dishwasher use. The higher heat deflection temperature and low thermal conductivity of PPO contribute to better preservation of food quality and safer handling under thermal stress.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), making it a safer option for food containers exposed to varying temperatures and acidic foods. PPO is often certified by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EFSA for direct food contact, ensuring compliance with stringent food safety standards. Although polypropylene is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and regulatory approvals, PPO's enhanced barrier properties reduce the risk of contamination and leaching, improving overall food safety.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), maintaining structural integrity and preventing water absorption in humid conditions. PPO also offers enhanced chemical resistance, effectively withstanding exposure to acids, bases, and various solvents commonly found in food storage environments. While polypropylene provides moderate resistance, PPO's durability makes it a preferred choice for food containers requiring long-term preservation against moisture and chemical degradation.
Impact on Food Flavor and Odor
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior resistance to absorption and migration of food odors and flavors compared to polypropylene, minimizing the risk of flavor contamination. Polypropylene (PP) may allow some degree of flavor transfer due to its relatively higher permeability and interaction with food components, which can alter taste profiles over time. The inert nature of PPO ensures that food containers retain original food quality without imparting unwanted smells or tastes, making it ideal for sensitive or aromatic food storage.
Cost-Effectiveness for Manufacturers
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior heat resistance and dimensional stability compared to polypropylene (PP), which reduces product defects and enhances durability in food containers. While PPO incurs higher initial raw material costs, its long-term cost-effectiveness stems from lower production downtime and reduced waste due to improved performance. Manufacturers prioritizing longevity and quality may find PPO more economical despite its higher upfront expense, whereas PP remains favored for large-scale, cost-sensitive applications due to its lower material cost and ease of processing.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), making it a durable choice for food containers with enhanced longevity, which reduces waste over time. PPO's production involves higher energy consumption but provides better recyclability and less environmental degradation due to its resistance to thermal and oxidative breakdown. Polypropylene, while widely used due to its low cost and lightweight properties, often degrades more quickly and has limited recycling efficiency, contributing to increased plastic pollution and environmental impact.
Conclusion: Choosing the Ideal Material for Food Containers
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for high-temperature food containers that require dishwasher and microwave safety. Polypropylene (PP) excels in cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and recyclability, well-suited for everyday disposable containers and cold food storage. Selecting between PPO and PP depends on specific needs: PPO for durability and safety in high-heat applications, and PP for economic, lightweight, and versatile food packaging solutions.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polypropylene for Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com