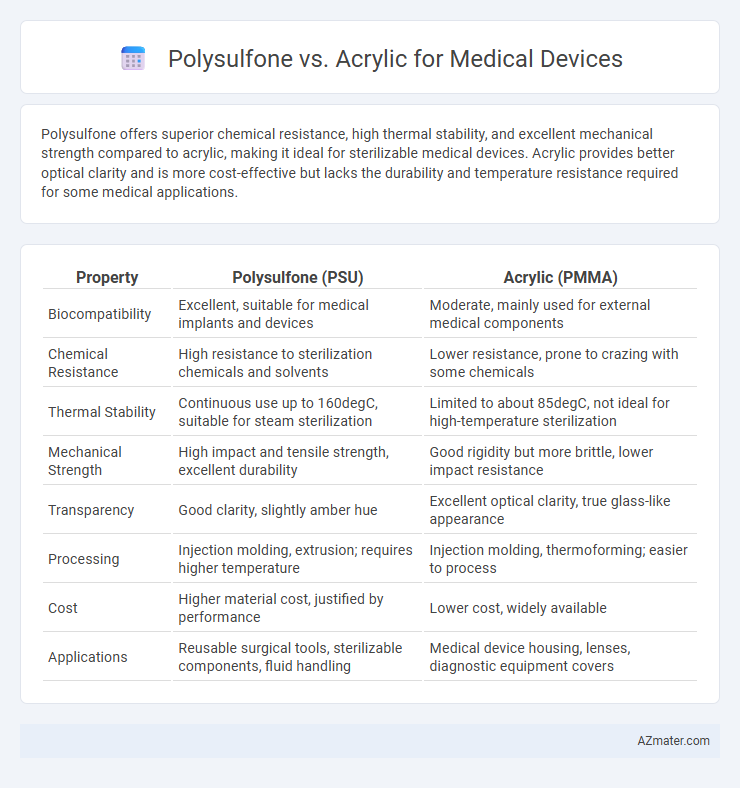
Polysulfone offers superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and excellent mechanical strength compared to acrylic, making it ideal for sterilizable medical devices. Acrylic provides better optical clarity and is more cost-effective but lacks the durability and temperature resistance required for some medical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Acrylic (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, suitable for medical implants and devices | Moderate, mainly used for external medical components |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to sterilization chemicals and solvents | Lower resistance, prone to crazing with some chemicals |
| Thermal Stability | Continuous use up to 160degC, suitable for steam sterilization | Limited to about 85degC, not ideal for high-temperature sterilization |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact and tensile strength, excellent durability | Good rigidity but more brittle, lower impact resistance |
| Transparency | Good clarity, slightly amber hue | Excellent optical clarity, true glass-like appearance |
| Processing | Injection molding, extrusion; requires higher temperature | Injection molding, thermoforming; easier to process |
| Cost | Higher material cost, justified by performance | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Reusable surgical tools, sterilizable components, fluid handling | Medical device housing, lenses, diagnostic equipment covers |
Introduction to Medical Device Materials
Polysulfone and acrylic are widely used in medical device materials due to their biocompatibility and durability. Polysulfone offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for sterilizable medical applications. Acrylic provides clarity and lightweight properties, often chosen for devices requiring transparency and aesthetic appeal.
Overview of Polysulfone
Polysulfone is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional thermal stability, excellent chemical resistance, and superior mechanical strength, making it ideal for use in medical devices requiring sterilization and durability. Its transparency and biocompatibility enable clear visibility and safe interaction with biological environments, which is critical in applications such as surgical instruments, sterilization trays, and fluid handling components. Compared to acrylic, polysulfone offers enhanced resistance to high temperatures and repeated sterilization cycles, ensuring long-term reliability and performance in demanding medical settings.
Overview of Acrylic
Acrylic, also known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is widely used in medical devices due to its excellent clarity, biocompatibility, and resistance to chemicals. Its superior optical transparency and ease of fabrication make it ideal for applications requiring visual monitoring and precision molding. Acrylic's rigidity and moderate impact resistance provide reliable performance in devices such as lenses, housings, and surgical instruments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to acrylic, making it ideal for medical devices requiring high durability and resistance to impact. Its tensile strength typically ranges from 60 to 75 MPa, whereas acrylic usually offers around 50 to 70 MPa, demonstrating polysulfone's enhanced toughness and flexibility under stress. This mechanical robustness ensures polysulfone components maintain structural integrity in demanding healthcare environments, outperforming acrylic in long-term reliability.
Chemical Resistance and Sterilization
Polysulfone exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to acrylic, maintaining integrity against strong acids, bases, and alcohols, making it ideal for harsh medical environments. It withstands multiple sterilization methods, including autoclaving, gamma radiation, and ethylene oxide, without significant degradation. Acrylic, while offering good optical clarity, is more prone to chemical attack and can degrade under repeated sterilization, limiting its use in reusable medical devices.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Polysulfone exhibits excellent optical clarity with a high degree of transparency and is resistant to yellowing under prolonged UV exposure, making it ideal for medical devices requiring sustained visibility. Acrylic offers superior light transmittance, typically around 92%, providing exceptional clarity and brilliance but is more prone to scratching and may degrade under sterilization methods. Choosing between polysulfone and acrylic depends on balancing clarity demands with chemical resistance and sterilization compatibility in medical device applications.
Biocompatibility and Safety
Polysulfone exhibits superior biocompatibility and safety in medical devices due to its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and low leachables, making it ideal for long-term implants and sterilization processes. Acrylic, while offering good optical clarity and cost-effectiveness, may pose higher risks of chemical leachates and less resistance to repeated sterilization, limiting its use in critical medical applications. When prioritizing patient safety and regulatory compliance, polysulfone stands out as the preferred polymer for devices requiring durable, biocompatible materials.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polysulfone offers higher durability and chemical resistance for medical devices, often justifying its higher price through extended product life and reduced replacement frequency. Acrylic provides a cost-effective alternative with easier availability and simpler fabrication processes, making it suitable for non-critical components. Choosing between polysulfone and acrylic depends on balancing upfront material costs with long-term performance requirements and supply chain reliability.
Common Applications in Medical Devices
Polysulfone is widely used in medical devices requiring high heat resistance and steam sterilization, such as dialysis membranes, surgical instrument components, and sterilization trays. Acrylic is preferred for applications needing optical clarity and rigidity, including medical device housings, lenses, and diagnostic equipment covers. Both materials offer biocompatibility, but polysulfone's chemical resistance and durability make it ideal for reusable medical tools, whereas acrylic suits disposable or visual components.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Polysulfone offers exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and superior mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding medical devices requiring sterilization and prolonged use. Acrylic provides excellent optical clarity and biocompatibility, suitable for applications like lenses or casings where transparency and patient safety are critical. Selecting the right material depends on balancing durability, sterilization methods, and specific device functionality to ensure optimal performance and compliance with medical standards.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Acrylic for Medical Device
 azmater.com
azmater.com