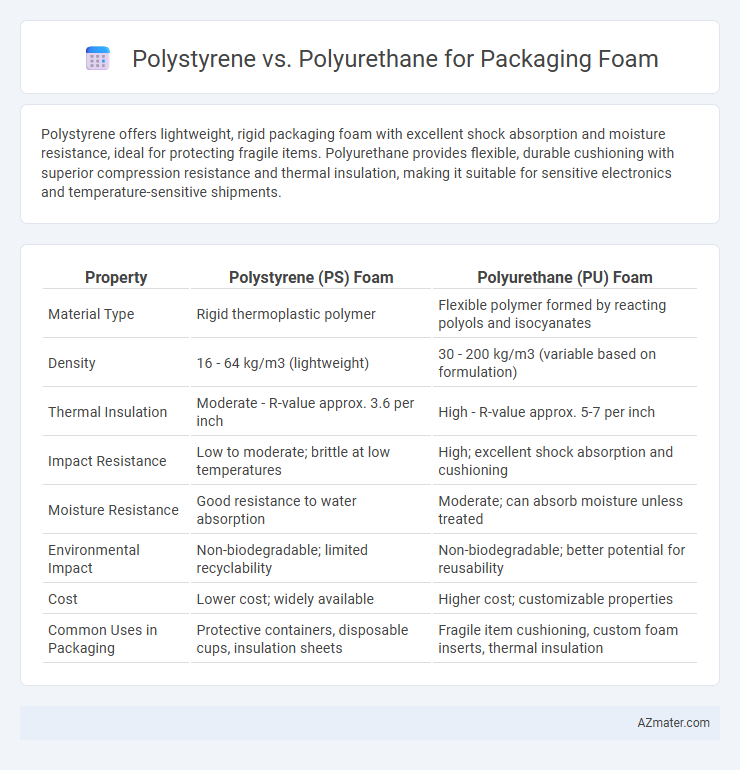
Polystyrene offers lightweight, rigid packaging foam with excellent shock absorption and moisture resistance, ideal for protecting fragile items. Polyurethane provides flexible, durable cushioning with superior compression resistance and thermal insulation, making it suitable for sensitive electronics and temperature-sensitive shipments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) Foam | Polyurethane (PU) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Rigid thermoplastic polymer | Flexible polymer formed by reacting polyols and isocyanates |
| Density | 16 - 64 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 30 - 200 kg/m3 (variable based on formulation) |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate - R-value approx. 3.6 per inch | High - R-value approx. 5-7 per inch |
| Impact Resistance | Low to moderate; brittle at low temperatures | High; excellent shock absorption and cushioning |
| Moisture Resistance | Good resistance to water absorption | Moderate; can absorb moisture unless treated |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable; limited recyclability | Non-biodegradable; better potential for reusability |
| Cost | Lower cost; widely available | Higher cost; customizable properties |
| Common Uses in Packaging | Protective containers, disposable cups, insulation sheets | Fragile item cushioning, custom foam inserts, thermal insulation |
Introduction to Packaging Foam Materials
Polystyrene and polyurethane are two widely used materials for packaging foam, each offering distinct properties suited for different applications. Polystyrene foam provides excellent rigidity and cushioning, making it ideal for protecting fragile items against impact during shipping. Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and resilience, enabling better shock absorption and long-term durability in packaging solutions.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam is a lightweight, rigid material commonly used in packaging due to its excellent cushioning properties and moisture resistance. It is made from expanded polystyrene beads that form a closed-cell structure, providing effective shock absorption and insulation. This foam type is cost-effective and widely utilized for protecting fragile items during shipping and handling.
Overview of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and flexibility compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for protective packaging of fragile items. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent shock absorption and resistance to moisture, which enhances durability during shipping and storage. The material's versatility allows customization in density and firmness to meet specific packaging requirements across various industries.
Key Differences in Material Properties
Polystyrene foam offers excellent rigidity, lightweight characteristics, and high impact resistance, making it ideal for structural packaging and protecting delicate electronics. In contrast, polyurethane foam provides superior flexibility, cushioning, and thermal insulation, excelling in shock absorption for fragile items during transit. Polystyrene is more resistant to moisture and chemical exposure, while polyurethane tends to degrade faster under prolonged environmental stress, affecting long-term durability.
Insulation and Cushioning Performance
Polystyrene foam offers excellent insulation with a high R-value per inch, making it ideal for temperature-sensitive packaging, while its rigid structure provides moderate cushioning. Polyurethane foam excels in cushioning performance due to its superior flexibility and energy absorption properties, effectively protecting fragile items from impact. Both materials provide thermal insulation, but polyurethane's adaptive density often results in enhanced shock resistance compared to the more brittle polystyrene.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polystyrene foam, commonly used in packaging, poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradability and difficulty in recycling, often accumulating in landfills and oceans for centuries. Polyurethane foam offers better potential for recycling and can be formulated for biodegradability, yet it still relies on petrochemical resources and may release harmful substances during degradation. Sustainable packaging solutions increasingly favor innovative bio-based polyurethanes or alternative materials designed to minimize environmental impact and enhance circular economy practices.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Polystyrene foam typically offers a lower production cost compared to polyurethane foam, making it a more budget-friendly option for large-scale packaging applications. However, polyurethane provides superior cushioning and durability, which can reduce product damage and associated costs over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including material prices, protective performance, and waste management, is essential for making an economically sound packaging foam choice.
Applications in Packaging Industries
Polystyrene foam is widely used in packaging industries for its excellent shock absorption and lightweight properties, making it ideal for protecting fragile electronics and appliances during shipping. Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and higher cushioning performance, commonly employed in packaging for delicate items requiring custom-fit protection such as medical devices and automotive components. Both materials enable efficient thermal insulation, with polyurethane often favored for temperature-sensitive goods due to its better thermal resistance.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polystyrene foam is widely used in packaging due to its lightweight and cushioning properties but faces scrutiny over environmental safety and stringent disposal regulations, particularly concerning its non-biodegradable nature and potential release of styrene, a suspected carcinogen. Polyurethane foam offers enhanced safety compliance by meeting stricter fire retardancy and chemical safety standards, supported by certifications such as UL94 and REACH, making it preferable for applications requiring rigorous regulatory adherence. Both materials must comply with FDA and EPA packaging guidelines, yet polyurethane's adaptability to safer formulations positions it as a more sustainable choice for protective packaging solutions.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Polystyrene foam offers lightweight cushioning with excellent impact resistance and is ideal for protecting fragile items during shipping, while polyurethane foam provides superior flexibility and shock absorption for packaging irregularly shaped or heavier products. Consider factors such as product weight, fragility, and environmental conditions to determine the best foam type, with polystyrene being cost-effective for simple packaging and polyurethane excelling in custom and high-performance protection. Choosing the right foam enhances product safety, reduces damage-related costs, and improves overall packaging efficiency.
Infographic: Polystyrene vs Polyurethane for Packaging Foam
 azmater.com
azmater.com