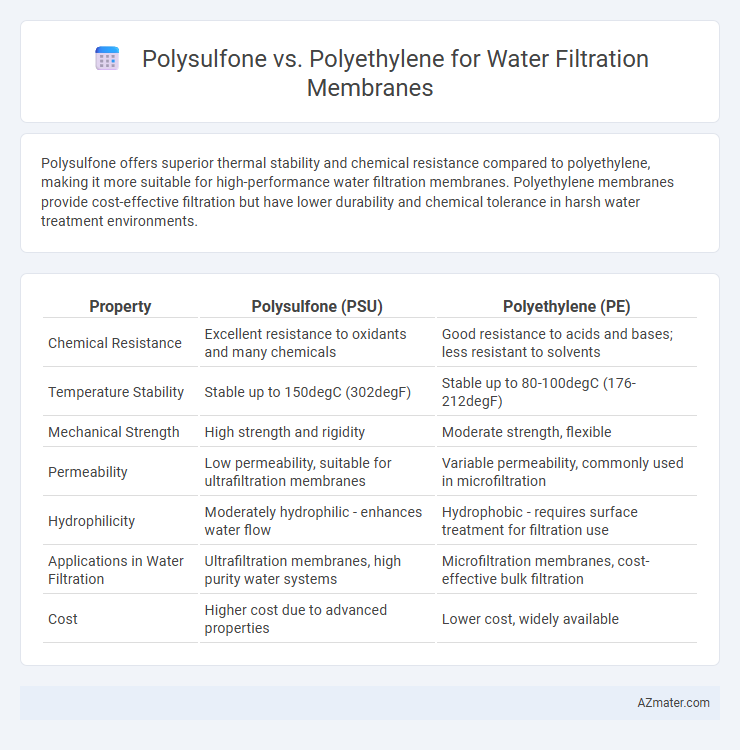
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, making it more suitable for high-performance water filtration membranes. Polyethylene membranes provide cost-effective filtration but have lower durability and chemical tolerance in harsh water treatment environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oxidants and many chemicals | Good resistance to acids and bases; less resistant to solvents |
| Temperature Stability | Stable up to 150degC (302degF) | Stable up to 80-100degC (176-212degF) |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and rigidity | Moderate strength, flexible |
| Permeability | Low permeability, suitable for ultrafiltration membranes | Variable permeability, commonly used in microfiltration |
| Hydrophilicity | Moderately hydrophilic - enhances water flow | Hydrophobic - requires surface treatment for filtration use |
| Applications in Water Filtration | Ultrafiltration membranes, high purity water systems | Microfiltration membranes, cost-effective bulk filtration |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Water Filtration Membranes
Water filtration membranes utilize materials like polysulfone and polyethylene to effectively remove contaminants from water, ensuring safe drinking quality. Polysulfone membranes are known for their thermal stability and chemical resistance, ideal for high-temperature applications and aggressive cleaning processes. Polyethylene membranes offer cost-effective filtration with good mechanical strength, often favored in low-temperature, less demanding environments.
Overview of Polysulfone (PSU) Membranes
Polysulfone (PSU) membranes are widely used in water filtration due to their excellent thermal and chemical stability, making them ideal for harsh operational environments. These membranes offer high mechanical strength and resistance to oxidation, supporting long-term durability in ultrafiltration and microfiltration applications. PSU membranes enable effective removal of bacteria, viruses, and suspended solids, contributing to high water purity and safety standards.
Overview of Polyethylene (PE) Membranes
Polyethylene (PE) membranes are widely used in water filtration due to their excellent chemical resistance, durability, and hydrophobic properties, which make them effective for microfiltration and ultrafiltration applications. PE membranes typically exhibit high tensile strength and low fouling tendencies, allowing for extended operational lifespan and consistent performance in filtering particulates and microorganisms. Their cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication contribute to widespread industrial use, particularly in systems requiring robust filtration under varying pH and temperature conditions.
Material Properties Comparison: Polysulfone vs Polyethylene
Polysulfone membranes offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, making them ideal for high-temperature water filtration applications. Polyethylene membranes, while more cost-effective and flexible, exhibit lower mechanical strength and permeability under extreme conditions. The choice between polysulfone and polyethylene depends on the required durability, chemical exposure, and operating temperature for water filtration systems.
Filtration Efficiency and Performance
Polysulfone membranes exhibit higher filtration efficiency compared to polyethylene due to their superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, allowing better retention of contaminants and longer operational lifespan. The porous structure of polysulfone facilitates consistent water flux and minimizes fouling, enhancing overall filtration performance in both microfiltration and ultrafiltration applications. Polyethylene membranes, while cost-effective, generally show lower permeability and reduced durability under harsh water conditions, limiting their effectiveness in demanding water treatment processes.
Chemical and Thermal Stability
Polysulfone exhibits superior chemical resistance and maintains structural integrity in a wide pH range, making it ideal for aggressive water filtration environments, whereas polyethylene is more susceptible to chemical degradation. In terms of thermal stability, polysulfone can withstand continuous operating temperatures up to 150degC, significantly outperforming polyethylene, which typically deforms at temperatures above 80degC. These properties make polysulfone membranes more reliable for high-temperature and chemically harsh water treatment applications.
Fouling Resistance and Maintenance
Polysulfone membranes exhibit superior fouling resistance compared to polyethylene due to their hydrophilic surface, which reduces organic and microbial adhesion during water filtration. The chemical stability and thermal resistance of polysulfone enable easier cleaning protocols and longer membrane lifespan, minimizing maintenance frequency. Polyethylene membranes, while cost-effective, tend to accumulate fouling more rapidly, necessitating more frequent replacement and intensive cleaning efforts.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polysulfone membranes exhibit higher initial costs compared to polyethylene membranes, but their superior chemical resistance and thermal stability extend operational lifespan and reduce replacement frequency in water filtration systems. Polyethylene membranes, while more affordable upfront, often require more frequent maintenance and replacement due to lower durability, increasing long-term operational expenses. Cost-effectiveness analysis favors polysulfone for applications demanding longevity and consistent performance, whereas polyethylene suits budget-sensitive projects with lower filtration demands.
Common Applications in Water Filtration
Polysulfone membranes are commonly used in water filtration for applications requiring high thermal stability and chemical resistance, such as municipal water treatment and industrial wastewater filtration. Polyethylene membranes, favored for their hydrophobic properties and cost-effectiveness, are typically applied in microfiltration processes and pre-filtration stages to remove particulates and suspended solids. Both materials are essential in water treatment systems, with polysulfone offering superior durability for long-term use and polyethylene providing efficient particulate filtration in less demanding environments.
Choosing the Right Membrane: Factors to Consider
Polysulfone membranes offer superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for harsh water treatment environments, while polyethylene membranes provide excellent flexibility and cost-effectiveness for less aggressive conditions. Key factors to consider when choosing between these materials include the chemical composition of the water, temperature ranges, and desired membrane lifespan. Evaluating membrane porosity, fouling resistance, and mechanical strength ensures optimal filtration performance tailored to specific water quality requirements.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyethylene for Water Filtration Membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com