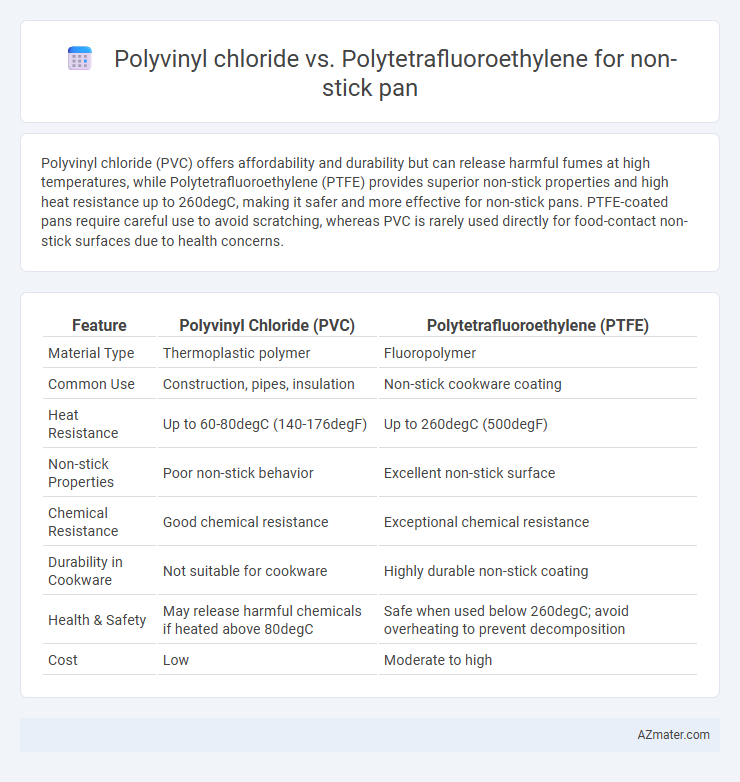
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers affordability and durability but can release harmful fumes at high temperatures, while Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior non-stick properties and high heat resistance up to 260degC, making it safer and more effective for non-stick pans. PTFE-coated pans require careful use to avoid scratching, whereas PVC is rarely used directly for food-contact non-stick surfaces due to health concerns.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Fluoropolymer |
| Common Use | Construction, pipes, insulation | Non-stick cookware coating |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 60-80degC (140-176degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Non-stick Properties | Poor non-stick behavior | Excellent non-stick surface |
| Chemical Resistance | Good chemical resistance | Exceptional chemical resistance |
| Durability in Cookware | Not suitable for cookware | Highly durable non-stick coating |
| Health & Safety | May release harmful chemicals if heated above 80degC | Safe when used below 260degC; avoid overheating to prevent decomposition |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Polyvinyl Chloride and Polytetrafluoroethylene
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in construction and household products due to its durability and chemical resistance but is rarely used in cookware because it lacks heat resistance. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, is a fluoropolymer renowned for its excellent non-stick properties, high-temperature stability, and chemical inertness, making it ideal for non-stick pans. PTFE's molecular structure provides superior resistance to heat and chemical degradation compared to PVC, which enhances safety and performance in cookware applications.
Chemical Structure Comparison: PVC vs PTFE
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) consists of repeating vinyl chloride units with a carbon backbone bonded to chlorine atoms, giving it rigidity and chemical resistance, while polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) features a carbon backbone fully fluorinated with fluorine atoms, resulting in exceptional non-stick properties and high thermal stability. The strong carbon-fluorine bonds in PTFE create a low surface energy material ideal for non-stick pans, whereas PVC's chlorine content provides less thermal resilience and non-stick capability. PTFE's molecular structure minimizes intermolecular forces, leading to superior non-reactivity and durability compared to PVC in cookware applications.
Heat Resistance: Which Material Performs Better?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior heat resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with PTFE maintaining stability up to 260degC (500degF) and beyond, whereas PVC begins to degrade at temperatures above 80degC (176degF). This makes PTFE the preferred choice for non-stick pans, where sustained high cooking temperatures are common. The high melting point and chemical inertness of PTFE ensure durability and safety in cookware applications, outperforming PVC significantly in heat resistance.
Non-stick Properties: Effectiveness and Longevity
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior non-stick properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), providing exceptional food release and ease of cleaning. PTFE coatings maintain their effectiveness and resist degradation at high cooking temperatures, ensuring long-lasting non-stick performance. In contrast, PVC lacks inherent non-stick capability and deteriorates quickly under heat, making it unsuitable for durable cookware coatings.
Safety and Food-Grade Considerations
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is widely preferred over polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for non-stick pans due to its superior chemical inertness and resistance to high temperatures, minimizing the risk of harmful chemical leaching during cooking. PVC contains plasticizers and additives that may release toxic compounds when heated, raising food safety concerns. PTFE coatings, when used within manufacturer temperature guidelines, provide a safer, food-grade surface that resists degradation and ensures non-stick performance without compromising health.
Durability and Lifespan in Kitchen Use
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) when used in non-stick pans due to its exceptional resistance to high temperatures and chemical degradation. PVC tends to degrade faster under constant heat exposure, leading to a compromised non-stick surface and potential release of harmful chemicals. PTFE-coated pans maintain their non-stick properties and structural integrity over extended periods, making them more reliable for frequent kitchen use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in non-stick pans poses significant environmental challenges due to the release of toxic chlorine-based compounds during manufacturing and disposal, contributing to persistent organic pollution and hindering recyclability. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known for its chemical inertness and durability, offers improved sustainability by reducing the need for frequent replacement, but its production involves greenhouse gas emissions and potential release of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a persistent environmental contaminant. Choosing PTFE-coated pans over PVC-based alternatives favors lower environmental toxicity and enhanced product longevity, aligning better with sustainable consumption goals.
Cost Comparison: PVC vs PTFE Non-stick Pans
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) non-stick pans are generally more affordable than polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) pans due to lower material and manufacturing costs. PTFE pans, often marketed under brand names like Teflon, typically command higher prices reflecting their superior non-stick performance and heat resistance. Consumers seeking budget-friendly options often opt for PVC coatings despite PTFE's longer lifespan and better resistance to high temperatures.
Market Availability and Common Uses
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is rarely used for non-stick pans due to its lower heat resistance and tendency to release harmful fumes when heated, limiting its market availability in cookware. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known by the brand name Teflon, dominates the non-stick pan market because of its excellent heat resistance, non-reactivity, and superior non-stick properties. PTFE-coated pans are widely used for everyday cooking tasks like frying and sauteing, making them a staple in both household kitchens and commercial food service settings.
Conclusion: Which is Better for Non-stick Pans?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is superior for non-stick pans due to its exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and unparalleled non-stick properties, making it safer and more effective for cooking. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) lacks the heat resistance required for cooking applications and can release harmful chemicals when exposed to high temperatures, making it unsuitable for non-stick cookware. Therefore, PTFE coatings remain the preferred choice for durable, food-safe non-stick pans.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Non-stick pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com