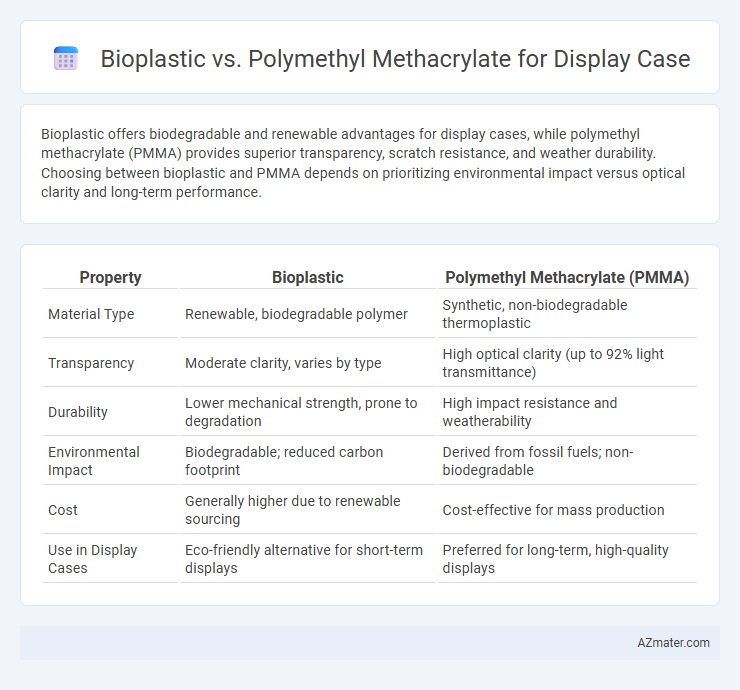
Bioplastic offers biodegradable and renewable advantages for display cases, while polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior transparency, scratch resistance, and weather durability. Choosing between bioplastic and PMMA depends on prioritizing environmental impact versus optical clarity and long-term performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Renewable, biodegradable polymer | Synthetic, non-biodegradable thermoplastic |
| Transparency | Moderate clarity, varies by type | High optical clarity (up to 92% light transmittance) |
| Durability | Lower mechanical strength, prone to degradation | High impact resistance and weatherability |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable; reduced carbon footprint | Derived from fossil fuels; non-biodegradable |
| Cost | Generally higher due to renewable sourcing | Cost-effective for mass production |
| Use in Display Cases | Eco-friendly alternative for short-term displays | Preferred for long-term, high-quality displays |
Introduction to Display Case Materials
Bioplastic and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) are prominent materials used in display cases, each offering unique properties tailored for protection and presentation. Bioplastics are renewable, biodegradable alternatives derived from natural sources, emphasizing sustainability and environmental impact reduction. PMMA, a synthetic acrylic polymer, is renowned for its exceptional clarity, UV resistance, and durability, making it ideal for high-visibility display applications.
What is Bioplastic?
Bioplastic is a type of polymer derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or cellulose, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics like polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). It is biodegradable or compostable under specific conditions, reducing environmental impact and waste accumulation commonly associated with conventional plastics. In display cases, bioplastics provide eco-friendly options with adequate durability and transparency, although PMMA often outperforms bioplastics in terms of clarity, UV resistance, and strength.
What is Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)?
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight and shatter-resistant alternative to glass in display cases. PMMA offers excellent optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, making it ideal for showcasing products while maintaining durability. Compared to bioplastics, PMMA typically provides superior mechanical strength and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring longer-lasting display protection.
Environmental Impact: Bioplastic vs PMMA
Bioplastics are derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch or sugarcane, making them biodegradable and reducing reliance on fossil fuels, which lowers their overall carbon footprint compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PMMA, a petroleum-based acrylic polymer, is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to plastic pollution due to its persistence in the environment. While PMMA offers superior durability and clarity for display cases, bioplastics provide an eco-friendly alternative by minimizing environmental impact through compostability and reduced greenhouse gas emissions during production.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Bioplastic display cases exhibit moderate durability and strength, often suitable for lightweight and eco-friendly applications, but they generally lack the rigidity and impact resistance of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). Polymethyl methacrylate provides superior mechanical strength, high scratch resistance, and excellent clarity, making it the preferred choice for display cases requiring long-term durability and exposure to environmental stress. When prioritizing strength and longevity, PMMA outperforms bioplastics, especially in commercial and high-traffic display environments.
Clarity and Aesthetic Appeal
Bioplastic display cases offer moderate clarity with a slightly hazier finish compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which provides exceptional optical transparency and a glass-like appearance. PMMA is highly favored for aesthetic appeal due to its superior gloss, color retention, and resistance to yellowing over time. While bioplastic prioritizes environmental sustainability, PMMA excels in delivering pristine clarity and a refined display presentation.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Bioplastic display cases generally incur higher initial costs due to limited large-scale production and reliance on renewable feedstocks, whereas polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers cost-effective manufacturing with widespread availability and established supply chains. PMMA is more readily available globally, benefiting from mature production processes and economies of scale that reduce material expenses for display case fabrication. While bioplastics present sustainability advantages, their fluctuating raw material prices and smaller production volumes often lead to higher per-unit costs compared to the consistently priced and abundant PMMA options.
Maintenance and Longevity
Bioplastic display cases often require more frequent maintenance due to their lower resistance to UV exposure and susceptibility to scratches compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which offers superior durability and clarity over time. PMMA is highly resistant to yellowing and weathering, significantly extending the longevity of display cases in both indoor and outdoor environments. The enhanced scratch resistance and chemical stability of PMMA reduce the need for repairs and replacements, making it a cost-effective choice for long-term displays.
Application Suitability in Display Cases
Bioplastic offers eco-friendly advantages with high biodegradability, ideal for short-term, disposable display cases and products emphasizing sustainability. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior clarity, scratch resistance, and UV stability, making it better suited for long-lasting, high-visibility display cases requiring durability and optical excellence. Choosing between bioplastic and PMMA depends on the display's environmental impact goals and performance requirements for transparency and longevity.
Future Trends in Sustainable Display Materials
Bioplastic offers a promising alternative to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) for display cases due to its biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint, aligning with growing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products. Advances in bio-based polymers enhance bioplastic durability and clarity, making it increasingly competitive with PMMA in display case applications. The future of sustainable display materials favors innovations in bioplastic composites that integrate recyclability and performance, driving industry adoption beyond traditional petroleum-based plastics like PMMA.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Display case
 azmater.com
azmater.com