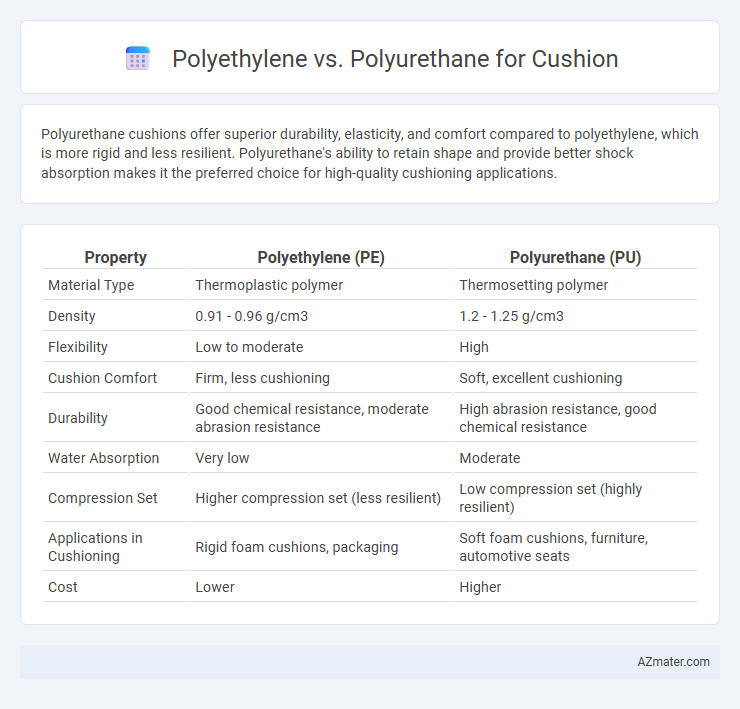
Polyurethane cushions offer superior durability, elasticity, and comfort compared to polyethylene, which is more rigid and less resilient. Polyurethane's ability to retain shape and provide better shock absorption makes it the preferred choice for high-quality cushioning applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermosetting polymer |
| Density | 0.91 - 0.96 g/cm3 | 1.2 - 1.25 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Low to moderate | High |
| Cushion Comfort | Firm, less cushioning | Soft, excellent cushioning |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, moderate abrasion resistance | High abrasion resistance, good chemical resistance |
| Water Absorption | Very low | Moderate |
| Compression Set | Higher compression set (less resilient) | Low compression set (highly resilient) |
| Applications in Cushioning | Rigid foam cushions, packaging | Soft foam cushions, furniture, automotive seats |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Cushion Materials
Polyethylene and polyurethane are two widely used materials for cushions, each offering distinct properties tailored to comfort and durability. Polyethylene cushions are known for their lightweight, water-resistant, and firm structure, making them ideal for outdoor and marine applications. Polyurethane foam provides superior softness, flexibility, and breathability, enhancing comfort in indoor furniture and automotive seating.
Overview of Polyethylene and Polyurethane
Polyethylene is a lightweight, durable thermoplastic known for its excellent moisture resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for cushioning applications that require water resistance and low maintenance. Polyurethane, a versatile polymer, offers superior elasticity and cushioning properties, providing enhanced comfort and impact absorption in various seating and padding uses. Both materials differ significantly in terms of flexibility, resilience, and suitability for specific cushioning needs, influencing their selection based on application requirements.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Polyethylene cushions are typically manufactured through rotational molding or foam expansion, resulting in lightweight, durable, and water-resistant foam products ideal for basic cushioning needs. Polyurethane cushions are produced using chemical foaming processes, often involving reaction injection molding or slabstock foam production, which allow for a wide range of density and firmness customization, enhancing comfort and resilience. The manufacturing complexity of polyurethane supports advanced cushioning designs with better elasticity and energy absorption compared to the simpler and more cost-effective polyethylene processes.
Cushioning Performance: Resilience and Comfort
Polyurethane cushions exhibit superior cushioning performance due to their higher resilience, allowing them to quickly regain shape after compression, enhancing comfort and support during prolonged use. Polyethylene cushions, while durable and resistant to moisture, offer less elasticity and tend to become compressed over time, resulting in reduced cushioning effectiveness. Selecting polyurethane provides better long-term comfort, especially in applications requiring consistent cushioning and pressure distribution.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to polyethylene foam, maintaining its shape and resilience under prolonged compression and heavy use in cushions. Polyurethane's cellular structure allows for better energy absorption and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-traffic furniture applications. In contrast, polyethylene foam tends to break down faster and lose its cushioning properties over time, especially in environments subject to frequent pressure or moisture exposure.
Moisture Resistance and Maintenance
Polyethylene cushions offer superior moisture resistance due to their closed-cell structure, preventing water absorption and reducing mold growth risk. Polyurethane cushions, especially open-cell types, tend to absorb moisture, requiring more frequent maintenance to avoid mildew and deterioration. For applications demanding low maintenance and high moisture resistance, polyethylene is the preferred material.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene cushions offer recyclability advantages due to their thermoplastic nature, enabling repeated melting and reshaping, which reduces landfill waste; however, they rely on non-renewable petroleum sources. Polyurethane cushions, often derived from fossil fuels and containing isocyanates, present challenges in biodegradability and end-of-life disposal, leading to longer environmental persistence. Sustainable alternatives include bio-based polyethylene and water-blown polyurethane formulations, emphasizing reduced carbon footprints and improved recyclability in cushion manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Polyethylene vs Polyurethane
Polyethylene cushions generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to polyurethane, making them a budget-friendly option for basic cushioning needs. Polyurethane cushions, while initially more expensive, provide superior comfort, durability, and longer lifespan, which can reduce replacement frequency and overall expenses in the long term. Cost comparison reveals that polyethylene suits short-term or cost-sensitive projects, whereas polyurethane delivers better value for extended use despite higher initial investment.
Common Applications in Cushion Design
Polyethylene foam is widely used in cushion design for packaging, sports equipment, and insulation due to its lightweight, moisture resistance, and shock absorption properties. Polyurethane foam offers superior comfort and flexibility, making it the preferred material for furniture cushions, automotive seating, and mattresses where support and durability are critical. Both materials excel in cushioning applications but are selected based on specific performance requirements such as resilience, softness, and environmental factors.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning with excellent flexibility, durability, and high resilience, making it ideal for ergonomic applications requiring long-term comfort and support. Polyethylene foam is lightweight, moisture-resistant, and provides firm support, suited for protective packaging or outdoor cushioning where water exposure is a concern. Selecting between polyurethane and polyethylene depends on whether you need soft, durable comfort or rigid, moisture-resistant support to best meet your usage environment.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polyurethane for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com