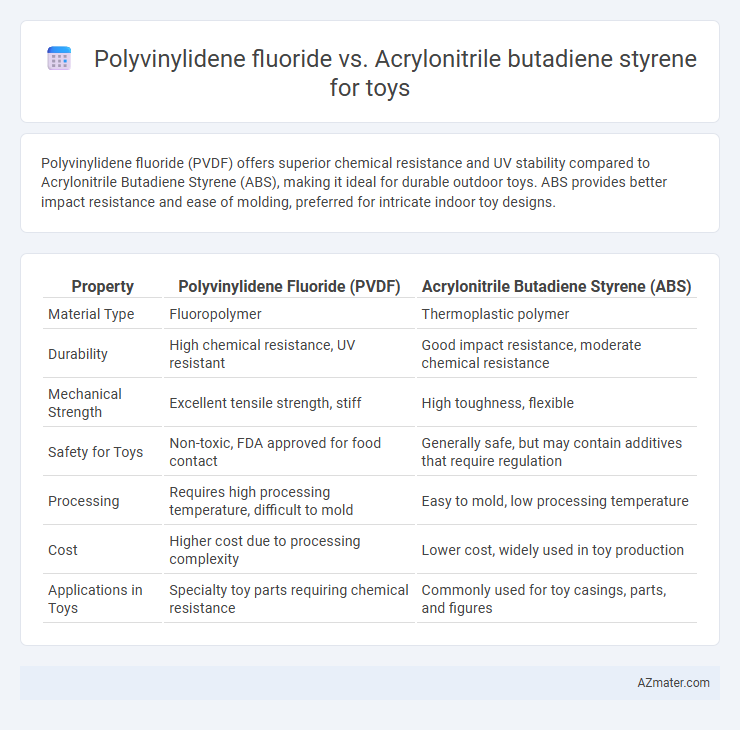
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it ideal for durable outdoor toys. ABS provides better impact resistance and ease of molding, preferred for intricate indoor toy designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Fluoropolymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Durability | High chemical resistance, UV resistant | Good impact resistance, moderate chemical resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent tensile strength, stiff | High toughness, flexible |
| Safety for Toys | Non-toxic, FDA approved for food contact | Generally safe, but may contain additives that require regulation |
| Processing | Requires high processing temperature, difficult to mold | Easy to mold, low processing temperature |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing complexity | Lower cost, widely used in toy production |
| Applications in Toys | Specialty toy parts requiring chemical resistance | Commonly used for toy casings, parts, and figures |
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional chemical resistance, durability, and resistance to UV radiation, making it suitable for outdoor and long-lasting toy components. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a common thermoplastic favored in the toy industry for its toughness, impact resistance, and ease of molding into intricate shapes, offering excellent surface finish and vibrant color options. Both materials provide valuable properties, with PVDF excelling in chemical stability and ABS in mechanical robustness and manufacturing versatility.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) features a semi-crystalline polymer structure composed of repeating CH2-CF2 units, offering excellent chemical resistance and durability for toys exposed to harsh environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is an amorphous terpolymer synthesized from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene monomers, providing high impact strength and toughness ideal for toy manufacturing. The fluorine atoms in PVDF confer superior chemical stability, whereas ABS's rubbery butadiene phase enhances shock absorption but is less resistant to solvents.
Mechanical Strength: PVDF vs ABS in Toy Manufacturing
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior mechanical strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it highly resistant to impact and wear in toy manufacturing. ABS provides good toughness and flexibility but falls short of PVDF's high tensile strength and chemical resistance. For toys requiring durability under stress and harsh conditions, PVDF outperforms ABS in maintaining structural integrity over time.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance Properties
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), with PVDF maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 150degC while ABS typically deforms around 105degC. The chemical resistance and higher melting point of PVDF make it ideal for toys exposed to elevated temperatures or sterilization processes. ABS, although widely used for toys due to impact resistance and ease of molding, offers limited performance in high-heat environments relative to PVDF.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns for Children’s Toys
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and low toxicity, making it a safer choice for children's toys compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), which can release potentially harmful compounds like styrene during degradation. PVDF's non-reactive and stable nature reduces the risk of harmful exposure, ensuring compliance with stringent safety standards for children's products. ABS, while durable and cost-effective, requires careful consideration and certification to avoid toxic risks associated with plasticizers and additives often used in toy manufacturing.
Durability and Impact Resistance: Which Lasts Longer?
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance and long-term durability, making it highly resilient to environmental stress and UV exposure, which enhances toy longevity. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and toughness, absorbing shocks effectively to prevent breakage during play. PVDF is ideal for applications requiring extended durability in harsh conditions, while ABS provides better protection against mechanical impacts, influencing toy lifespan based on specific use environments.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability during processing, making it suitable for toys requiring durability and exposure to harsh environments. In contrast, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides superior impact resistance and easier molding with lower processing temperatures, enabling faster cycle times and cost-effective mass production. Manufacturing with PVDF demands higher processing temperatures and specialized equipment, whereas ABS's versatility supports diverse design complexities and efficient injection molding for toy components.
Colorability and Surface Finish for Toy Design
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent colorability with vibrant, UV-resistant hues ideal for long-lasting toy aesthetics, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides a wide range of color options but may fade faster under sunlight exposure. PVDF exhibits a smooth, glossy surface finish that enhances visual appeal and tactile feel, making it suitable for premium toy designs requiring high-quality surfaces. ABS, known for its matte to semi-gloss finishes, offers good surface texture but can show wear and scratches more easily compared to the durable finish of PVDF.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and durability in toy applications, but its environmental impact is higher due to energy-intensive production and limited recyclability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). ABS is widely favored for toys because of its easier recyclability and lower environmental footprint during manufacturing, supporting circular economy initiatives. The biodegradability of neither polymer is significant; however, ABS's established recycling infrastructure enhances its sustainability profile in toy production.
Cost Analysis: PVDF vs ABS for Toy Production
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and durability but comes at a significantly higher material cost compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which remains a cost-effective choice for toy manufacturing due to its lower raw material price and ease of processing. ABS provides excellent impact resistance and is widely used in mass-produced toys, reducing overall production expenses through faster molding cycles and lower energy consumption. The choice between PVDF and ABS hinges on balancing cost constraints with performance requirements, where ABS typically delivers budget-friendly scalability for high-volume toy production.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com