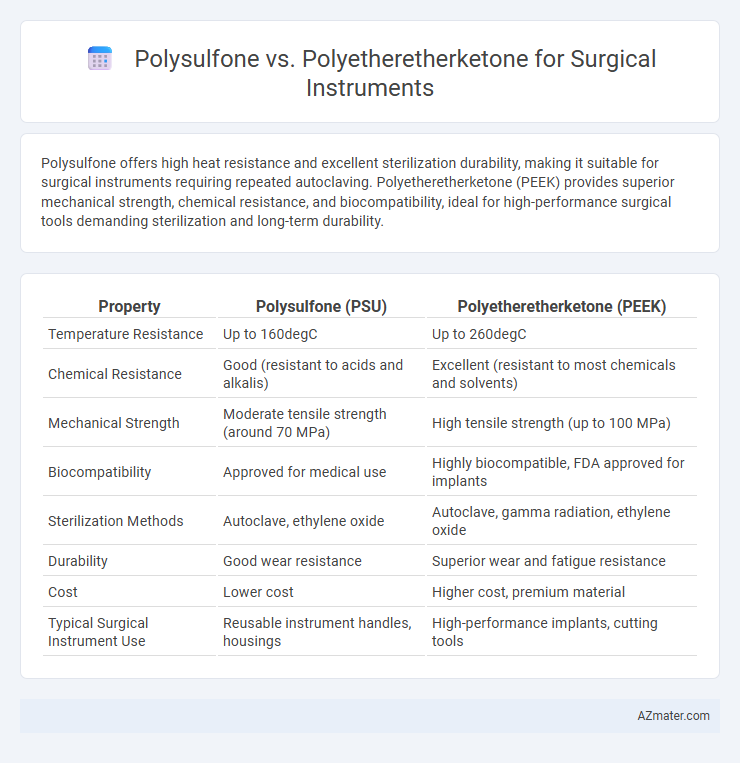
Polysulfone offers high heat resistance and excellent sterilization durability, making it suitable for surgical instruments requiring repeated autoclaving. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) provides superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility, ideal for high-performance surgical tools demanding sterilization and long-term durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 160degC | Up to 260degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resistant to acids and alkalis) | Excellent (resistant to most chemicals and solvents) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength (around 70 MPa) | High tensile strength (up to 100 MPa) |
| Biocompatibility | Approved for medical use | Highly biocompatible, FDA approved for implants |
| Sterilization Methods | Autoclave, ethylene oxide | Autoclave, gamma radiation, ethylene oxide |
| Durability | Good wear resistance | Superior wear and fatigue resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost, premium material |
| Typical Surgical Instrument Use | Reusable instrument handles, housings | High-performance implants, cutting tools |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polyetheretherketone
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) are high-performance polymers widely used in surgical instruments due to their exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility. Polysulfone offers excellent toughness, transparency, and ease of sterilization, making it suitable for applications requiring repeated autoclaving. Polyetheretherketone provides superior mechanical strength, higher temperature resistance, and long-term durability, ideal for demanding surgical environments where instrument longevity is critical.
Chemical Structure and Material Composition
Polysulfone features aromatic rings connected by sulfone groups and ether linkages, providing thermal stability and chemical resistance essential for surgical instruments. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) consists of repeating units with ketone and ether groups in its backbone, offering superior mechanical strength and biocompatibility. The chemical structure of PEEK results in higher crystallinity and rigidity compared to the amorphous, more flexible nature of polysulfone, influencing their selection based on surgical instrument performance requirements.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) are prominent materials in surgical instruments, with PEEK exhibiting superior mechanical strength and durability due to its higher tensile strength (up to 90 MPa) and exceptional resistance to wear and chemical degradation. PSU, while offering good thermal stability and toughness, typically has lower mechanical strength, around 70 MPa tensile strength, making it less durable under repeated sterilization cycles and mechanical stress. PEEK's outstanding fatigue resistance and ability to withstand aggressive sterilization processes position it as the preferred material for high-performance surgical tools requiring long-term reliability.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polysulfone exhibits excellent thermal stability with a continuous use temperature up to 150degC, making it suitable for moderate heat exposure in surgical instruments. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) outperforms polysulfone with superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at continuous temperatures around 250degC and excellent chemical resistance during sterilization. The higher melting point and greater glass transition temperature of PEEK ensure enhanced durability and performance in high-temperature surgical environments.
Sterilization Compatibility and Performance
Polysulfone exhibits excellent steam sterilization compatibility with resistance to repeated autoclaving cycles at temperatures around 134degC, maintaining mechanical strength and dimensional stability, making it suitable for surgical instruments subjected to high-temperature sterilization. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) outperforms Polysulfone in chemical resistance and sustained mechanical performance after exposure to high-temperature steam sterilization, withstanding temperatures up to 260degC without degradation, ideal for advanced surgical instruments requiring sterilization by autoclaving or gamma radiation. The superior thermal stability and biocompatibility of PEEK provide extended durability and reliability in surgical applications, whereas Polysulfone offers cost-effectiveness and adequate performance for less demanding sterilization protocols.
Biocompatibility in Surgical Applications
Polysulfone exhibits excellent biocompatibility with high resistance to chemical degradation and sterilization processes, making it suitable for reusable surgical instruments. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) offers superior biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and resistance to bodily fluids, which is critical for implantable surgical applications requiring long-term stability. Both materials are widely used, but PEEK's enhanced bioinertness and toughness provide significant advantages in demanding surgical environments.
Cost Analysis: Polysulfone vs PEEK
Polysulfone (PSU) offers a significantly lower material cost compared to Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), making it a more budget-friendly option for manufacturing surgical instruments. While PEEK provides superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, these advantages come with a higher price point that can impact overall production expenses. Cost analysis reveals that choosing polysulfone can reduce upfront material costs by up to 40%, which is critical for large-scale instrument production where cost efficiency is essential.
Weight and Design Flexibility
Polysulfone offers a lightweight profile ideal for surgical instruments requiring ease of maneuverability, whereas polyetheretherketone (PEEK) provides a sturdier structure but with slightly increased weight, benefiting durability. Design flexibility is enhanced in polysulfone due to its excellent thermoformability and ease in intricate molding, while PEEK excels in high-performance applications demanding chemical resistance and mechanical strength. Selecting between polysulfone and PEEK depends on balancing the need for reduced instrument weight against the requirement for robust design and long-term stability in surgical environments.
Applications in Surgical Instrument Manufacturing
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) are extensively used in surgical instrument manufacturing due to their thermal stability and biocompatibility. PEEK offers superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for reusable surgical tools subjected to sterilization processes like autoclaving. Polysulfone's lightweight and excellent dimensional stability suit disposable surgical components requiring precision and cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Material for Surgical Instruments
Polysulfone offers excellent heat resistance and chemical stability, making it suitable for surgical instruments requiring repeated sterilization cycles. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) stands out for its superior mechanical strength, biocompatibility, and resistance to wear and corrosion, ideal for high-performance surgical tools. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors such as sterilization methods, mechanical demands, and biocompatibility requirements specific to the surgical application.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyetheretherketone for Surgical Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com