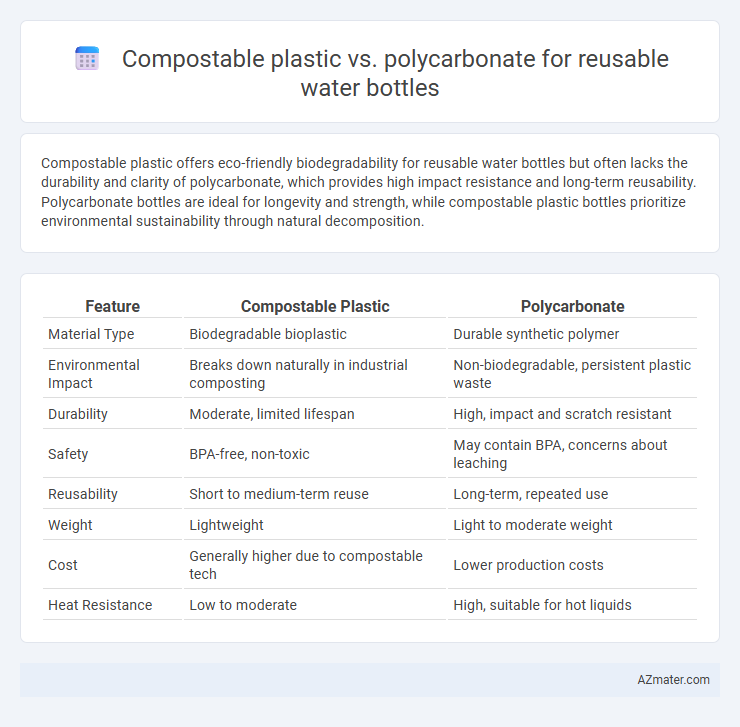
Compostable plastic offers eco-friendly biodegradability for reusable water bottles but often lacks the durability and clarity of polycarbonate, which provides high impact resistance and long-term reusability. Polycarbonate bottles are ideal for longevity and strength, while compostable plastic bottles prioritize environmental sustainability through natural decomposition.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Compostable Plastic | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable bioplastic | Durable synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Breaks down naturally in industrial composting | Non-biodegradable, persistent plastic waste |
| Durability | Moderate, limited lifespan | High, impact and scratch resistant |
| Safety | BPA-free, non-toxic | May contain BPA, concerns about leaching |
| Reusability | Short to medium-term reuse | Long-term, repeated use |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to moderate weight |
| Cost | Generally higher due to compostable tech | Lower production costs |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate | High, suitable for hot liquids |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Water Bottles
Compostable plastic and polycarbonate are two prominent materials used in eco-friendly reusable water bottles, each offering distinct environmental benefits and durability features. Compostable plastics, derived from renewable resources like cornstarch, break down naturally in industrial composting conditions, reducing long-term landfill waste. Polycarbonate, a durable and lightweight plastic derived from petroleum, is known for its impact resistance and longevity, but its environmental footprint is higher compared to compostable alternatives.
Understanding Compostable Plastics
Compostable plastics are derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch or sugarcane, designed to break down under industrial composting conditions within 90 to 180 days, reducing environmental pollution compared to conventional plastics. These materials, certified by standards like ASTM D6400 and EN 13432, offer a biodegradable alternative to polycarbonate, which is a durable, BPA-containing plastic known for its strength but persistence in landfills and potential health concerns. Understanding the limitations of compostable plastics, including their need for specific composting facilities and sensitivity to heat and moisture, is crucial when choosing a reusable water bottle material for sustainable use and disposal.
What is Polycarbonate?
Polycarbonate is a durable, lightweight thermoplastic polymer widely used in reusable water bottles for its high impact resistance and clarity. Unlike compostable plastics, polycarbonate offers excellent strength and longevity, making it ideal for everyday use but requires specific recycling processes due to its synthetic origin. Its BPA content has raised health concerns, prompting the development of BPA-free alternatives in water bottle manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Compostable Plastic vs Polycarbonate
Compostable plastic water bottles break down into non-toxic components within months under industrial composting conditions, significantly reducing landfill waste and microplastic pollution. Polycarbonate bottles, while durable and reusable, contribute to long-term environmental burden due to their resistance to biodegradation and potential release of bisphenol A (BPA) during degradation. Selecting compostable plastics minimizes carbon footprint and plastic pollution, whereas polycarbonate's longevity offers fewer replacements but poses challenges in end-of-life disposal.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Compostable plastics generally have lower durability and shorter longevity compared to polycarbonate, making them less suitable for long-term reusable water bottles. Polycarbonate offers high impact resistance, maintaining integrity under frequent use and extreme temperatures, which significantly extends the product's lifespan. Compostable plastics tend to degrade faster when exposed to moisture and UV light, resulting in a reduced usable life span.
Safety and Health Considerations
Compostable plastic water bottles are often made from plant-based materials like PLA, which break down more easily in the environment but may have lower heat resistance and potential leachate concerns under high temperatures. Polycarbonate bottles, while durable and clear, can release bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical linked to health risks, though many manufacturers now offer BPA-free alternatives to mitigate these safety issues. Assessing safety and health involves weighing the biodegradability and chemical exposure factors, with polycarbonate providing sturdiness and compostable plastics offering eco-friendly disposal but sometimes compromising on chemical stability.
Cost Analysis: Compostable vs Polycarbonate Bottles
Compostable water bottles typically have higher production costs due to raw material expenses and specialized manufacturing processes, resulting in a price range 20-40% above standard polycarbonate bottles. Polycarbonate bottles are more cost-effective for large-scale production, benefiting from established supply chains and economies of scale, which often lower unit costs by up to 30%. Long-term cost efficiency for polycarbonate bottles is enhanced by durability and reuse potential, whereas compostable bottles may incur additional expenses from shorter life spans and composting disposal requirements.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Compostable plastics offer limited design flexibility due to their lower thermal stability and reduced durability compared to polycarbonate, which allows intricate shapes and sleek finishes ideal for reusable water bottles. Polycarbonate supports high-impact resistance and clear transparency, providing superior aesthetic appeal with glossy, durable surfaces that can withstand repeated use. Designers favor polycarbonate for its ability to maintain vibrant colors and complex forms, while compostable plastics often require simpler designs to preserve structural integrity.
End-of-Life Disposal and Recycling Options
Compostable plastics for reusable water bottles break down in industrial composting facilities within 90 to 180 days, reducing landfill waste but require proper sorting to avoid contamination. Polycarbonate bottles are durable and widely recyclable through specialized plastic recycling streams, though they may accumulate in landfills if not properly disposed of. Both materials demand well-established waste management systems to maximize environmental benefits through efficient recycling or composting processes.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Compostable plastic offers an eco-friendly alternative for reusable water bottles, breaking down naturally under industrial composting conditions and reducing plastic waste. Polycarbonate provides durability, impact resistance, and clarity, making it ideal for long-term use and heavier daily wear. Choosing the right material depends on prioritizing environmental sustainability with compostable plastics or opting for the strength and longevity of polycarbonate for repeated use.
Infographic: Compostable plastic vs Polycarbonate for Reusable water bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com