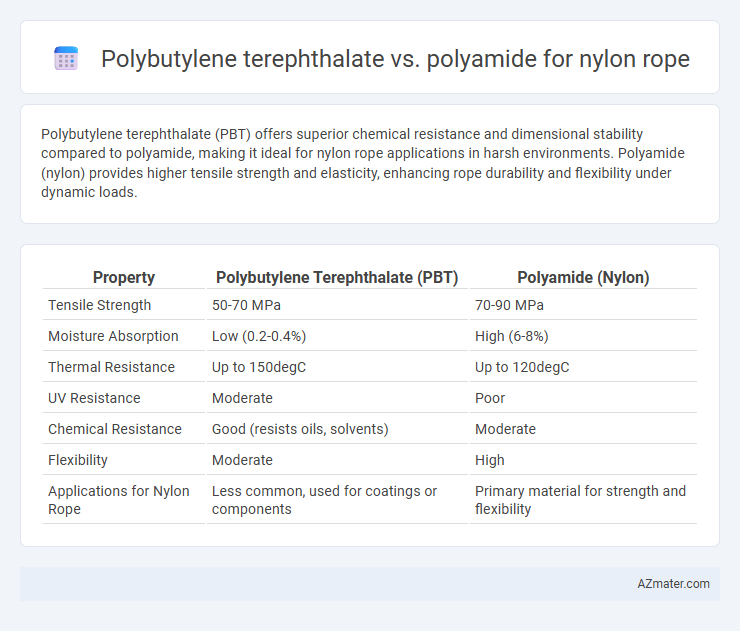
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability compared to polyamide, making it ideal for nylon rope applications in harsh environments. Polyamide (nylon) provides higher tensile strength and elasticity, enhancing rope durability and flexibility under dynamic loads.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 50-70 MPa | 70-90 MPa |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.2-0.4%) | High (6-8%) |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC | Up to 120degC |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | Poor |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resists oils, solvents) | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Applications for Nylon Rope | Less common, used for coatings or components | Primary material for strength and flexibility |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate and Polyamide
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for durable and high-strength applications like rope manufacturing. Polyamide, commonly referred to as Nylon, is a versatile synthetic polymer characterized by its high tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, widely used in ropes for its superior performance under dynamic loads. Comparing PBT and polyamide for nylon ropes highlights differences in moisture absorption, flexibility, and environmental resistance, critical factors influencing rope longevity and functionality.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is an aromatic polyester composed of terephthalic acid and 1,4-butanediol, featuring ester linkages that impart high chemical resistance and dimensional stability. Polyamide (Nylon) consists of repeating amide groups formed from diamines and dicarboxylic acids or amino acids, providing strong hydrogen bonding that enhances tensile strength and abrasion resistance. The chemical structure of PBT contributes to its rigidity and resistance to hydrolysis, whereas polyamide's amide bonds allow greater flexibility and moisture absorption in nylon ropes.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyamide (Nylon) rope exhibits superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) rope, making it more suitable for high-stress applications. Polyamide fibers typically offer tensile strengths ranging from 70 to 90 MPa, while PBT ropes generally fall below this range due to lower crystallinity and impact resistance. The mechanical durability and elasticity of Nylon provide enhanced shock absorption and longevity under dynamic loads compared to the relatively stiffer and less resilient PBT.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent dimensional stability and strong resistance to abrasion, making it durable for nylon rope applications where wear resistance is crucial. Polyamide (nylon) excels in toughness and impact resistance, providing superior durability under dynamic loads and repeated flexing. Both materials withstand wear effectively, but polyamide typically delivers enhanced toughness in harsh, high-stress environments.
Moisture Absorption and Environmental Effects
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits significantly lower moisture absorption compared to polyamide (nylon), making it more dimensionally stable and less prone to weakening in humid or wet environments. Nylon rope tends to absorb moisture up to 8-10%, which can lead to reduced tensile strength and elongation, whereas PBT maintains mechanical properties with moisture uptake well below 1%. Environmentally, PBT offers better resistance to hydrolytic degradation and UV exposure, contributing to longer lifespan and less environmental impact through degradation products compared to the more hygroscopic and UV-sensitive nylon.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior flexibility in nylon ropes, enhancing ease of handling and reducing stiffness compared to polyamide fibers. The inherent elasticity of PBT allows for better resistance to bending and twisting, which improves knot retention and overall rope maneuverability. Polyamide, while strong, tends to be less flexible and can feel stiffer during handling, making PBT a preferred choice for applications requiring enhanced dexterity and comfort.
Thermal Properties and Temperature Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent thermal stability with a melting point around 223degC, making it resistant to deformation under high temperature applications in ropes. Polyamide (Nylon) typically has a melting point between 215degC and 265degC depending on the type, but its performance can degrade faster under prolonged heat exposure due to moisture absorption and thermal aging. PBT generally provides superior dimensional stability and lower thermal expansion compared to Nylon, ensuring better temperature resistance and consistent mechanical properties in demanding environments.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers cost efficiency through lower raw material prices and simpler processing compared to polyamide (nylon), making it a budget-friendly option for rope manufacturing. Polyamide fibers dominate the market due to their superior strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, but typically come at higher costs and more complex production. Market availability favors polyamide ropes, with established supply chains and broader industrial adoption, while PBT ropes remain niche with limited suppliers and usage scenarios.
Application Suitability for Rope Manufacturing
Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon, exhibits superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it highly suitable for demanding rope manufacturing applications such as marine, climbing, and industrial uses. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability but lacks the elasticity and durability required for high-stress rope applications. The choice between PBT and Polyamide hinges on specific performance needs, with Nylon preferred for flexibility and load-bearing capacities in ropes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Material for Nylon Rope
Polyamide offers superior flexibility, high tensile strength, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it the preferred choice for nylon rope applications requiring durability and reliability. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), while providing good chemical resistance and dimensional stability, generally lacks the mechanical robustness essential for heavy-duty rope performance. For optimal nylon rope manufacturing, polyamide remains the material of choice due to its balanced mechanical properties and proven track record in demanding environments.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyamide for Nylon rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com