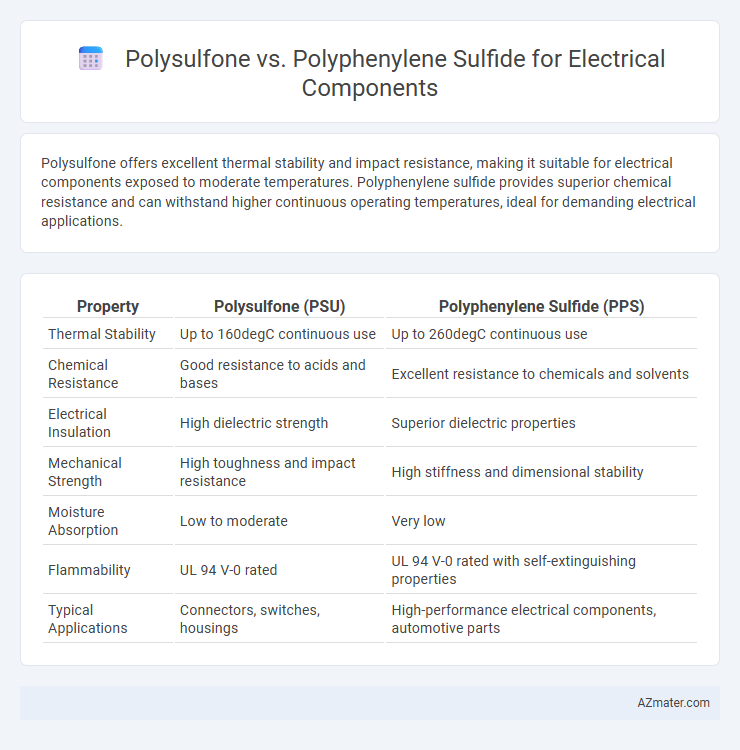
Polysulfone offers excellent thermal stability and impact resistance, making it suitable for electrical components exposed to moderate temperatures. Polyphenylene sulfide provides superior chemical resistance and can withstand higher continuous operating temperatures, ideal for demanding electrical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 160degC continuous use | Up to 260degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and bases | Excellent resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength | Superior dielectric properties |
| Mechanical Strength | High toughness and impact resistance | High stiffness and dimensional stability |
| Moisture Absorption | Low to moderate | Very low |
| Flammability | UL 94 V-0 rated | UL 94 V-0 rated with self-extinguishing properties |
| Typical Applications | Connectors, switches, housings | High-performance electrical components, automotive parts |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polyphenylene Sulfide
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) are high-performance thermoplastics extensively used in electrical components due to their excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance. Polysulfone offers superior impact strength and transparency, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and design flexibility. Polyphenylene Sulfide excels in high-temperature environments with outstanding dimensional stability and flame retardancy, suitable for harsh industrial electrical settings.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polysulfone (PSU) is an amorphous thermoplastic polymer composed of aromatic rings linked by sulfone and ether groups, providing excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance suitable for electrical components. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) consists of a semi-crystalline structure formed by repeating phenylene rings connected by sulfur atoms, offering superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability under high-temperature conditions. The chemical structure of PPS enables better resistance to harsh chemical environments compared to PSU, making PPS more favorable for high-performance electrical applications requiring long-term durability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) exhibit distinct mechanical properties critical for electrical components, with PSU offering excellent impact resistance and flexibility, maintaining tensile strength around 60-75 MPa and elongation at break up to 50%. PPS provides superior dimensional stability and higher stiffness, featuring tensile strengths typically between 70-90 MPa and a lower elongation at break near 10-20%, suitable for high-temperature applications. Both polymers demonstrate good chemical resistance, but PPS's higher modulus and thermal stability make it preferable for components requiring rigid mechanical performance under harsh environmental conditions.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent thermal stability with continuous use temperatures up to 150degC, making it suitable for electrical components exposed to moderate heat. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) exhibits superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at continuous use temperatures around 200degC and exceptional chemical resistance, ideal for high-temperature electrical applications. The choice between PSU and PPS depends on the specific thermal demands, with PPS preferred for higher thermal stability and sustained operational heat resistance in electrical component manufacturing.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polysulfone offers excellent electrical insulation with a high dielectric strength of around 500 V/mil, making it suitable for moderate temperature electrical components. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) boasts superior thermal stability up to 260degC and maintains strong electrical insulation properties, with a dielectric constant typically between 3 and 4, ideal for high-performance applications. PPS's resistance to chemical exposure and moisture further enhances its reliability in harsh electrical environments compared to polysulfone.
Flame Retardancy and Safety Standards
Polysulfone (PSU) exhibits excellent flame retardancy with a UL 94 V-0 rating, making it suitable for electrical components requiring high thermal stability and self-extinguishing properties. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) offers superior resistance to high temperatures and chemical exposure, meeting rigorous safety standards such as UL 94 V-0 and IEC 60332-1 flame tests. Both polymers ensure compliance with electrical safety regulations, but PPS is preferred in environments demanding enhanced flame retardancy and long-term durability under heat stress.
Processability and Manufacturing Techniques
Polysulfone offers excellent processability through injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming, enabling precise and cost-effective manufacturing of complex electrical components. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) demands higher processing temperatures, typically processed via injection molding and compression molding, which provides superior thermal and chemical resistance but requires specialized equipment to maintain material integrity. Selection between Polysulfone and PPS hinges on balancing ease of manufacturing against the need for enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance in electrical applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Polysulfone generally offers lower initial material costs compared to Polyphenylene Sulfide, making it a more budget-friendly option for electrical component manufacturing. However, Polyphenylene Sulfide provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, potentially reducing long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that while Polysulfone is cost-effective upfront, Polyphenylene Sulfide's durability can lead to greater economic benefits in high-performance or harsh environments.
Application Suitability in Electrical Components
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) differ significantly in application suitability for electrical components due to their thermal and chemical properties. PPS exhibits exceptional thermal stability up to 260degC and superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical connectors, circuit boards, and insulating parts exposed to harsh environments. Polysulfone offers good mechanical strength and dimensional stability but has a lower maximum continuous use temperature around 150degC, limiting its application primarily to moderate temperature electrical housings and insulating components.
Summary: Choosing Between Polysulfone and Polyphenylene Sulfide
Polysulfone offers excellent thermal stability up to 150degC and superior clarity, making it ideal for electrical components requiring visibility and moderate heat resistance. Polyphenylene sulfide withstands higher temperatures up to 260degC and provides outstanding chemical resistance, suited for harsh electrical environments and durable insulating parts. Selecting between these materials depends on the specific thermal demands and chemical exposure of the electrical application.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyphenylene Sulfide for Electrical Component
 azmater.com
azmater.com