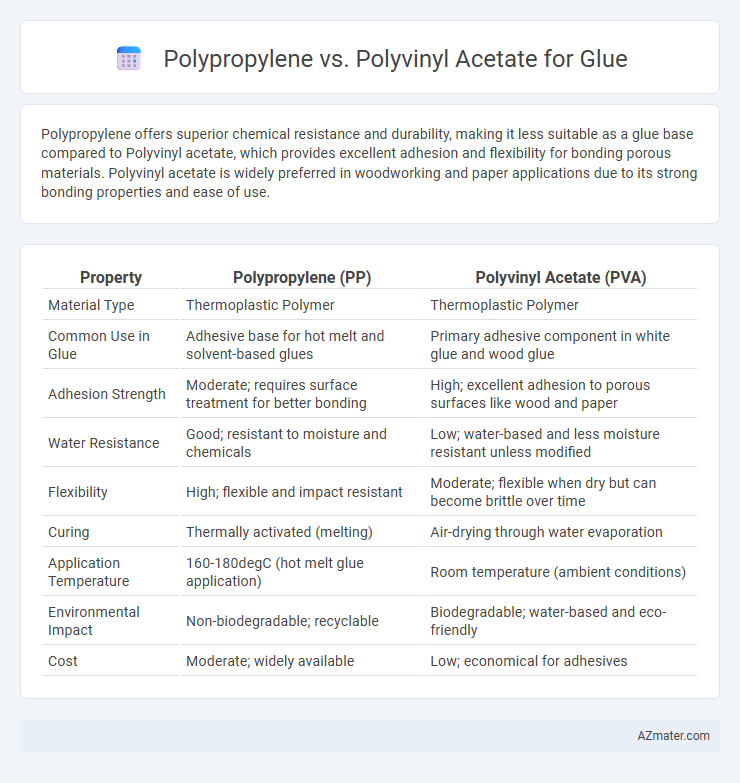
Polypropylene offers superior chemical resistance and durability, making it less suitable as a glue base compared to Polyvinyl acetate, which provides excellent adhesion and flexibility for bonding porous materials. Polyvinyl acetate is widely preferred in woodworking and paper applications due to its strong bonding properties and ease of use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Common Use in Glue | Adhesive base for hot melt and solvent-based glues | Primary adhesive component in white glue and wood glue |
| Adhesion Strength | Moderate; requires surface treatment for better bonding | High; excellent adhesion to porous surfaces like wood and paper |
| Water Resistance | Good; resistant to moisture and chemicals | Low; water-based and less moisture resistant unless modified |
| Flexibility | High; flexible and impact resistant | Moderate; flexible when dry but can become brittle over time |
| Curing | Thermally activated (melting) | Air-drying through water evaporation |
| Application Temperature | 160-180degC (hot melt glue application) | Room temperature (ambient conditions) |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable; recyclable | Biodegradable; water-based and eco-friendly |
| Cost | Moderate; widely available | Low; economical for adhesives |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyvinyl Acetate Glues
Polypropylene glues offer strong, water-resistant adhesion suited for bonding non-porous surfaces and plastics, making them ideal for industrial applications. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues are water-based, flexible adhesives commonly used in woodworking, paper crafting, and porous material bonding due to their fast-drying and non-toxic properties. Both adhesives serve distinct purposes, with polypropylene glues excelling in durability and chemical resistance, while PVA glues provide ease of use and versatility in household and educational projects.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer composed of repeated propylene monomers with a non-polar, hydrocarbon backbone, providing chemical resistance and good tensile strength but poor adhesion to polar surfaces. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) is a synthetic polymer formed by the polymerization of vinyl acetate monomers, featuring polar acetate groups that enhance its adhesive properties, especially on porous materials like wood and paper. The differing chemical structures--non-polar long hydrocarbon chains in polypropylene versus polar acetate side groups in PVA--directly influence their suitability as adhesives, with PVA being more commonly used in glue formulations due to its superior bonding capacity.
Adhesive Properties Comparison
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) exhibits strong adhesion to porous surfaces like wood and paper due to its excellent water-based bonding capabilities, making it ideal for woodworking and crafts. Polypropylene, however, inherently has low surface energy and poor adhesion without surface treatment, resulting in weak bonding for most substrates. Therefore, PVA demonstrates superior adhesive properties over polypropylene in typical glue applications where strong, durable bonds to porous materials are required.
Application Areas and Use Cases
Polypropylene is commonly used in industrial adhesive applications requiring strong, durable bonds and resistance to chemicals, heat, and moisture, making it ideal for packaging, automotive parts, and textiles. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) excels in woodworking, paper bonding, and craft projects due to its excellent adhesion to porous materials, fast drying time, and non-toxic nature. While polypropylene-based adhesives are suited for tough, structural uses, polyvinyl acetate glues dominate household and office environments where flexibility and ease of use are prioritized.
Strength and Durability
Polypropylene-based adhesives exhibit superior strength and durability due to their high tensile strength and excellent resistance to chemical and environmental factors, making them ideal for heavy-duty bonding applications. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues offer moderate strength with strong adhesion to porous materials but tend to degrade over time when exposed to moisture and temperature fluctuations. For long-lasting, robust bonds in demanding conditions, polypropylene adhesives generally outperform polyvinyl acetate formulations.
Water Resistance and Environmental Performance
Polypropylene-based adhesives exhibit superior water resistance compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues, maintaining bond strength under prolonged moisture exposure. Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer with excellent chemical stability and durability, making it ideal for outdoor applications where water exposure is frequent. Environmentally, PVA is biodegradable and derived from vinyl acetate monomers, offering better eco-friendliness than polypropylene, which is petroleum-based and less readily recyclable.
Ease of Application and Curing Time
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue offers superior ease of application due to its water-based formula, allowing smooth spread and easy cleanup, making it ideal for woodworking and crafts. Polypropylene-based adhesives typically require heat or special solvents for curing, resulting in longer and more complex curing times compared to the quick-drying nature of PVA glues, which usually set within 30 minutes to an hour under ambient conditions. The faster curing and simpler application process of polyvinyl acetate make it more user-friendly for general-purpose bonding tasks.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Polypropylene-based adhesives typically offer superior chemical resistance and lower toxicity compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues, making them safer for prolonged use and indoor applications. Polyvinyl acetate is biodegradable and water-based, contributing to a reduced environmental footprint, but it can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during drying, impacting air quality. Polypropylene adhesives, being more chemically inert, have a lower environmental impact over their lifecycle due to their durability and reduced emissions but may pose recycling challenges due to their synthetic nature.
Cost and Availability
Polypropylene-based adhesives typically have higher production costs due to more complex manufacturing processes and specialized formulation requirements, leading to less widespread availability compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues. Polyvinyl acetate adhesives benefit from low raw material costs and extensive global production, making them more affordable and readily accessible for general use. The overall cost-efficiency and mass-market availability of PVA make it the preferred choice for applications requiring economical and easily sourced adhesive solutions.
Choosing the Right Adhesive: Key Considerations
Polypropylene adhesives offer robust chemical resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for bonding plastics and outdoor applications. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) adhesives provide strong bonding for porous materials like wood and paper, with excellent drying times and ease of use. Selecting the right adhesive depends on substrate compatibility, environmental conditions, and desired bond strength, ensuring optimal performance for specific projects.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyvinyl acetate for Glue
 azmater.com
azmater.com