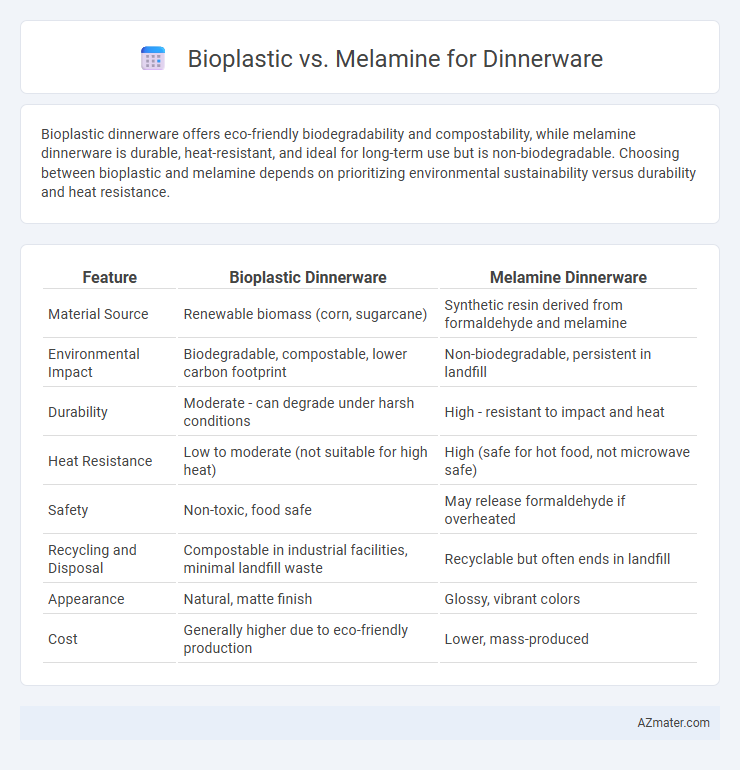
Bioplastic dinnerware offers eco-friendly biodegradability and compostability, while melamine dinnerware is durable, heat-resistant, and ideal for long-term use but is non-biodegradable. Choosing between bioplastic and melamine depends on prioritizing environmental sustainability versus durability and heat resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic Dinnerware | Melamine Dinnerware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable biomass (corn, sugarcane) | Synthetic resin derived from formaldehyde and melamine |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, persistent in landfill |
| Durability | Moderate - can degrade under harsh conditions | High - resistant to impact and heat |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate (not suitable for high heat) | High (safe for hot food, not microwave safe) |
| Safety | Non-toxic, food safe | May release formaldehyde if overheated |
| Recycling and Disposal | Compostable in industrial facilities, minimal landfill waste | Recyclable but often ends in landfill |
| Appearance | Natural, matte finish | Glossy, vibrant colors |
| Cost | Generally higher due to eco-friendly production | Lower, mass-produced |
Introduction to Bioplastic and Melamine Dinnerware
Bioplastic dinnerware is made from renewable plant-based materials like cornstarch and sugarcane, offering a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics. Melamine dinnerware, composed of melamine resin, is known for its durability, heat resistance, and vibrant designs, making it popular for everyday use and outdoor dining. Both materials provide different benefits in sustainability, durability, and aesthetic appeal for modern dinnerware solutions.
Composition and Material Origins
Bioplastic dinnerware is primarily derived from renewable plant-based sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or cellulose, making it biodegradable and eco-friendly. Melamine dinnerware is composed of melamine resin, a durable thermosetting plastic synthesized from formaldehyde and urea, originating from petrochemical sources. The natural composition of bioplastic contrasts with the synthetic, petroleum-based origins of melamine, influencing their environmental impact and material properties.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bioplastic dinnerware, derived from renewable plant-based materials like cornstarch or sugarcane, offers biodegradability and compostability, significantly reducing landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional plastics. Melamine dinnerware, made from formaldehyde-based resins, is durable and heat-resistant but non-biodegradable, contributing to persistent plastic pollution and environmental toxicity when disposed of improperly. Choosing bioplastic over melamine supports a lower carbon footprint and enhanced circular economy benefits due to its renewable sourcing and reduced environmental persistence.
Durability and Longevity
Bioplastic dinnerware offers moderate durability with resistance to cracking and warping but tends to degrade faster under prolonged heat and UV exposure, limiting its longevity compared to melamine. Melamine dinnerware is highly durable, resistant to chipping, scratches, and stains, and can withstand repeated daily use without significant wear, making it ideal for long-term use. While bioplastics provide eco-friendly benefits, melamine's superior strength and lifespan make it the preferred choice for durable, long-lasting dinnerware.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Bioplastic dinnerware made from plant-based materials complies with FDA and EU food contact regulations, ensuring non-toxicity and safe use with hot and cold foods. Melamine dinnerware, while durable, raises concerns due to potential formaldehyde release when exposed to high temperatures, leading to strict regulatory limits by agencies like the FDA. Consumers seeking safer options often prefer bioplastic for its biodegradability and adherence to rigorous food safety standards.
Aesthetic and Design Versatility
Bioplastic dinnerware offers a modern, eco-friendly aesthetic with smooth finishes and adaptable colors, ideal for contemporary and customizable table settings. Melamine provides a classic, glossy look with intricate patterns and vibrant prints, making it popular for traditional and durable dinnerware designs. Both materials enable diverse design options but differ in texture and environmental impact, influencing consumer choice based on style preferences and sustainability values.
Heat and Dishwasher Resistance
Bioplastic dinnerware typically offers moderate heat resistance, often withstanding temperatures up to 120degC (248degF), while melamine dinnerware can endure higher temperatures around 160degC (320degF) without warping. Melamine is more resistant to dishwasher cycles, maintaining its glossy finish and structural integrity after repeated washes compared to some bioplastics which may degrade or lose quality over time. Choosing melamine ensures better durability under high heat conditions and prolonged dishwasher use, ideal for everyday dining applications.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Bioplastic dinnerware generally has a higher production cost due to biodegradable raw materials and specialized manufacturing processes, resulting in a price point 15-30% above conventional options. Melamine dinnerware is widely available and cost-effective, benefiting from mass production economies and a stable supply chain, with prices typically 20-40% lower than bioplastic alternatives. Market availability favors melamine for widespread retail and bulk purchasing, while bioplastic remains niche, mainly accessible through eco-conscious brands and specialty stores.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumers are increasingly favoring bioplastic dinnerware due to its eco-friendly properties, biodegradability, and alignment with sustainable living trends. Melamine remains popular for its durability, heat resistance, and affordability, appealing to users seeking long-lasting, practical dinnerware options. Market data indicates a growing shift towards bioplastic products as environmental awareness rises, influencing purchasing decisions across millennial and Gen Z demographics.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Tableware
The future outlook for sustainable tableware favors bioplastic due to its biodegradable properties and lower environmental impact compared to melamine, which is based on non-renewable petrochemicals and poses recycling challenges. Innovations in bioplastic formulations aim to enhance durability and heat resistance, making them more viable for everyday dinnerware use. Growing consumer demand and stricter environmental regulations are driving the shift toward bioplastic solutions in sustainable tableware production.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Melamine for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com