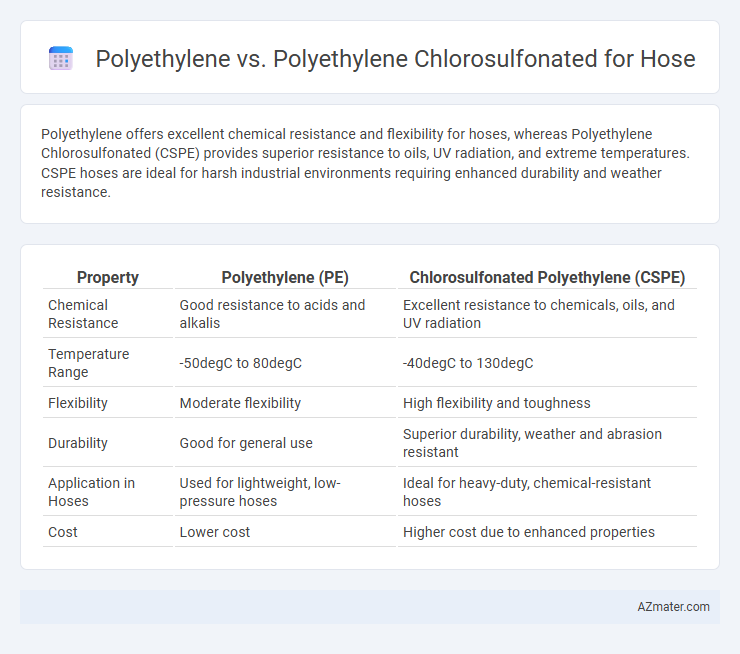
Polyethylene offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility for hoses, whereas Polyethylene Chlorosulfonated (CSPE) provides superior resistance to oils, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures. CSPE hoses are ideal for harsh industrial environments requiring enhanced durability and weather resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent resistance to chemicals, oils, and UV radiation |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 80degC | -40degC to 130degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and toughness |
| Durability | Good for general use | Superior durability, weather and abrasion resistant |
| Application in Hoses | Used for lightweight, low-pressure hoses | Ideal for heavy-duty, chemical-resistant hoses |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polyethylene Chlorosulfonated
Polyethylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in hose manufacturing for its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability. Polyethylene Chlorosulfonated (CSPE) is a modified polyethylene known for enhanced resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals, making it ideal for demanding industrial hose applications. The key distinction lies in CSPE's chlorosulfonated polymer structure, which provides superior weathering performance compared to standard polyethylene.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Polyethylene consists of long chains of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms, forming a simple hydrocarbon polymer with a non-polar, linear structure that provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. Polyethylene Chlorosulfonated (CSPE) includes chlorine and sulfonyl chloride groups attached to the polyethylene backbone, introducing polar functional groups that enhance oil, chemical, and weather resistance while improving thermal stability. The introduction of chlorine and sulfonyl groups alters the polymer's chemical composition, making CSPE more suitable for harsh environments compared to the more inert and less chemically resistant standard polyethylene.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene (PE) offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility with a tensile strength ranging from 20 to 37 MPa and a density of approximately 0.91 to 0.96 g/cm3, making it ideal for lightweight hose applications. Polyethylene Chlorosulfonated (CSM) exhibits superior heat resistance, enhanced abrasion resistance, and improved weathering performance due to its chlorosulfonated structure, with tensile strength typically between 18 to 30 MPa and a higher density of about 1.25 g/cm3. While PE hoses excel in chemical inertness and ease of processing, CSM hoses outperform in durability under harsh environmental conditions and elevated temperatures, crucial for industrial and outdoor uses.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Polyethylene hoses offer moderate mechanical strength with good flexibility, making them suitable for low to medium pressure applications. Polyethylene chlorosulfonated (CSM) hoses exhibit superior mechanical strength and enhanced flexibility due to their chemical cross-linking and chlorosulfonation, which improve durability and resistance to wear. These properties make CSM hoses ideal for demanding industrial environments requiring high abrasion resistance and elasticity.
Resistance to Chemicals and Environmental Factors
Polyethylene (PE) offers moderate resistance to a wide range of chemicals including acids, bases, and alcohols, making it suitable for general-purpose hoses exposed to various substances. Polyethylene Chlorosulfonated (CSPE) significantly enhances chemical resistance, providing exceptional durability against harsh solvents, oils, and oxidizing agents, as well as outstanding resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and ozone degradation. CSPE's superior environmental stability makes it the preferred choice for hoses operating in extreme outdoor conditions or chemical-intensive environments.
Temperature Performance and Durability
Polyethylene hoses offer moderate temperature resistance typically up to 120degF, making them suitable for general-purpose applications with moderate thermal demands. Polyethylene chlorosulfonated (CSM) hoses exhibit superior temperature performance, withstanding continuous exposure up to 250degF and temporary spikes beyond 300degF, ideal for harsh environments involving heat and chemicals. The chlorosulfonated modification significantly enhances durability by providing greater resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and chemical degradation, extending hose lifespan in rigorous industrial settings.
Application Suitability in Hose Manufacturing
Polyethylene is widely used for hose manufacturing due to its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and affordability, making it suitable for general-purpose applications like water and air transport. Polyethylene chlorosulfonated (CSPE) provides superior resistance to oils, ozone, and UV radiation, making it ideal for industrial hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions and aggressive chemicals. CSPE's enhanced durability and resistance properties extend hose lifespan in demanding applications, whereas standard polyethylene is preferred for cost-effective, less rigorous uses.
Cost-Effectiveness and Production Considerations
Polyethylene offers lower material and production costs compared to polyethylene chlorosulfonated, making it more cost-effective for standard hose applications. Polyethylene chlorosulfonated provides superior chemical resistance and durability, justifying higher expenses in specialized industrial hoses. Manufacturing processes for polyethylene are simpler and faster, whereas polyethylene chlorosulfonated requires more complex processing to achieve enhanced performance characteristics.
Safety, Regulatory, and Environmental Impact
Polyethylene (PE) hoses offer excellent chemical resistance and low toxicity, making them safe for potable water applications and compliant with FDA and EPA regulations. Polyethylene Chlorosulfonated (CSM) hoses provide enhanced chemical and heat resistance but may release hazardous byproducts during degradation, requiring careful handling and adherence to OSHA and REACH guidelines. Environmentally, PE hoses are more biodegradable and recyclable, whereas CSM hoses pose greater challenges in disposal due to their chlorosulfonated compounds and potential environmental persistence.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Hoses
Selecting the right hose material depends on the specific application requirements, where polyethylene offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility for general use, while chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) provides superior ozone, weather, and heat resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments. Polyethylene is cost-effective and suitable for water, air, and light chemical transfer, whereas CSPE hoses excel in industrial settings with exposure to UV rays, oils, and extreme temperatures. Prioritizing the hose's durability, environmental exposure, and chemical compatibility ensures optimal performance and lifespan.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polyethylene Chlorosulfonated for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com