Bioplastic Lego bricks are made from renewable plant-based materials, offering environmental benefits like biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) bricks provide superior durability, impact resistance, and color stability, making them the standard choice for long-lasting Lego sets.
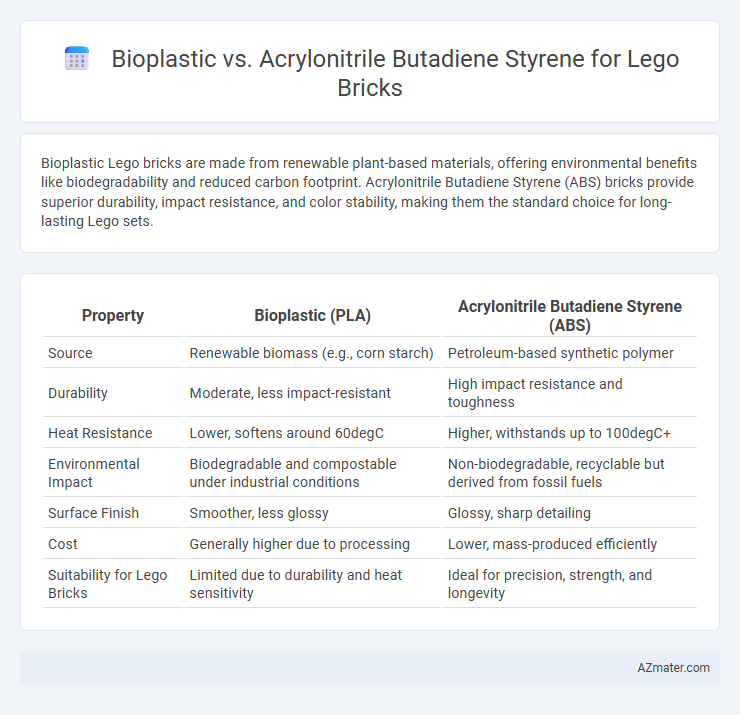
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic (PLA) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable biomass (e.g., corn starch) | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Durability | Moderate, less impact-resistant | High impact resistance and toughness |
| Heat Resistance | Lower, softens around 60degC | Higher, withstands up to 100degC+ |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and compostable under industrial conditions | Non-biodegradable, recyclable but derived from fossil fuels |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, less glossy | Glossy, sharp detailing |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Lower, mass-produced efficiently |
| Suitability for Lego Bricks | Limited due to durability and heat sensitivity | Ideal for precision, strength, and longevity |
Introduction: The Shift in Lego Brick Materials
Lego has initiated a significant shift from traditional Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) towards bioplastics to enhance sustainability in toy manufacturing. ABS, known for its durability and vibrant color retention, presents environmental challenges due to its petroleum-based composition and limited recyclability. Bioplastic alternatives, derived from renewable resources like sugarcane, aim to reduce carbon footprint and promote eco-friendly production without compromising the quality and structural integrity essential for Lego bricks.
Understanding Bioplastics: Definition and Types
Bioplastics are derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, and cellulose, contrasting with conventional plastics like Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which are petroleum-based. Key types of bioplastics used in manufacturing include polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), and starch blends, each offering varying degrees of biodegradability and mechanical strength. While ABS remains the standard for LEGO bricks due to its durability and impact resistance, bioplastics represent a sustainable alternative with evolving formulations aimed at matching these performance qualities.
What is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in manufacturing Lego bricks due to its strength, durability, and impact resistance. ABS offers excellent dimensional stability and vibrant color retention, making it ideal for precise and long-lasting toy components. Compared to bioplastics, ABS provides superior mechanical properties, which ensure the bricks maintain their shape and functionality over repeated assembly and play cycles.
Environmental Impact: Bioplastic vs ABS
Bioplastic used in Lego bricks offers a significant reduction in carbon footprint compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), as it is derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane and cornstarch. ABS, a petroleum-based plastic, contributes to higher greenhouse gas emissions during production and poses challenges for recycling due to its complex chemical structure. Bioplastics also tend to degrade more readily under composting conditions, potentially reducing long-term environmental pollution compared to the persistent nature of ABS in landfills.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Bioplastic Lego bricks typically offer moderate durability with biodegradability, yet they often fall short of the mechanical strength and impact resistance of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) bricks. ABS is renowned for its high tensile strength, rigidity, and excellent resistance to wear, making it the preferred material for long-lasting, robust Lego construction. The superior strength-to-weight ratio of ABS ensures better clutch power and durability under repetitive stress compared to bioplastics.
Cost Analysis: Bioplastic vs ABS Manufacturing
Manufacturing LEGO bricks from bioplastic generally involves higher raw material costs compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), due to the premium pricing of biodegradable polymers and complex processing requirements. ABS remains cost-effective with established production infrastructure, lower material expenses, and efficient molding processes, resulting in lower overall manufacturing costs. Despite the environmental benefits of bioplastics, the economic scalability and durability of ABS make it the preferred choice for cost-sensitive, high-volume LEGO brick production.
Safety and Health Considerations
Bioplastic used in Lego bricks offers enhanced safety due to its biodegradable and non-toxic properties, reducing potential exposure to harmful chemicals during handling and disposal compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which may contain residual styrene, a possible carcinogen. ABS provides superior durability and impact resistance but poses concerns related to off-gassing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing or prolonged use. Selecting bioplastic over ABS supports environmental health by minimizing plastic pollution and limiting exposure to hazardous substances associated with traditional petrochemical-based polymers.
Compatibility with Existing Lego Systems
Bioplastic Lego bricks are designed to maintain full compatibility with existing Lego systems, ensuring seamless integration with traditional ABS bricks. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is the standard material for Lego, prized for its durability and precision molding, providing consistent clutch power across sets. Transitioning to bioplastics requires meticulous calibration to match the exact dimensions and fit of ABS bricks, preserving the structural integrity and play experience valued by Lego users.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception of bioplastic Lego bricks emphasizes environmental sustainability and reduced carbon footprint, appealing to eco-conscious buyers. In contrast, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is valued for durability, color vibrancy, and structural integrity, making it preferred by traditional Lego enthusiasts. Market trends indicate a growing demand for bioplastics driven by regulatory pressures and increased awareness, while ABS remains dominant due to its proven performance and manufacturing cost-efficiency.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Sustainable Lego Bricks
The future outlook for Lego bricks centers on advancing bioplastic alternatives that reduce environmental impact while maintaining the durability and precision of traditional acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) materials. Innovations in plant-based polymers and biodegradable composites aim to enhance the sustainability of Lego production without compromising the color vibrancy and mechanical strength essential for building integrity. Ongoing research into recyclable additives and efficient manufacturing processes promises to accelerate the evolution of sustainable Lego bricks, aligning with global goals for circular economy practices in the toy industry.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Lego Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com