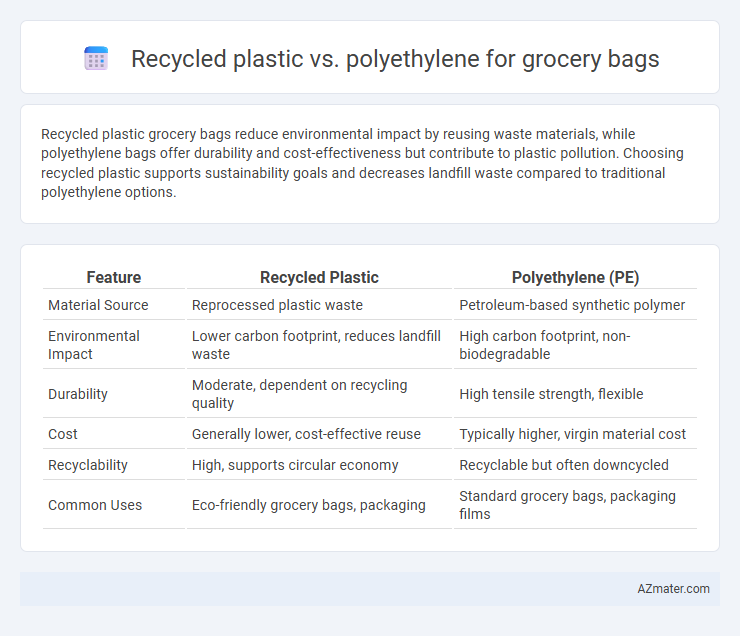
Recycled plastic grocery bags reduce environmental impact by reusing waste materials, while polyethylene bags offer durability and cost-effectiveness but contribute to plastic pollution. Choosing recycled plastic supports sustainability goals and decreases landfill waste compared to traditional polyethylene options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Plastic | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Reprocessed plastic waste | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Durability | Moderate, dependent on recycling quality | High tensile strength, flexible |
| Cost | Generally lower, cost-effective reuse | Typically higher, virgin material cost |
| Recyclability | High, supports circular economy | Recyclable but often downcycled |
| Common Uses | Eco-friendly grocery bags, packaging | Standard grocery bags, packaging films |
Introduction to Grocery Bag Materials
Grocery bags are primarily made from materials such as recycled plastic and polyethylene, each offering distinct environmental and functional benefits. Recycled plastic bags utilize post-consumer waste, reducing landfill impact and conserving resources, while polyethylene bags, typically high-density (HDPE) or low-density (LDPE), are valued for their durability and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the differences in material composition and sustainability profiles is essential for selecting eco-friendly and efficient grocery bag options.
Overview of Recycled Plastic Bags
Recycled plastic bags are made from post-consumer and post-industrial plastic waste, offering a sustainable alternative to virgin polyethylene bags by reducing landfill and ocean pollution. These bags maintain comparable strength and durability while significantly lowering carbon footprint and resource consumption. Advances in recycling technology enable the production of high-quality recycled plastic grocery bags that meet consumer demands and environmental regulations.
Polyethylene Bags: Properties and Usage
Polyethylene bags, primarily made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or low-density polyethylene (LDPE), offer exceptional flexibility, moisture resistance, and durability, making them ideal for grocery packaging. These bags are lightweight, cost-effective, and recyclable, contributing to widespread use in retail environments while maintaining strength sufficient to carry heavy groceries without tearing. Their chemical resistance and impermeability protect food items from contamination and moisture, enhancing shelf life and customer convenience.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled plastic grocery bags significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering the demand for virgin polyethylene production, which is energy-intensive and relies heavily on fossil fuels. Polyethylene bags contribute to plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing and disposal, whereas recycled plastic bags promote waste diversion from landfills and reduce carbon footprint. Opting for recycled plastic helps conserve natural resources and supports circular economy practices in the packaging industry.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Recycled plastic grocery bags demonstrate comparable durability and strength to traditional polyethylene bags, offering enhanced environmental benefits without compromising performance. Advanced processing techniques improve tensile strength and resistance to tearing in recycled plastics, making them suitable for multiple uses and heavy loads. Polyethylene bags, while cost-effective and widely used, often exhibit lower resistance to impact and stretching compared to high-grade recycled plastic alternatives.
Cost Efficiency of Each Material
Recycled plastic grocery bags typically offer cost savings due to lower raw material expenses and reduced manufacturing energy compared to virgin polyethylene bags. Polyethylene bags, while generally more uniform and reliable in quality, incur higher production costs linked to petroleum-based raw materials and stricter environmental regulations. Choosing recycled plastic enhances cost efficiency through decreased material procurement costs and supports sustainability goals, making it a viable option for budget-conscious retailers.
Consumer Acceptance and Perception
Consumers increasingly prefer recycled plastic grocery bags due to their environmental benefits and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional polyethylene bags. Studies reveal higher acceptance of recycled plastic bags, as shoppers associate them with sustainability and responsible consumption. Despite polyethylene's durability and low cost, consumer perception favors recycled alternatives for promoting eco-friendly practices and reducing plastic waste.
Recycling and End-of-Life Scenarios
Recycled plastic grocery bags reduce environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and lowering demand for virgin polyethylene, which is a petroleum-based material. Polyethylene bags, though widely recyclable, often face contamination and inefficient recycling processes, leading to a higher likelihood of landfill disposal or incineration. End-of-life scenarios for recycled plastic bags emphasize closed-loop recycling, promoting sustainable material reuse and reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional polyethylene bags.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Recycled plastic grocery bags must meet strict regulatory standards such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) guidelines and the European Union's Waste Framework Directive to ensure environmental safety and material integrity. Polyethylene bags, commonly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), are regulated under standards like the U.S. FDA for food contact and ASTM for mechanical properties, ensuring durability and consumer safety. Compliance with these regulations impacts the recyclability, biodegradability, and overall environmental footprint of grocery bags, influencing manufacturer choices and market availability.
Future Trends in Grocery Bag Materials
Recycled plastic grocery bags are gaining traction due to increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products, while polyethylene remains widely used for its durability and cost-effectiveness. Future trends indicate a shift toward biodegradable additives in recycled plastics and bio-based polyethylene alternatives to reduce carbon footprints. Innovations in material blending and smart packaging technologies are expected to enhance the functionality and eco-friendliness of grocery bags.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Polyethylene for Grocery bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com