Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance and non-stick properties for food containers, ensuring minimal flavor retention and enhanced durability. Polycarbonate provides excellent impact resistance and transparency but may pose concerns related to BPA leaching in food storage applications.
Table of Comparison
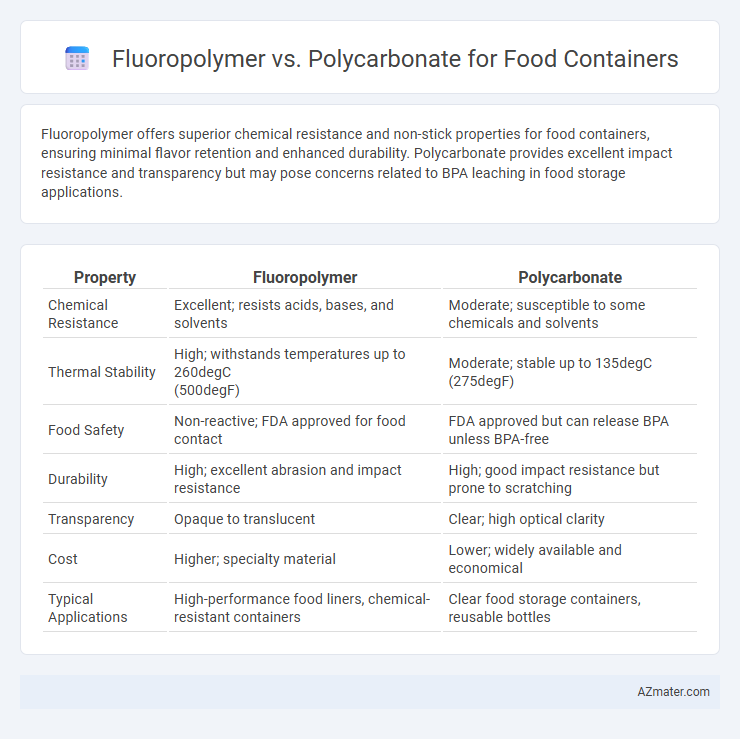
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent; resists acids, bases, and solvents | Moderate; susceptible to some chemicals and solvents |
| Thermal Stability | High; withstands temperatures up to 260degC (500degF) |
Moderate; stable up to 135degC (275degF) |
| Food Safety | Non-reactive; FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved but can release BPA unless BPA-free |
| Durability | High; excellent abrasion and impact resistance | High; good impact resistance but prone to scratching |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Clear; high optical clarity |
| Cost | Higher; specialty material | Lower; widely available and economical |
| Typical Applications | High-performance food liners, chemical-resistant containers | Clear food storage containers, reusable bottles |
Introduction to Fluoropolymer and Polycarbonate
Fluoropolymers, known for their exceptional chemical resistance, non-stick properties, and durability, are widely used in food containers requiring high-performance materials that withstand harsh cleaning agents and food acids. Polycarbonate offers excellent impact resistance, transparency, and heat resistance, making it a common choice for reusable food containers and packaging that demands clarity and toughness. Choosing between fluoropolymer and polycarbonate depends on the specific food safety requirements, environmental conditions, and durability needs of the container application.
Material Properties Comparison
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior chemical resistance, non-stick surface, and high thermal stability up to 260degC, making them ideal for food containers requiring durability and resistance to harsh cleaning agents. Polycarbonate offers excellent impact strength, transparency, and heat resistance up to 135degC, but can degrade under prolonged exposure to acidic or alkaline substances. Fluoropolymers provide better long-term performance in environments involving extreme temperatures and aggressive food acids compared to polycarbonate.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Fluoropolymer food containers exhibit exceptional chemical resistance and non-reactivity, meeting FDA and EFSA standards for food contact safety, making them ideal for preserving food quality without risk of contamination. Polycarbonate containers, while durable and clear, may pose safety concerns due to BPA content, leading to restrictions and bans in many regions for food contact use. Regulatory agencies increasingly favor fluoropolymers for applications requiring high-temperature resistance and compliance with stringent migration limits, ensuring safer food storage options.
Chemical Resistance in Food Storage
Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance compared to polycarbonate, making it highly effective for storing acidic and oily foods without risk of degradation or leaching. Polycarbonate containers may be susceptible to chemical breakdown when exposed to certain food acids or alcohols, potentially compromising food safety over time. Fluoropolymer's inert nature ensures long-term stability and non-reactivity, ideal for preserving food quality and preventing contamination during storage.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Fluoropolymer materials exhibit exceptional chemical resistance and high durability, making them ideal for food containers exposed to harsh cleaning agents or extreme temperatures. Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and toughness, providing excellent protection against drops and mechanical stress, which is essential for daily use containers. Comparing both, fluoropolymers ensure longevity in corrosive environments, while polycarbonate excels in withstanding physical impacts without cracking or breaking.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Fluoropolymer containers exhibit superior temperature tolerance, withstanding extreme heat up to 260degC (500degF) without degradation, making them ideal for high-heat food storage and cooking applications. Polycarbonate containers typically tolerate temperatures up to 135degC (275degF) but may deform or release BPA at higher temperatures, limiting their use in microwave or oven settings. Fluoropolymers offer enhanced chemical resistance and non-stick properties, ensuring long-term durability and food safety under rigorous temperature cycling compared to polycarbonate.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Fluoropolymer food containers offer superior resistance to stains and odors, making them exceptionally easy to clean and maintain compared to polycarbonate containers, which are prone to retaining food residues and discoloration over time. The non-stick, chemically inert surface of fluoropolymers prevents bacterial buildup and simplifies washing, reducing the need for harsh cleaning agents. Polycarbonate containers require careful handling to avoid scratches and clouding, which can compromise both cleanliness and durability.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Fluoropolymer food containers typically incur higher production costs due to specialized manufacturing processes and premium raw materials, resulting in a price premium compared to polycarbonate containers, which benefit from widespread production and lower material expenses. Market availability for polycarbonate containers is significantly broader, supported by extensive distribution networks and diverse product offerings, while fluoropolymer containers are more niche and less commonly stocked by major retailers. The choice between these materials hinges on balancing fluoropolymer's superior chemical resistance and non-stick properties against polycarbonate's cost-efficiency and accessibility in the consumer food storage market.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Fluoropolymer food containers offer exceptional chemical resistance and durability but pose challenges in recycling due to their complex fluorinated polymers, which require specialized processing to break down safely. Polycarbonate containers, while less chemically resistant, are more widely recycled in conventional municipal systems, though concerns over BPA leakage have led to increased demand for BPA-free alternatives. The environmental impact of fluoropolymers includes persistence and difficulty in degradation, whereas polycarbonate's impact centers on potential chemical leaching and less durability, influencing their respective life cycles and recyclability options.
Best Applications for Food Containers
Fluoropolymer food containers excel in chemical resistance and non-stick properties, making them ideal for storing acidic or oily foods without degradation or flavor transfer. Polycarbonate containers offer superior impact resistance and clarity, allowing easy content visibility and durability under frequent use, especially suited for cold and dry food storage. Both materials provide BPA-free options, but fluoropolymers are preferred for high-temperature or microwave applications due to their thermal stability.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polycarbonate for Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com