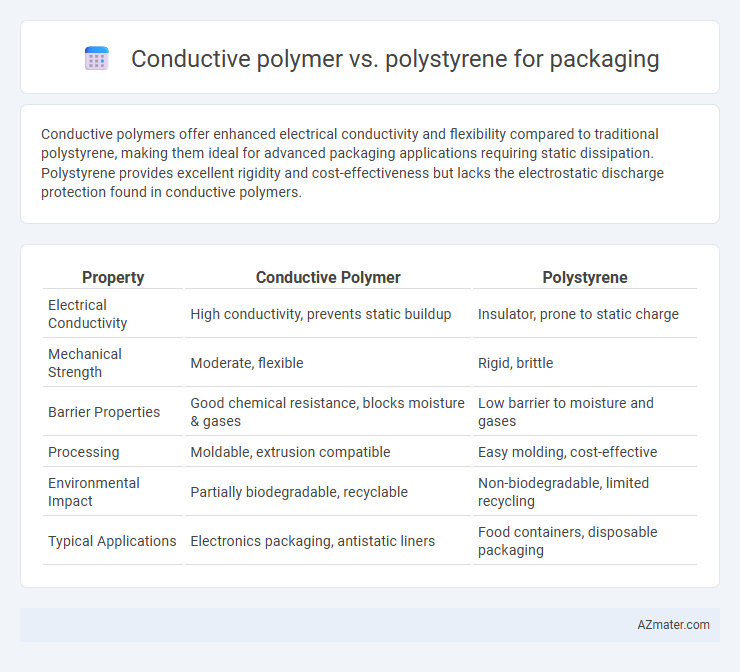
Conductive polymers offer enhanced electrical conductivity and flexibility compared to traditional polystyrene, making them ideal for advanced packaging applications requiring static dissipation. Polystyrene provides excellent rigidity and cost-effectiveness but lacks the electrostatic discharge protection found in conductive polymers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Polymer | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High conductivity, prevents static buildup | Insulator, prone to static charge |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, flexible | Rigid, brittle |
| Barrier Properties | Good chemical resistance, blocks moisture & gases | Low barrier to moisture and gases |
| Processing | Moldable, extrusion compatible | Easy molding, cost-effective |
| Environmental Impact | Partially biodegradable, recyclable | Non-biodegradable, limited recycling |
| Typical Applications | Electronics packaging, antistatic liners | Food containers, disposable packaging |
Introduction to Packaging Materials: Conductive Polymers vs Polystyrene
Conductive polymers offer unique electrical conductivity and antistatic properties, making them ideal for packaging sensitive electronic components and preventing electrostatic discharge damage. Polystyrene, a widely used rigid polymer, provides excellent insulation, lightweight characteristics, and cost-efficiency, suitable for protective packaging and cushioning applications. The choice between conductive polymers and polystyrene depends on the specific packaging requirements, balancing conductivity needs and mechanical strength.
Overview of Conductive Polymers in Packaging
Conductive polymers in packaging offer enhanced electrical conductivity, enabling applications in antistatic and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding packaging solutions. These polymers, such as polyaniline, polypyrrole, and PEDOT:PSS, provide flexibility, lightweight properties, and environmental stability compared to traditional insulative polymers like polystyrene. Their integration improves product protection, reduces static buildup, and supports smart packaging innovations in electronics and sensitive equipment transport.
Polystyrene: Properties and Applications in Packaging
Polystyrene is a lightweight, rigid thermoplastic known for its excellent clarity, insulation properties, and cost-effectiveness, making it widely used in packaging applications such as food containers, disposable cutlery, and protective packaging. Its ability to be easily molded and customized into various shapes enhances its utility in safely protecting fragile items during shipping. Despite its advantages, polystyrene's environmental impact and limited recyclability pose challenges that drive the search for more sustainable alternatives.
Electrical Conductivity: A Key Differentiator
Conductive polymers exhibit significant electrical conductivity, making them ideal for antistatic and electromagnetic shielding packaging applications, whereas polystyrene is inherently an electrical insulator with negligible conductivity. The intrinsic conductivity of conductive polymers stems from their conjugated p-electron systems, enabling charge transport that polystyrene's saturated hydrocarbon structure lacks. This fundamental difference positions conductive polymers as superior choices for packaging requiring reliable electrical performance to protect sensitive electronic components.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Conductive polymers exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polystyrene, offering enhanced resistance to impact and deformation under stress. Their molecular structure provides greater flexibility and elongation, reducing brittleness commonly associated with polystyrene packaging materials. This results in longer-lasting protection for contents, making conductive polymers preferable for applications requiring robust mechanical performance and extended lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Conductive polymers exhibit superior environmental benefits over traditional polystyrene by offering enhanced recyclability and biodegradability, reducing overall landfill waste and pollution. Polystyrene, a petroleum-based plastic, contributes significantly to environmental degradation through slow decomposition and the release of toxic compounds during incineration. Sustainable packaging increasingly favors conductive polymers for their potential to minimize carbon footprint and support circular economy initiatives within the packaging industry.
Cost and Production Considerations
Conductive polymers generally have higher production costs compared to polystyrene due to complex synthesis processes and the use of specialized materials, impacting overall packaging expenses. Polystyrene is favored for its low cost, ease of mass production, and widespread availability, making it a cost-effective solution for packaging applications. However, conductive polymers offer added value for specific uses requiring electrical conductivity, which can justify their increased production investment in niche packaging markets.
Safety and Regulatory Aspects
Conductive polymers in packaging offer enhanced safety by reducing static electricity risks, crucial for sensitive electronic components, and comply with regulations such as RoHS and REACH that restrict hazardous substances. Polystyrene, while widely used, presents concerns due to its potential leaching of styrene monomers, which are regulated by FDA and EFSA to ensure consumer safety. Regulatory bodies emphasize strict migration limits and proper material certification, making conductive polymers a safer alternative in environments demanding high electrical safety and compliance.
Application Suitability: Which to Choose?
Conductive polymers are ideal for packaging applications requiring static dissipation and electromagnetic interference shielding, commonly used in electronics and sensitive device packaging. Polystyrene, known for its rigidity, lightweight nature, and excellent insulation properties, excels in food containers, disposable cutlery, and protective packaging due to its impact resistance and moisture barrier capabilities. Choosing between conductive polymers and polystyrene depends on the need for electrical conductivity and durability versus cost-effectiveness and physical protection in packaging design.
Future Trends in Packaging Material Innovation
Conductive polymers offer enhanced electrical conductivity and antistatic properties, making them ideal for smart packaging applications compared to traditional polystyrene, which is widely used for insulation but lacks functional responsiveness. Future trends in packaging innovation emphasize the integration of conductive polymers with biodegradable substrates to improve sustainability and enable features such as real-time sensor integration and interactive packaging. Advances in nanotechnology and polymer composites are expected to further enhance the mechanical strength and conductivity of conductive polymers, positioning them as a key material in next-generation packaging solutions.
Infographic: Conductive polymer vs Polystyrene for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com