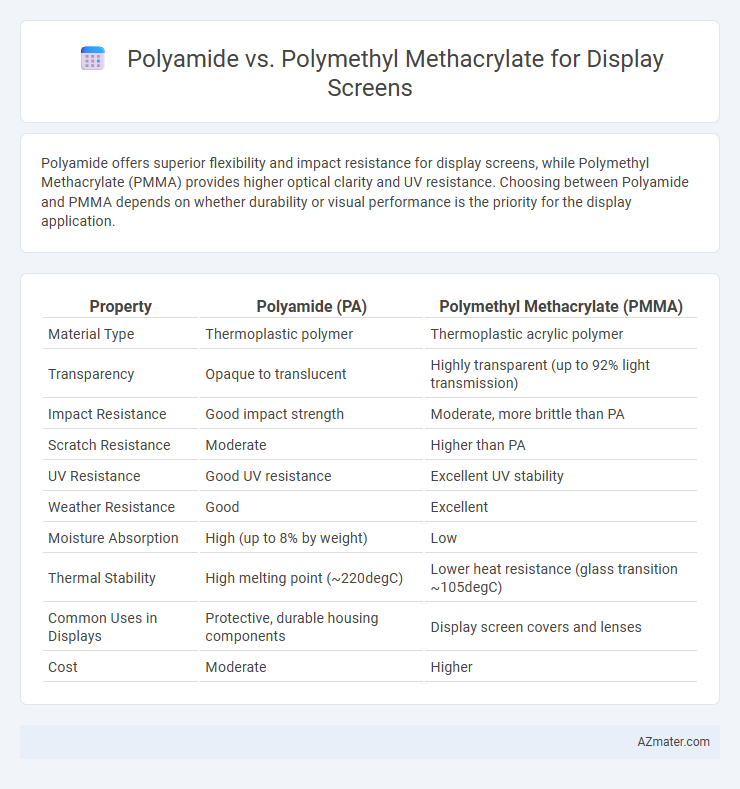
Polyamide offers superior flexibility and impact resistance for display screens, while Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides higher optical clarity and UV resistance. Choosing between Polyamide and PMMA depends on whether durability or visual performance is the priority for the display application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyamide (PA) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic acrylic polymer |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent (up to 92% light transmission) |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact strength | Moderate, more brittle than PA |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | Higher than PA |
| UV Resistance | Good UV resistance | Excellent UV stability |
| Weather Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Moisture Absorption | High (up to 8% by weight) | Low |
| Thermal Stability | High melting point (~220degC) | Lower heat resistance (glass transition ~105degC) |
| Common Uses in Displays | Protective, durable housing components | Display screen covers and lenses |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Display Screen Materials
Polyamide and Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) are key materials used in display screen manufacturing due to their distinct mechanical and optical properties. Polyamide offers exceptional toughness, thermal resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for flexible and impact-resistant screen applications. PMMA provides superior clarity, weather resistance, and UV stability, which enhances display brightness and durability in outdoor environments.
Overview of Polyamide
Polyamide, known for its excellent mechanical strength and flexibility, offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in display screen applications. Its high thermal stability and resistance to abrasion make it ideal for touchscreens and protective covers. Polyamide's ability to maintain clarity and performance under diverse environmental conditions positions it as a reliable material for advanced display technologies.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its exceptional clarity, UV resistance, and high light transmittance, making it a popular choice for display screens. Its superior scratch resistance and weatherability outperform many other plastics, including polyamide, while maintaining good impact strength and dimensional stability. PMMA's lightweight nature combined with its ease of fabrication contributes to its wide use in LCD screens, protective covers, and digital display panels.
Optical Properties: Clarity and Transparency
Polyamide exhibits moderate clarity and transparency, with a yellowish tint that may slightly affect display screen visibility, while polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior optical clarity with over 92% light transmittance, making it ideal for high-quality transparent displays. PMMA's glass-like transparency and low haze levels enhance image sharpness and color accuracy, crucial for touchscreens and advanced display technologies. Polyamide's optical properties are more suited for protective layers where durability is prioritized over perfect transparency.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyamide exhibits superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), making it more suitable for high-stress display screen applications. PMMA offers excellent clarity and scratch resistance but is more brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical stress. The enhanced durability of polyamide stems from its higher tensile strength and flexibility, ensuring longer-lasting performance in demanding environments.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polyamide exhibits superior chemical resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, making it highly durable for display screens exposed to harsh environments. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent environmental stability with strong resistance to UV radiation and weathering, maintaining clarity over time without yellowing. While polyamide provides enhanced toughness and abrasion resistance, PMMA is preferred for optical clarity and long-term outdoor performance in display applications.
Fabrication and Processing Differences
Polyamide exhibits excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, allowing for flexible, impact-resistant display screens through extrusion and injection molding processes. In contrast, Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity but is more brittle, commonly fabricated via casting or injection molding with precise temperature control to avoid stress cracking. Processing polyamide requires higher temperature and moisture control, whereas PMMA demands careful annealing to enhance scratch resistance and dimensional stability in display applications.
Cost Analysis: Polyamide vs PMMA
Polyamide offers a cost-effective solution for display screens due to its lower raw material and processing expenses compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA). PMMA generally incurs higher costs owing to its superior optical clarity and scratch resistance, which require more complex manufacturing techniques and premium materials. When balancing initial investment and performance needs, polyamide stands out for budget-sensitive projects, while PMMA caters to applications demanding higher visual quality despite the increased cost.
Suitability for Touchscreen Applications
Polyamide offers excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and durability, making it highly suitable for touchscreen applications that require frequent handling and bending. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior optical clarity and scratch resistance but lacks the mechanical robustness needed for flexible or dynamic touchscreens. For high-performance touch displays, polyamide's combination of toughness and flexibility typically outperforms PMMA in maintaining screen integrity under repeated touch interactions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Display Screens
Polyamide offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for rugged or curved display screens, while Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides higher optical clarity and scratch resistance suitable for high-definition, flat displays. Cost-efficiency and environmental factors also play crucial roles; Polyamide is more durable under stress but less transparent than PMMA, which excels in light transmission. Selecting the right material depends on the display requirements for durability, visual performance, and environmental exposure, aligning with the specific application's demands.
Infographic: Polyamide vs Polymethyl Methacrylate for Display Screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com