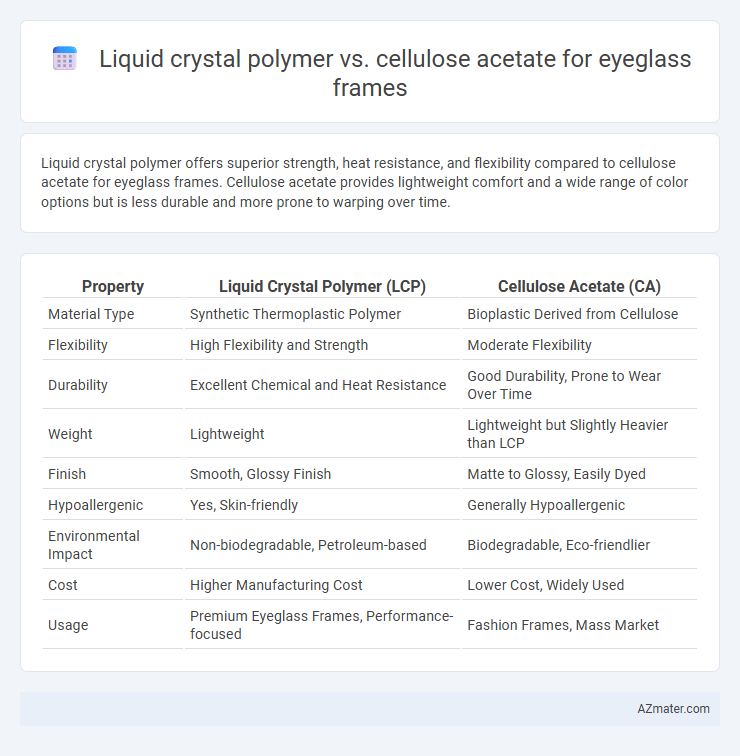
Liquid crystal polymer offers superior strength, heat resistance, and flexibility compared to cellulose acetate for eyeglass frames. Cellulose acetate provides lightweight comfort and a wide range of color options but is less durable and more prone to warping over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Cellulose Acetate (CA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Thermoplastic Polymer | Bioplastic Derived from Cellulose |
| Flexibility | High Flexibility and Strength | Moderate Flexibility |
| Durability | Excellent Chemical and Heat Resistance | Good Durability, Prone to Wear Over Time |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but Slightly Heavier than LCP |
| Finish | Smooth, Glossy Finish | Matte to Glossy, Easily Dyed |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes, Skin-friendly | Generally Hypoallergenic |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, Petroleum-based | Biodegradable, Eco-friendlier |
| Cost | Higher Manufacturing Cost | Lower Cost, Widely Used |
| Usage | Premium Eyeglass Frames, Performance-focused | Fashion Frames, Mass Market |
Overview of Liquid Crystal Polymer and Cellulose Acetate
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional strength, heat resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for durable eyeglass frames. Cellulose acetate, derived from natural cotton or wood fibers, offers a lightweight, hypoallergenic option with vibrant color possibilities and a smooth, glossy finish. While LCP frames excel in longevity and resistance to deformation, cellulose acetate frames provide aesthetic versatility and comfort for everyday wear.
Material Composition and Structure
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) eyeglass frames feature a unique molecular structure of highly ordered polymer chains, offering exceptional strength, flexibility, and heat resistance compared to cellulose acetate. Cellulose acetate, derived from plant cellulose, consists of a semi-synthetic polymer with a less organized structure, resulting in lighter weight but lower durability and heat tolerance. The crystalline arrangement in LCP contributes to its superior performance in maintaining shape and resisting deformation under stress, while cellulose acetate provides a more customizable surface finish and color variety.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) eyeglass frames exhibit superior tensile strength and flexibility compared to cellulose acetate, providing enhanced durability and resistance to impact. Cellulose acetate offers excellent hypoallergenic properties and a broader range of color customization but tends to be less resistant to heat and environmental degradation. The lightweight nature of LCP combined with its chemical resistance makes it ideal for long-lasting, high-performance eyewear, whereas cellulose acetate's natural origin appeals to users seeking eco-friendly and affordable options.
Durability and Longevity
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) eyeglass frames exhibit exceptional durability due to their high tensile strength and resistance to heat and chemicals, ensuring long-lasting performance even under daily stress. In contrast, cellulose acetate frames, while lightweight and flexible, are more prone to wear, discoloration, and brittleness over time, especially when exposed to moisture and UV light. The superior structural integrity and environmental resistance of LCP make it a preferred choice for consumers seeking eyeglass frames with enhanced longevity and minimal maintenance.
Weight and Comfort in Daily Wear
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) eyeglass frames are significantly lighter than cellulose acetate, enhancing all-day comfort by reducing pressure on the nose and ears. LCP's high strength-to-weight ratio provides superior durability without added bulk, making it ideal for active lifestyles. Cellulose acetate frames, while stylish and flexible, tend to be heavier, which can lead to discomfort during prolonged wear compared to the lightweight, comfortable feel of liquid crystal polymer options.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior design flexibility for eyeglass frames due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and ability to be molded into intricate shapes without compromising durability. In contrast, cellulose acetate provides a broader palette of aesthetic options with its natural translucency, rich colors, and custom patterning capabilities, making it popular for fashion-forward eyewear. While LCP frames excel in slim, modern designs with a sleek finish, cellulose acetate frames stand out for their vibrant, classic looks and extensive customization choices.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) eyeglass frames exhibit superior environmental stability with high recyclability and low chemical waste during production, making them a sustainable choice in optical manufacturing. In contrast, cellulose acetate, derived from renewable plant sources, offers biodegradability and lower carbon footprint but involves intensive water use and chemical treatments in its processing. Comparing both materials, LCP frames lead in long-term durability and recyclability, while cellulose acetate contributes positively to biodegradability and renewable resource utilization.
Cost Differences and Market Availability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) eyeglass frames are generally more expensive than cellulose acetate frames due to higher raw material costs and advanced manufacturing processes. Cellulose acetate is widely available and cost-effective, making it a popular choice in the mass market, while LCP frames target premium segments with superior durability and flexibility. Market availability of cellulose acetate dominates globally, whereas LCP eyewear is primarily found in specialized collections and high-end retailers.
Suitable User Demographics
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) eyeglass frames are ideal for active individuals and professionals seeking high durability, lightweight design, and superior flexibility, particularly suitable for athletes, tech workers, and those with sensitive skin due to its hypoallergenic properties. Cellulose acetate frames appeal to fashion-conscious users, including young adults and trendsetters, who prioritize stylish, customizable designs and vibrant colors, while also benefiting from the material's affordability and eco-friendliness. Both materials cater specifically to distinct lifestyle needs and aesthetic preferences, influencing their popularity among different demographic groups.
Final Recommendation: Choosing the Right Material
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers exceptional strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for durable and lightweight eyeglass frames. Cellulose acetate provides a more affordable, hypoallergenic, and easily customizable option with vibrant color possibilities but lacks the high performance of LCP under stress. For those seeking premium durability and modern aesthetics, LCP is the optimal choice, while cellulose acetate suits budget-conscious buyers prioritizing style versatility.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Cellulose acetate for Eyeglass Frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com