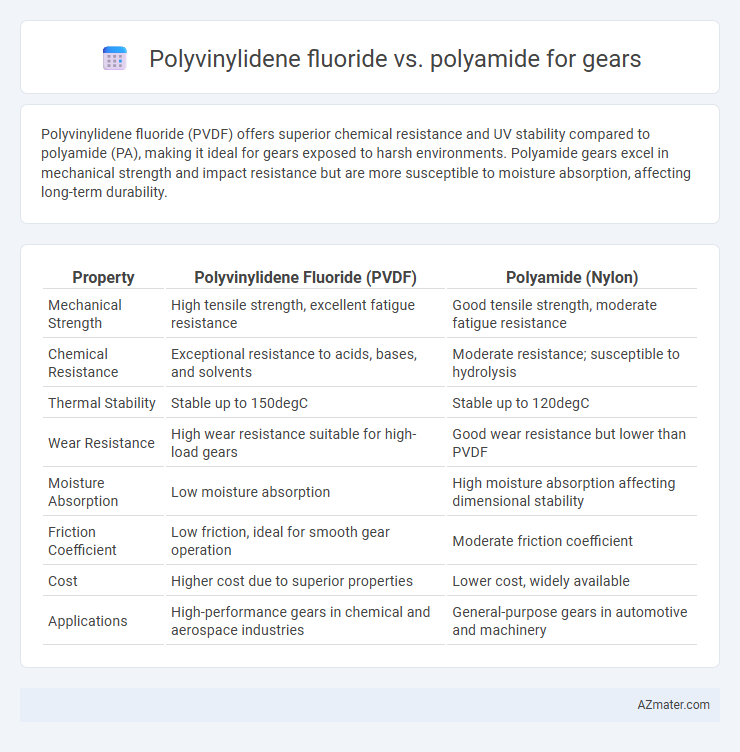
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability compared to polyamide (PA), making it ideal for gears exposed to harsh environments. Polyamide gears excel in mechanical strength and impact resistance but are more susceptible to moisture absorption, affecting long-term durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, excellent fatigue resistance | Good tensile strength, moderate fatigue resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Moderate resistance; susceptible to hydrolysis |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 150degC | Stable up to 120degC |
| Wear Resistance | High wear resistance suitable for high-load gears | Good wear resistance but lower than PVDF |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | High moisture absorption affecting dimensional stability |
| Friction Coefficient | Low friction, ideal for smooth gear operation | Moderate friction coefficient |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | High-performance gears in chemical and aerospace industries | General-purpose gears in automotive and machinery |
Introduction to High-Performance Polymers in Gear Manufacturing
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and polyamide (PA) are high-performance polymers widely used in gear manufacturing for their distinct mechanical and chemical properties. PVDF offers exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and low friction, making it ideal for environments demanding durability and minimal wear. Polyamide provides superior toughness, impact resistance, and dimensional stability under load, making it suitable for heavy-duty gear applications requiring high strength and resilience.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability, making it suitable for demanding gear applications. Compared to polyamide, PVDF offers superior resistance to UV radiation, solvents, and acids, ensuring durability in harsh environments. Its low friction coefficient and excellent wear resistance contribute to enhanced gear performance and longevity in industrial settings.
Overview of Polyamide (PA)
Polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, is a high-performance thermoplastic renowned for its excellent mechanical strength, wear resistance, and low friction properties, making it ideal for gear applications. It offers superior impact resistance and good chemical stability compared to many polymers, including Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), making it suitable for gears operating under high-load and high-stress conditions. Polyamide also demonstrates excellent dimensional stability and moisture absorption characteristics, which are critical factors influencing gear durability and performance in varying environments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: PVDF vs Polyamide
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polyamide, offering higher tensile strength and better resistance to impact and abrasion, making it ideal for demanding gear applications. Polyamide, while flexible and lightweight, typically shows lower mechanical robustness and increased susceptibility to wear under heavy loads. PVDF's enhanced chemical resistance and thermal stability contribute to its durability, ensuring long-lasting performance in harsh operational environments where polyamide may degrade faster.
Wear and Friction Properties
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior wear resistance and lower friction coefficients compared to polyamide, making it highly suitable for gear applications requiring enhanced durability. The chemical stability and self-lubricating properties of PVDF contribute to its reduced material degradation under high-load and high-speed conditions. In contrast, polyamide gears tend to absorb moisture, which can increase friction and wear, affecting long-term performance.
Chemical Resistance in Gear Applications
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyamide (PA) in gear applications, especially against acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for aggressive chemical environments. Polyamide tends to absorb moisture and degrade when exposed to strong chemicals, reducing its mechanical properties and lifespan in harsh conditions. PVDF's low permeability and excellent resistance to hydrocarbon-based fluids ensure greater durability and consistent performance in chemically demanding gear systems.
Thermal Stability and Operating Temperature Ranges
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior thermal stability with an operating temperature range from approximately -40degC to 150degC, making it well-suited for high-temperature gear applications. In contrast, polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, operates effectively between -40degC to 100degC but tends to degrade or deform at elevated temperatures beyond this range. The enhanced thermal resistance of PVDF ensures consistent performance and dimensional stability in demanding environments where polyamide gears may fail due to thermal softening or oxidation.
Machinability and Processing
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and easier machinability compared to polyamide (PA), featuring low moisture absorption that enhances dimensional stability during processing. Polyamide exhibits higher toughness and wear resistance but requires more precise control over temperature and humidity to avoid warping and machining difficulties. Machining PVDF typically involves lower cutting forces and better surface finish due to its rigidity and thermal stability, whereas polyamide's flexibility can lead to tool chatter and greater post-machining finishing time.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers higher chemical resistance and durability but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to polyamide (PA), which is more affordable and widely available. Polyamide gears benefit from broad market accessibility and lower material costs, making them suitable for large-scale manufacturing. The choice between PVDF and polyamide hinges on budget constraints and the required longevity of the gear application.
Application Suitability: Choosing Between PVDF and Polyamide
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers exceptional chemical resistance and high thermal stability, making it ideal for gears used in aggressive environments such as chemical processing or high-temperature applications. Polyamide (Nylon) provides superior mechanical strength, wear resistance, and low friction properties, suited for gears in automotive, industrial machinery, and consumer products where durability and load-bearing capacity are essential. Selecting between PVDF and Polyamide depends on the operating conditions, with PVDF preferred for corrosive or high-temperature settings and Polyamide favored for high-stress, mechanically demanding gear applications.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polyamide for Gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com