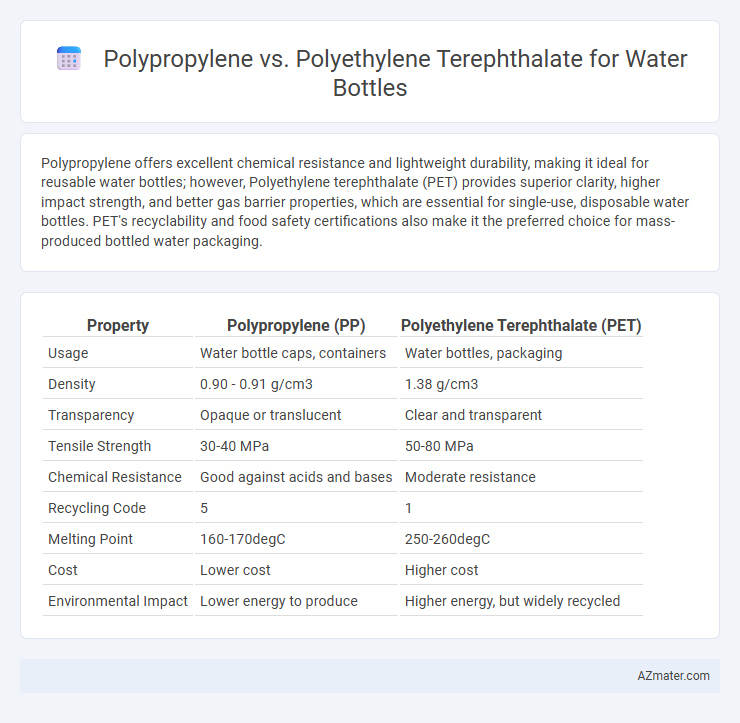
Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance and lightweight durability, making it ideal for reusable water bottles; however, Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides superior clarity, higher impact strength, and better gas barrier properties, which are essential for single-use, disposable water bottles. PET's recyclability and food safety certifications also make it the preferred choice for mass-produced bottled water packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Water bottle caps, containers | Water bottles, packaging |
| Density | 0.90 - 0.91 g/cm3 | 1.38 g/cm3 |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Tensile Strength | 30-40 MPa | 50-80 MPa |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and bases | Moderate resistance |
| Recycling Code | 5 | 1 |
| Melting Point | 160-170degC | 250-260degC |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Environmental Impact | Lower energy to produce | Higher energy, but widely recycled |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high chemical resistance, durability, and lightweight properties, making it a common choice for reusable water bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a strong, transparent polymer widely used in disposable water bottles due to its excellent gas barrier properties and recyclability. Both materials offer distinct benefits in water bottle manufacturing, balancing factors such as strength, clarity, and environmental impact.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polypropylene (PP) features a semi-crystalline structure with a repeating propylene monomer, providing high chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and good impact strength, making it lightweight and flexible for water bottle production. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) consists of aromatic rings and ester functional groups in its polymer chain, resulting in excellent clarity, higher tensile strength, and greater barrier properties against oxygen and carbon dioxide. The distinct chemical structures influence durability and performance; PP excels in chemical inertness and flexibility, while PET offers superior gas barrier properties and transparency crucial for preserving water quality and appearance.
Manufacturing Processes for Water Bottles
Polypropylene water bottles are manufactured using injection molding and blow molding processes, offering high resistance to heat and chemical corrosion. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles are produced primarily through stretch blow molding, which enhances clarity, tensile strength, and gas barrier properties. The manufacturing process for PET enables lightweight, transparent bottles widely used in the beverage industry due to superior recyclability and durability compared to polypropylene.
Durability and Strength Differences
Polypropylene offers excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making it highly durable for reusable water bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides superior tensile strength and clarity but can be more brittle under high stress compared to polypropylene. PET's strength makes it ideal for single-use bottles needing resistance to pressure, while polypropylene's toughness supports long-term durability and repeated use.
Barrier Properties: Oxygen and Moisture Resistance
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior oxygen and moisture barrier properties compared to polypropylene (PP), making it a preferred choice for water bottles requiring extended shelf life. PET's crystalline structure significantly reduces oxygen permeability, protecting water from oxidation and contamination. In contrast, PP offers moderate moisture resistance but higher oxygen permeability, which may not provide adequate protection for long-term water storage.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used for water bottles due to its strong resistance to leaching harmful chemicals, making it a safer choice for repeated use compared to polypropylene (PP), which can sometimes release ototoxic compounds under high heat exposure. The FDA classifies both PET and PP as safe for food contact, but PET's superior barrier properties reduce contamination risks, preserving water purity and reducing health hazards. Consumers concerned about chemical migration or endocrine disruptors often prefer PET bottles, especially when used in moderate temperature conditions.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) differ significantly in environmental impact and recyclability for water bottles. PET is widely recycled with an established global infrastructure, reducing landfill waste and energy consumption compared to PP, which has a less developed recycling stream and lower recycling rates. PP's lower carbon footprint during production offers some environmental advantages, but PET's higher recyclability makes it a more sustainable choice for water bottle packaging.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polypropylene (PP) offers cost efficiency due to its lower production expenses and widespread availability, making it a budget-friendly choice for water bottles in mass markets. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) dominates the water bottle market with superior clarity, recyclability, and strong consumer acceptance but comes at a higher production cost compared to PP. The extensive distribution networks and recycling infrastructure for PET enhance its market availability, whereas PP is favored for applications requiring durability and chemical resistance at a lower price point.
Performance in Different Water Storage Conditions
Polypropylene (PP) offers excellent chemical resistance and durability in various temperatures, making it ideal for water bottles exposed to fluctuating storage conditions, including hot and cold environments. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) excels in clarity and lightweight properties, but it has lower resistance to high temperatures and may degrade faster under prolonged heat or UV exposure. For long-term water storage, PP demonstrates superior performance in maintaining bottle integrity and preventing leaching, while PET is preferred for single-use or refrigerated water bottles due to its rigidity and transparency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Water Bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity, lightweight properties, and excellent barrier resistance, making it ideal for single-use water bottles requiring visibility and freshness preservation. Polypropylene (PP) provides higher temperature resistance, durability, and recyclability, better suited for reusable water bottles that demand toughness and longevity. Selecting between PET and PP depends on the water bottle's intended use, with PET favored for disposable convenience and PP preferred for sustainability and repeated use.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Water bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com