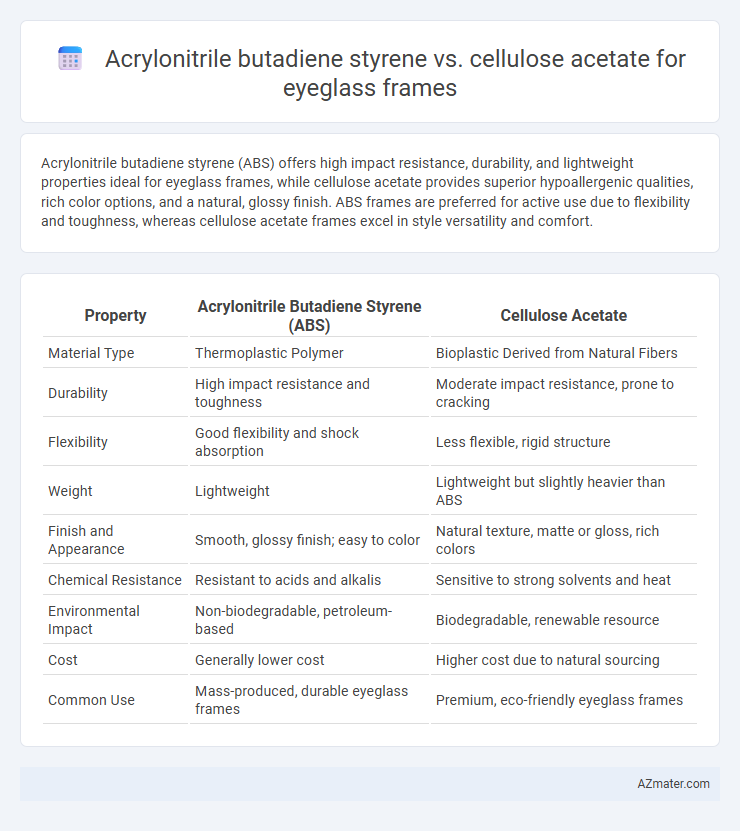
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance, durability, and lightweight properties ideal for eyeglass frames, while cellulose acetate provides superior hypoallergenic qualities, rich color options, and a natural, glossy finish. ABS frames are preferred for active use due to flexibility and toughness, whereas cellulose acetate frames excel in style versatility and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Cellulose Acetate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Bioplastic Derived from Natural Fibers |
| Durability | High impact resistance and toughness | Moderate impact resistance, prone to cracking |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility and shock absorption | Less flexible, rigid structure |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but slightly heavier than ABS |
| Finish and Appearance | Smooth, glossy finish; easy to color | Natural texture, matte or gloss, rich colors |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Sensitive to strong solvents and heat |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to natural sourcing |
| Common Use | Mass-produced, durable eyeglass frames | Premium, eco-friendly eyeglass frames |
Introduction to Eyeglass Frame Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it a popular choice for durable eyeglass frames. Cellulose acetate provides lightweight comfort and excellent hypoallergenic properties, favored for its natural look and customizable color options. Both materials serve distinct functional and aesthetic needs in eyeglass frame manufacturing, influencing user preference based on durability, weight, and design versatility.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in eyeglass frames due to its excellent impact resistance, lightweight nature, and versatility in molding complex shapes. Its chemical composition combines acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering durability, flexibility, and a smooth finish ideal for long-lasting eyewear. Compared to cellulose acetate, ABS provides superior strength and resistance to environmental stress, making it an optimal choice for active or everyday use frames.
Overview of Cellulose Acetate
Cellulose acetate is a bioplastic derived from natural sources like wood pulp and cotton fibers, widely favored for eyeglass frames due to its lightweight, hypoallergenic properties and vibrant color possibilities. Unlike acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), cellulose acetate offers superior breathability and flexibility, enhancing wearer comfort and durability. Its eco-friendly composition and ease of customization make cellulose acetate a popular choice for high-quality, stylish eyewear frames.
Weight and Comfort Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) eyeglass frames are lightweight and flexible, providing enhanced comfort for extended wear due to their low density and impact resistance. In contrast, cellulose acetate frames, while slightly heavier, offer a smooth, skin-friendly texture but may cause discomfort during prolonged use because of their rigidity and higher weight. Overall, ABS frames excel in weight reduction and flexibility, making them more comfortable for daily wear compared to cellulose acetate options.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) eyeglass frames offer superior durability due to their resistance to cracking, heat, and chemical exposure, making them ideal for everyday wear. In contrast, cellulose acetate frames provide good flexibility and aesthetic appeal but are generally less impact-resistant and more prone to damage under heavy stress. ABS materials maintain structural integrity better under impact, ensuring longer-lasting performance in demanding conditions.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior design flexibility for eyeglass frames due to its excellent molding properties, allowing intricate shapes and bold color variations. Cellulose acetate provides a higher aesthetic appeal with its natural translucency and rich color depth, enabling a more premium and artisanal look. Both materials support lightweight construction, but ABS excels in durability and versatility while cellulose acetate emphasizes luxury and unique finishes.
Hypoallergenic and Skin Compatibility
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers strong hypoallergenic properties with minimal risk of skin irritation, making it suitable for sensitive skin in eyeglass frames. Cellulose acetate, a natural polymer derived from cotton or wood pulp, is widely recognized for its excellent skin compatibility and breathability, reducing allergic reactions and enhancing comfort. Both materials provide reliable hypoallergenic benefits, but cellulose acetate often ranks higher in skin-friendly characteristics due to its biocompatibility and moisture absorption.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a petroleum-based plastic known for its durability but poses environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature and difficulty in recycling, contributing to long-term landfill waste. In contrast, cellulose acetate is derived from natural cellulose, making it more biodegradable and environmentally friendly, with the ability to decompose under proper conditions, reducing ecological footprint significantly. The use of cellulose acetate in eyeglass frames supports sustainable production practices by lowering dependence on fossil fuels and enhancing end-of-life waste management options.
Cost Effectiveness of ABS vs Cellulose Acetate
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers greater cost-effectiveness compared to cellulose acetate for eyeglass frames due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. ABS frames benefit from faster injection molding processes that reduce labor and production time, resulting in more affordable mass production. Cellulose acetate, derived from natural fibers, incurs higher costs linked to material sourcing and complex polishing, making ABS a budget-friendly choice without compromising durability.
Final Recommendation: Choosing the Right Material for Eyeglass Frames
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance, durability, and ease of molding, making it ideal for eyeglass frames that require robustness and long-lasting wear. Cellulose acetate provides excellent lightweight comfort, vibrant color options, and hypoallergenic properties, appealing to users with sensitive skin or style-conscious preferences. Selecting the right material depends on prioritizing either ABS for strength and resilience or cellulose acetate for comfort and aesthetic versatility in eyeglass frames.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Cellulose acetate for Eyeglass Frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com