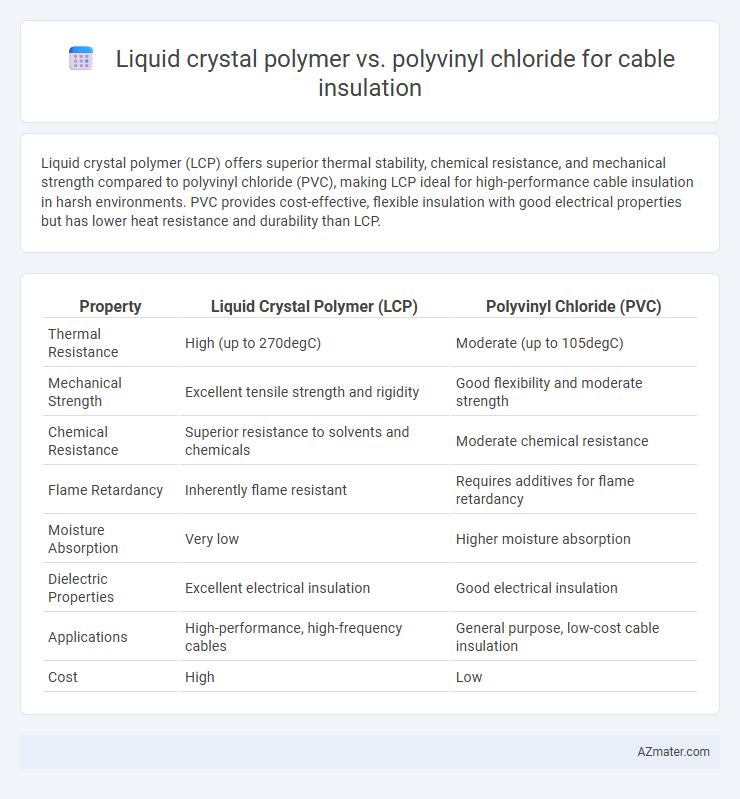
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making LCP ideal for high-performance cable insulation in harsh environments. PVC provides cost-effective, flexible insulation with good electrical properties but has lower heat resistance and durability than LCP.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 270degC) | Moderate (up to 105degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent tensile strength and rigidity | Good flexibility and moderate strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to solvents and chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Flame Retardancy | Inherently flame resistant | Requires additives for flame retardancy |
| Moisture Absorption | Very low | Higher moisture absorption |
| Dielectric Properties | Excellent electrical insulation | Good electrical insulation |
| Applications | High-performance, high-frequency cables | General purpose, low-cost cable insulation |
| Cost | High | Low |
Introduction to Cable Insulation Materials
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are widely used materials for cable insulation, each offering distinct properties suitable for specific applications. LCP provides superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for high-performance and demanding environments. In contrast, PVC is valued for its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and flame retardancy, commonly applied in general-purpose cable insulation where moderate mechanical and electrical properties are sufficient.
Overview of Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP)
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for advanced cable insulation applications. Its molecular structure enables excellent dimensional stability and low moisture absorption, which enhances cable reliability in harsh environments compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC). LCP also offers superior electrical insulation properties and flame retardancy, contributing to longer-lasting and safer cable performance.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, flame resistance, and cost-effectiveness in cable insulation applications. PVC offers good chemical resistance and durability, making it suitable for a variety of environments including indoor and outdoor use. Despite being less heat-resistant than liquid crystal polymers, PVC remains popular due to its flexibility and ease of processing in manufacturing insulated cables.
Mechanical Properties: LCP vs PVC
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior mechanical properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in cable insulation applications, exhibiting higher tensile strength and exceptional stiffness. LCP's inherent rigidity and thermal stability enable it to withstand mechanical stresses and harsh environments without deformation, unlike PVC, which can become brittle and degrade over time. These properties make LCP insulation ideal for high-performance cables requiring durability and reliable mechanical integrity under demanding conditions.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with continuous operating temperatures often exceeding 260degC, while PVC typically withstands up to 105degC. LCP's high melting point and low thermal expansion contribute to enhanced heat resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term exposure to elevated temperatures. In contrast, PVC tends to degrade and lose mechanical integrity under prolonged thermal stress, limiting its use in high-temperature cable insulation environments.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) demonstrates superior electrical insulation capabilities compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offering higher dielectric strength and lower dielectric constant, which reduces signal loss in high-frequency applications. LCP's molecular alignment provides excellent thermal stability and resistance to electrical degradation, making it ideal for cables operating under extreme conditions. PVC, while widely used for its cost-effectiveness and flexibility, exhibits lower dielectric performance and greater susceptibility to electrical breakdown over time.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), effectively withstanding exposure to solvents, acids, and alkalis without significant degradation. LCP also demonstrates enhanced durability in high-temperature environments, maintaining mechanical integrity and insulation properties under prolonged thermal stress. In contrast, PVC tends to soften and lose structural strength when exposed to harsh chemicals and elevated temperatures, making LCP a more reliable choice for demanding cable insulation applications.
Flexibility and Design Considerations
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior flexibility and high thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for cables requiring repeated bending and complex routing. LCP's molecular alignment provides excellent dimensional stability and resistance to creep, enabling thinner insulation layers and more compact cable designs. In contrast, PVC is less flexible and more prone to deformation under mechanical stress, limiting its use in applications demanding high flexibility and intricate design configurations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior environmental benefits over polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in cable insulation due to its high recyclability and lower toxic emissions during production and disposal. Unlike PVC, which releases harmful dioxins and requires plasticizers that pose ecological risks, LCP is inherently stable and free from hazardous additives, enhancing sustainability in manufacturing and end-of-life processes. The durability and chemical resistance of LCP contribute to longer cable lifespans, reducing waste generation and environmental footprint in electrical and electronic applications.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Material
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance cable insulation in aerospace, automotive, and electronics applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) remains cost-effective and versatile with good flame retardancy and flexibility, suitable for general-purpose electrical cables and indoor installations where mechanical stress and temperature extremes are less critical. Selecting between LCP and PVC depends on application-specific demands such as thermal endurance, environmental exposure, and regulatory compliance for safety standards.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Polyvinyl chloride for Cable insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com