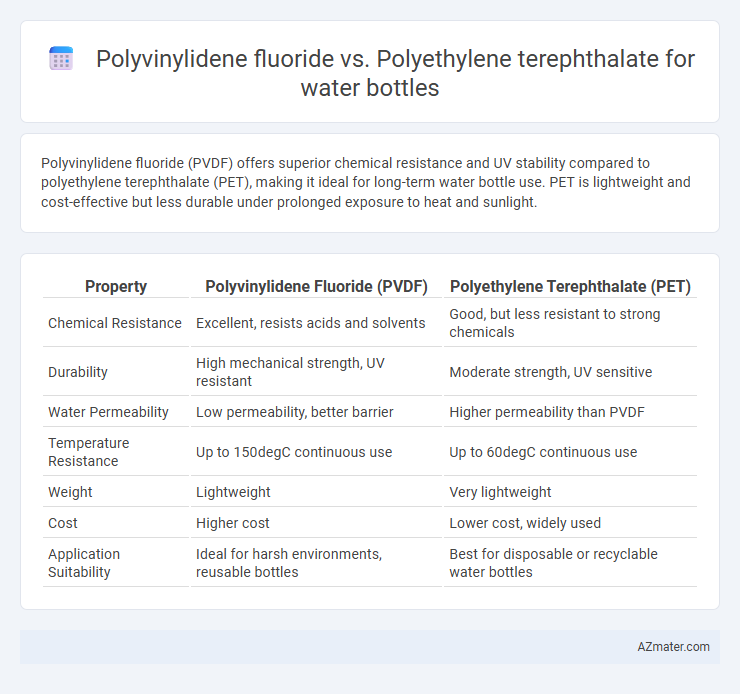
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it ideal for long-term water bottle use. PET is lightweight and cost-effective but less durable under prolonged exposure to heat and sunlight.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists acids and solvents | Good, but less resistant to strong chemicals |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, UV resistant | Moderate strength, UV sensitive |
| Water Permeability | Low permeability, better barrier | Higher permeability than PVDF |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC continuous use | Up to 60degC continuous use |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost, widely used |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for harsh environments, reusable bottles | Best for disposable or recyclable water bottles |
Introduction to PVDF and PET in Water Bottles
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for water bottles requiring durability and long-term safety. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a widely used thermoplastic polyester characterized by its lightweight nature, transparency, and strong barrier properties against moisture and carbon dioxide, ideal for disposable and reusable water bottles. The comparison of PVDF and PET focuses on their respective advantages in chemical stability, environmental impact, and suitability for different water bottle applications.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a fluoropolymer composed of repeating units of CH2-CF2, characterized by strong carbon-fluorine bonds that provide excellent chemical resistance and stability in water bottle applications. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) consists of repeating ester groups derived from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, offering a balanced combination of durability, transparency, and resistance to hydrolysis. The distinct chemical structure of PVDF results in superior resistance to chemical degradation compared to the ester linkages in PET, which are more prone to hydrolytic breakdown under prolonged exposure to moisture.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it more durable under high stress and harsh environmental conditions. PET provides good impact resistance and flexibility but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and repeated usage. PVDF's enhanced durability and resistance to cracking make it a preferred choice for long-lasting water bottles requiring high-performance materials.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior thermal stability and temperature resistance compared to Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), maintaining structural integrity up to 150degC, while PET typically withstands temperatures only up to 80degC before deformation occurs. PVDF's high melting point around 177degC and excellent chemical resistance make it ideal for applications requiring sterilization or exposure to hot liquids. PET is commonly used in standard water bottles due to its cost-effectiveness and clarity but is less suited for high-temperature environments where thermal degradation is a concern.
Barrier Properties: Oxygen and Moisture
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior oxygen and moisture barrier properties compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it highly effective for water bottle applications requiring minimal gas permeability. PVDF's low oxygen transmission rate (OTR) and excellent resistance to water vapor permeation help preserve water freshness and prevent contamination. PET, while widely used for its strength and clarity, exhibits higher permeability to oxygen and moisture, which may compromise long-term water quality in comparison to PVDF.
Safety and Food-Grade Compliance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and stability, making it highly safe for water bottle applications with minimal risk of leaching harmful substances. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely approved for food-grade use due to its excellent barrier properties and BPA-free composition, ensuring compliance with FDA and EFSA regulations. Both materials meet stringent safety standards, but PVDF provides enhanced durability under extreme conditions, while PET remains the industry standard for everyday water bottles.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), but PVDF's environmental impact is higher due to its complex fluoropolymer structure, which makes recycling challenging. PET is widely recycled and contributes significantly to reducing plastic waste in the water bottle industry, with established recycling infrastructures and lower carbon footprint during production. The biodegradability and circular economy integration of PET make it a more environmentally sustainable choice for single-use and reusable water bottles.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely favored in water bottle manufacturing due to its low cost and efficient production processes, making it highly cost-effective for mass production. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), while offering superior chemical resistance and durability, involves higher material costs and more complex manufacturing, limiting its use to specialized applications. The cost-efficiency of PET combined with scalable injection molding and blow molding techniques supports its dominance in the water bottle market.
Applications in Water Bottle Industry
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability, making it ideal for water bottles exposed to harsh environmental conditions and prolonged outdoor use. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) dominates the water bottle industry due to its lightweight nature, excellent transparency, and high strength-to-weight ratio, facilitating mass production and recyclability. PVDF's niche applications in water bottles involve specialty uses requiring durability and safety from chemical leachates, while PET remains the preferred choice for everyday consumer water bottle packaging.
Conclusion: Choosing Between PVDF and PET
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) remains the dominant choice for water bottles due to its excellent clarity, lightweight nature, and low cost, ideal for mass production and recycling efficiency. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for specialized applications requiring durability and long-term performance. Selecting between PVDF and PET depends on priorities such as cost-effectiveness and recyclability for PET versus advanced chemical and environmental resistance provided by PVDF.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Water bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com