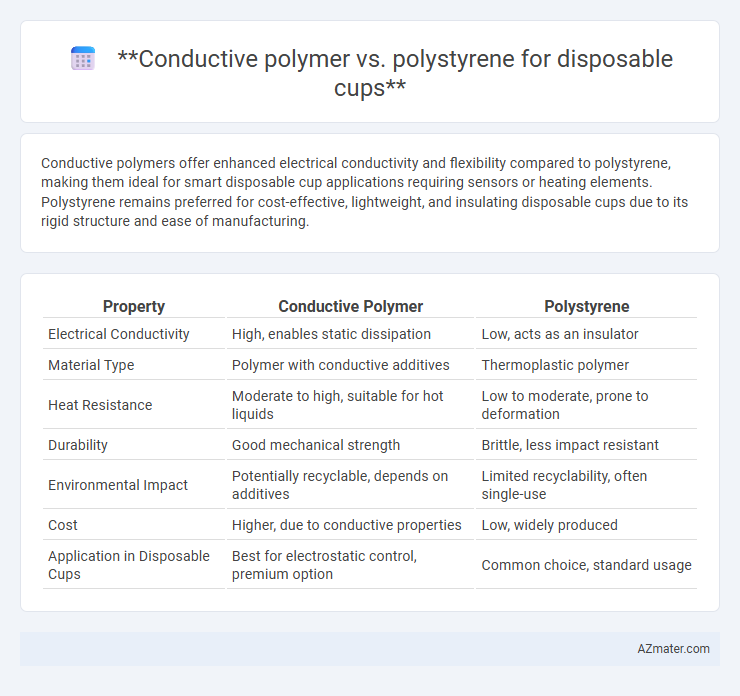
Conductive polymers offer enhanced electrical conductivity and flexibility compared to polystyrene, making them ideal for smart disposable cup applications requiring sensors or heating elements. Polystyrene remains preferred for cost-effective, lightweight, and insulating disposable cups due to its rigid structure and ease of manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Polymer | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High, enables static dissipation | Low, acts as an insulator |
| Material Type | Polymer with conductive additives | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate to high, suitable for hot liquids | Low to moderate, prone to deformation |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength | Brittle, less impact resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially recyclable, depends on additives | Limited recyclability, often single-use |
| Cost | Higher, due to conductive properties | Low, widely produced |
| Application in Disposable Cups | Best for electrostatic control, premium option | Common choice, standard usage |
Introduction to Disposable Cup Materials
Conductive polymers offer unique electrical properties and flexibility compared to traditional polystyrene materials commonly used in disposable cups. Polystyrene is favored for its rigidity, insulation, and cost-effectiveness but lacks conductivity and environmental benefits. The choice between conductive polymers and polystyrene hinges on balancing functional performance, user experience, and sustainability considerations in disposable cup applications.
Overview of Conductive Polymers
Conductive polymers, such as polyaniline and polypyrrole, exhibit unique electrical conductivity combined with the lightweight and flexible properties of traditional plastics, offering advantages over conventional polystyrene in disposable cup applications. These materials enable integration of antistatic and sensor functions directly into the cup material, enhancing safety and functionality without compromising insulation or durability. Their tunable conductivity and environmental stability make conductive polymers promising candidates for next-generation disposable food and beverage containers.
Properties of Polystyrene in Cup Manufacturing
Polystyrene offers excellent rigidity, clarity, and thermal insulation, making it a popular choice for disposable cups in the beverage industry. Its lightweight nature and effective barrier properties against moisture and oxygen help maintain beverage temperature and freshness. Polystyrene is also cost-effective and easily molded, ensuring efficient mass production of durable, single-use cups.
Environmental Impact: Conductive Polymer vs Polystyrene
Conductive polymers for disposable cups offer enhanced environmental benefits due to their potential biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional polystyrene, which is derived from non-renewable petroleum sources and contributes significantly to plastic pollution. Polystyrene cups are notorious for their persistence in landfills and oceans, releasing harmful chemicals during degradation, whereas conductive polymers can be engineered to decompose more efficiently, reducing long-term environmental damage. The shift towards conductive polymer-based disposable cups aligns with sustainable waste management practices and minimizes ecological toxicity.
Safety and Food Contact Considerations
Conductive polymers offer enhanced safety features due to their inherent antimicrobial properties and reduced chemical leaching, making them suitable for disposable cup applications with direct food contact. Polystyrene, while widely used for disposable cups, poses concerns related to styrene monomer migration and potential endocrine-disrupting effects when exposed to heat or fatty foods. Regulatory compliance with FDA and EFSA guidelines is crucial for both materials to ensure consumer health safety and minimize toxicological risks in food contact scenarios.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Conductive polymers generally have higher material and manufacturing costs compared to polystyrene, impacting their economic viability for disposable cups. Polystyrene remains a cost-effective option due to its low raw material price and established production infrastructure. However, the added functionality of conductive polymers may justify their use in niche markets despite the initial cost disparity.
Performance and Durability Analysis
Conductive polymers exhibit superior electrostatic dissipation and enhanced thermal stability compared to polystyrene, improving safety in disposable cup applications where static charge buildup can be problematic. Polystyrene offers good rigidity and cost-effectiveness but lacks the durability and resistance to mechanical stress that conductive polymers provide, leading to potential deformation under heat exposure. Performance testing reveals that conductive polymer cups maintain structural integrity and performance over extended use, whereas polystyrene cups are prone to cracking and reduced durability in hot beverage conditions.
Recyclability and Waste Management
Conductive polymers in disposable cups offer enhanced recyclability due to their ability to be processed alongside traditional plastics, reducing contamination in recycling streams compared to polystyrene, which is less frequently recycled and often ends up in landfills. The biodegradable potential of some conductive polymers further supports waste management by minimizing long-term environmental impact, contrasting with the persistence of polystyrene waste. Implementing conductive polymer materials enhances circular economy efforts by enabling more efficient material recovery and reducing plastic pollution in waste management systems.
Market Trends and Industry Adoption
The market for conductive polymers in disposable cups is rapidly growing due to increased demand for smart packaging and enhanced user interaction, with key players investing in research to improve material flexibility and conductivity. Polystyrene remains dominant in traditional disposable cup production due to its low cost and ease of manufacturing, but faces challenges from environmental concerns and regulatory pressures driving innovation toward sustainable alternatives. Industry adoption of conductive polymers is accelerating in sectors like foodservice and healthcare, where functionality such as temperature sensing and anti-microbial properties provide competitive advantages over conventional polystyrene cups.
Future Prospects for Disposable Cup Materials
Conductive polymers offer significant potential for future disposable cup materials due to their flexibility, biodegradability, and ability to integrate smart features like temperature sensitivity and environmental sensors. Polystyrene, despite its low cost and insulation properties, faces increasing regulatory restrictions and environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature and contribution to plastic pollution. Innovations in conductive polymer composites could revolutionize disposable cups by enhancing sustainability and functionality, positioning them as a more eco-friendly and technologically advanced alternative to traditional polystyrene cups.
Infographic: Conductive polymer vs Polystyrene for Disposable cup
 azmater.com
azmater.com