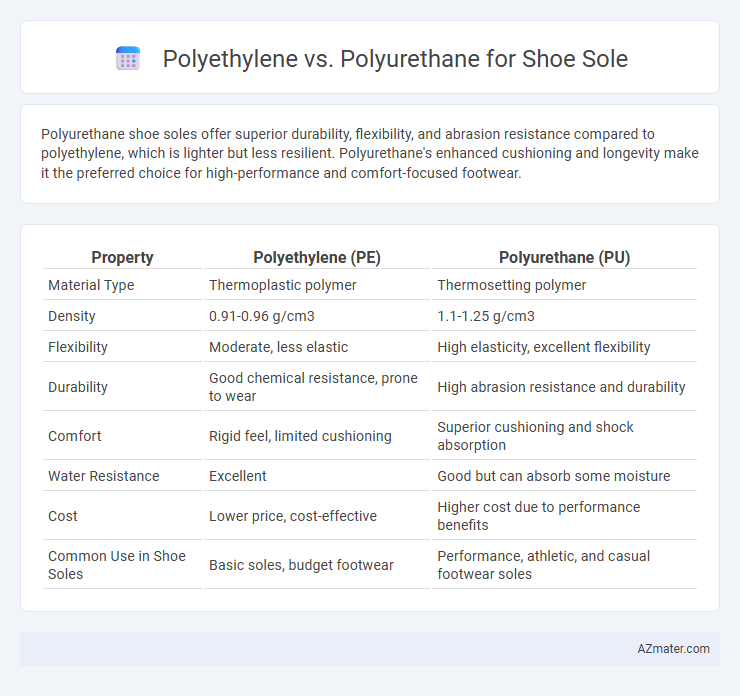
Polyurethane shoe soles offer superior durability, flexibility, and abrasion resistance compared to polyethylene, which is lighter but less resilient. Polyurethane's enhanced cushioning and longevity make it the preferred choice for high-performance and comfort-focused footwear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermosetting polymer |
| Density | 0.91-0.96 g/cm3 | 1.1-1.25 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Moderate, less elastic | High elasticity, excellent flexibility |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, prone to wear | High abrasion resistance and durability |
| Comfort | Rigid feel, limited cushioning | Superior cushioning and shock absorption |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good but can absorb some moisture |
| Cost | Lower price, cost-effective | Higher cost due to performance benefits |
| Common Use in Shoe Soles | Basic soles, budget footwear | Performance, athletic, and casual footwear soles |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polyurethane
Polyethylene is a lightweight, durable thermoplastic known for its chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for flexible shoe soles that require resilience and water resistance. Polyurethane is a versatile polymer characterized by excellent abrasion resistance, high elasticity, and superior cushioning properties, often preferred for high-performance shoe soles to enhance comfort and durability. Comparing polyethylene and polyurethane, polyurethane generally offers better shock absorption and wear resistance, while polyethylene provides a cost-effective, water-resistant alternative with good flexibility.
Material Composition and Properties
Polyethylene (PE) shoe soles are composed primarily of long-chain hydrocarbons, offering excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and high stiffness, making them durable but less flexible. Polyurethane (PU) soles consist of a polymer formed by reacting diisocyanates with polyols, providing superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and shock absorption ideal for comfort and performance. The material composition of PU enables better cushioning and flexibility compared to the rigid and lightweight nature of polyethylene, influencing their application in various footwear designs.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Polyurethane shoe soles exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to polyethylene soles due to their enhanced abrasion resistance and flexibility, which withstands repeated stress and wear. Polyurethane's inherent elasticity allows it to absorb impact better, reducing sole degradation over time and maintaining structural integrity in various environmental conditions. Polyethylene soles, while cost-effective, tend to crack and harden faster under prolonged use, resulting in shorter lifespan and decreased performance in high-activity footwear.
Comfort and Cushioning Differences
Polyurethane offers superior cushioning and shock absorption compared to polyethylene, making it a preferred choice for shoe soles that prioritize comfort during extended wear. Polyurethane's flexible and resilient properties provide enhanced support, reducing foot fatigue and improving overall comfort. Polyethylene, being more rigid and less elastic, typically delivers lower cushioning performance, thus feeling firmer underfoot and less suitable for high-impact activities.
Weight Considerations for Shoe Soles
Polyurethane shoe soles are generally lighter than polyethylene soles, offering improved comfort and reduced fatigue during extended wear. Polyurethane's lower density and higher flexibility contribute to better shock absorption and cushioning, enhancing overall performance. While polyethylene soles are durable and cost-effective, their increased weight can lead to less agility and slower response times in athletic or casual footwear.
Slip Resistance and Traction
Polyurethane shoe soles typically offer superior slip resistance and traction compared to polyethylene due to their higher flexibility and abrasion resistance. Polyurethane's ability to maintain grip on wet or oily surfaces makes it ideal for safety footwear and outdoor use. Polyethylene soles, while lightweight and durable, often lack the same level of slip control, making them less suitable for environments requiring maximum traction.
Flexibility and Performance in Footwear
Polyurethane outperforms polyethylene in shoe sole flexibility due to its superior elasticity and resilience, allowing for enhanced comfort and dynamic movement during wear. The material's ability to absorb impact and resist abrasion makes polyurethane soles ideal for high-performance footwear requiring both durability and cushioning. Polyethylene soles, while cost-effective and resistant to chemicals, tend to be stiffer and less adaptable, limiting their use in shoes designed for active or prolonged wear.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane shoe soles typically offer superior durability and flexibility but pose greater environmental challenges due to their reliance on petroleum-based chemicals and difficulty in recycling. Polyethylene soles, while less common in footwear, tend to have a lower carbon footprint and are more amenable to recycling processes, enhancing their sustainability profile. Choosing polyethylene over polyurethane can reduce toxic emissions and support circular economy practices in the footwear industry.
Cost Analysis in Manufacturing
Polyethylene offers a lower raw material cost and faster processing time, making it more economical for large-scale shoe sole manufacturing. Polyurethane exhibits superior durability and flexibility but incurs higher production expenses due to complex curing processes and specialized machinery. Manufacturers prioritize polyethylene when minimizing costs, while polyurethane is favored for premium, performance-oriented footwear despite the increased investment.
Best Applications for Each Material
Polyurethane excels in shoe soles requiring flexibility, durability, and shock absorption, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear. Polyethylene, known for its rigidity and chemical resistance, suits industrial or safety shoes where protection against harsh environments is critical. Selecting the appropriate material depends on balancing comfort, wear resistance, and specific application demands.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polyurethane for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com