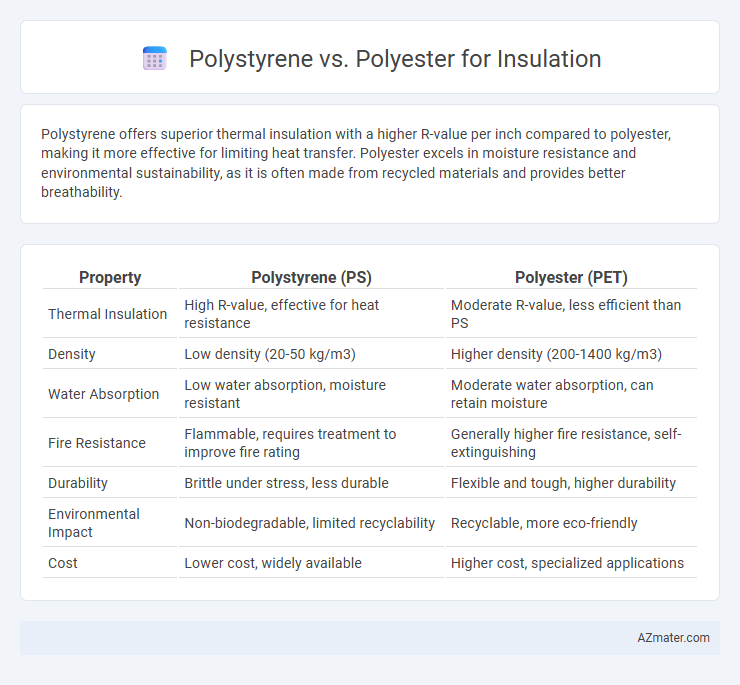
Polystyrene offers superior thermal insulation with a higher R-value per inch compared to polyester, making it more effective for limiting heat transfer. Polyester excels in moisture resistance and environmental sustainability, as it is often made from recycled materials and provides better breathability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polyester (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High R-value, effective for heat resistance | Moderate R-value, less efficient than PS |
| Density | Low density (20-50 kg/m3) | Higher density (200-1400 kg/m3) |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption, moisture resistant | Moderate water absorption, can retain moisture |
| Fire Resistance | Flammable, requires treatment to improve fire rating | Generally higher fire resistance, self-extinguishing |
| Durability | Brittle under stress, less durable | Flexible and tough, higher durability |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, limited recyclability | Recyclable, more eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized applications |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Polystyrene and polyester are two prominent insulation materials widely used in construction for thermal efficiency. Polystyrene, available as expanded (EPS) or extruded (XPS) foam, offers high rigidity, excellent moisture resistance, and an R-value typically ranging from 3.6 to 5 per inch. Polyester insulation, made from recycled fibers, provides sound absorption, flexibility, and an R-value around 3.2 to 3.8 per inch, making it ideal for eco-friendly applications and indoor environments.
Understanding Polystyrene: Types and Properties
Polystyrene insulation is available in two primary types: expanded polystyrene (EPS) and extruded polystyrene (XPS), each with distinct thermal resistance and moisture absorption characteristics. EPS offers a lower R-value per inch but is more cost-effective and breathable, making it suitable for wall cavities, while XPS provides higher R-value and superior moisture resistance, ideal for foundation and below-grade applications. Both types possess excellent compressive strength and long-term durability, contributing to energy efficiency and structural protection in building insulation.
Polyester Insulation: Composition and Characteristics
Polyester insulation is composed primarily of synthetic fibers derived from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it lightweight, flexible, and resistant to moisture and mold. Its open fiber structure enhances breathability and thermal performance, providing effective insulation in various applications. Unlike polystyrene, polyester insulation offers superior sound absorption and is often favored for eco-friendly building projects due to its recyclability and low environmental impact.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polystyrene insulation, available in expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) forms, offers thermal conductivity values typically ranging from 0.029 to 0.040 W/m*K, providing effective resistance against heat transfer in building envelopes. Polyester insulation, made from recycled PET fibers, has a thermal conductivity generally around 0.038 to 0.043 W/m*K, which is slightly higher than polystyrene, indicating marginally lower thermal performance. Polystyrene's lower thermal conductivity and higher R-values make it a preferred choice for applications requiring superior thermal insulation efficiency.
Moisture Resistance: Polystyrene vs Polyester
Polystyrene insulation exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, which minimizes water absorption and maintains insulating properties in damp environments. Polyester insulation, being more porous, tends to absorb moisture, potentially reducing its thermal efficiency and promoting mold growth. For applications requiring high moisture resistance, polystyrene is generally the preferred material.
Durability and Longevity
Polystyrene insulation offers exceptional durability due to its rigid, closed-cell structure, making it resistant to moisture, compression, and environmental wear over time. Polyester insulation, while flexible and resistant to mold and mildew, tends to have a shorter lifespan as it may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to heat and moisture. For long-term insulation solutions, polystyrene provides greater longevity and sustained thermal performance in demanding conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polystyrene insulation, derived from petroleum, poses environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradability and difficulty in recycling, contributing to landfill waste and microplastic pollution. Polyester insulation, often made from recycled plastic bottles, offers a more sustainable alternative with better recyclability and a lower carbon footprint throughout its lifecycle. Choosing polyester enhances environmental sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting circular economy practices in building materials.
Installation and Handling Differences
Polystyrene insulation is lightweight, rigid, and easy to cut, making installation straightforward with simple tools and minimal training, whereas polyester insulation is flexible, requiring careful handling to avoid compression and maintaining thickness for optimal performance. Polystyrene panels can be securely fitted into place using adhesive or mechanical fasteners, while polyester batts often need precise measuring and careful placement within framing cavities to prevent gaps. Handling polyester requires protective gear due to potential skin irritation from fibers, unlike polystyrene, which is non-irritant and produces little dust during installation.
Cost Analysis: Polystyrene vs Polyester
Polystyrene insulation typically offers a lower initial cost compared to polyester, making it a budget-friendly option for many construction projects. However, polyester insulation provides better long-term value due to its superior durability, moisture resistance, and environmental benefits, often resulting in reduced maintenance and replacement expenses. When analyzing cost effectiveness, factoring in lifecycle expenses such as energy savings and replacement frequency favors polyester despite its higher upfront price.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Needs
Polystyrene insulation offers excellent moisture resistance and high compressive strength, making it ideal for below-grade and basement applications. Polyester insulation provides superior sound absorption and eco-friendly benefits due to its recycled content, suitable for interior walls and noise reduction. Selecting the right insulation depends on factors like moisture exposure, thermal performance, soundproofing needs, and environmental impact.
Infographic: Polystyrene vs Polyester for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com