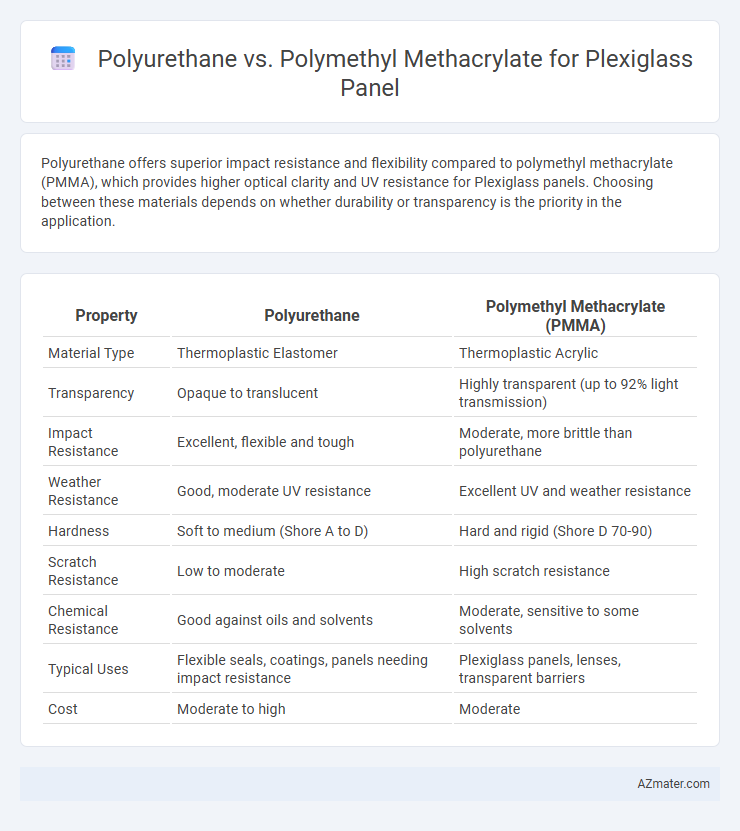
Polyurethane offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which provides higher optical clarity and UV resistance for Plexiglass panels. Choosing between these materials depends on whether durability or transparency is the priority in the application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Elastomer | Thermoplastic Acrylic |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent (up to 92% light transmission) |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, flexible and tough | Moderate, more brittle than polyurethane |
| Weather Resistance | Good, moderate UV resistance | Excellent UV and weather resistance |
| Hardness | Soft to medium (Shore A to D) | Hard and rigid (Shore D 70-90) |
| Scratch Resistance | Low to moderate | High scratch resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against oils and solvents | Moderate, sensitive to some solvents |
| Typical Uses | Flexible seals, coatings, panels needing impact resistance | Plexiglass panels, lenses, transparent barriers |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Plexiglass Panel Materials
Plexiglass panels primarily consist of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), a transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring clear, durable glazing. Polyurethane, while less common for transparent panels, offers superior flexibility and impact resistance, often used in protective coatings or laminates rather than solid panels. Understanding the material differences is crucial for selecting Plexiglass panels based on clarity, durability, and environmental exposure.
Overview of Polyurethane and Polymethyl Methacrylate
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer known for its elasticity, toughness, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for flexible and impact-resistant plexiglass panels. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), commonly called acrylic or plexiglass, is a rigid, transparent thermoplastic valued for its optical clarity, UV resistance, and weather durability. Both compounds serve distinct roles in plexiglass manufacturing, with polyurethane favored for flexibility and impact absorption, while PMMA excels in stiffness and visual clarity.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyurethane consists of repeating urethane linkages formed by the reaction of diisocyanates with polyols, providing flexibility and abrasion resistance in Plexiglass panels. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic polymer composed of methyl methacrylate monomers linked through polymerization, resulting in a rigid and glass-like structure. The distinct chemical structures influence their performance: polyurethane offers elasticity and impact resistance, while PMMA delivers high optical clarity and hardness in Plexiglass applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyurethane exhibits greater elasticity and impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it more suitable for applications requiring flexibility and toughness. PMMA offers superior hardness and scratch resistance, but it is more brittle and prone to cracking under high mechanical stress. The choice between polyurethane and PMMA for Plexiglass panels depends on balancing the need for impact durability with surface hardness and resistance to fracture.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity and transparency compared to polyurethane, making it the preferred choice for Plexiglass panels where visual performance is critical. PMMA exhibits high light transmittance of approximately 92%, with minimal yellowing over time, ensuring consistent clarity for applications such as windows and display cases. Polyurethane, while durable and impact-resistant, generally shows lower light transmittance and can become hazy or yellow under prolonged UV exposure, reducing its effectiveness for clear panel applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Polyurethane provides superior durability and excellent weather resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for outdoor Plexiglass panels exposed to harsh conditions. PMMA offers high clarity and UV resistance but can be more prone to scratching and may degrade faster under prolonged weather exposure. The chemical structure of polyurethane grants enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, resulting in longer lifespan and better performance in extreme temperatures and moisture.
Ease of Fabrication and Installation
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it easier to fabricate into complex shapes without cracking. PMMA, known for its rigidity and clarity, requires more precise cutting and drilling to avoid chipping during installation. While PMMA panels provide excellent UV resistance and optical clarity, polyurethane panels facilitate quicker installation due to their lightweight and adaptable nature.
Cost Analysis: Polyurethane vs PMMA
Polyurethane panels typically offer a lower initial cost compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), making them more budget-friendly for large-scale projects. PMMA, known for its superior clarity and UV resistance, often incurs higher expenses due to advanced manufacturing processes and raw material quality. Long-term cost analysis reveals that while PMMA may have a higher upfront investment, its durability and weather resistance can reduce maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Polyurethane is frequently used for impact-resistant coatings and flexible protective layers in construction and automotive industries, providing durability and UV resistance. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, excels in optical clarity and weather resistance, making it ideal for signage, display panels, and skylights. Both materials serve in protective glazing, but polyurethane offers superior flexibility while PMMA is preferred for rigid, transparent applications.
Which Material is Best for Your Plexiglass Panels?
Polyurethane offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for Plexiglass panels requiring durability and shock absorption. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent optical clarity and weather resistance, preferred for applications demanding transparency and UV stability. Choosing between them depends on whether durability or clarity is the priority for your Plexiglass panel application.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polymethyl Methacrylate for Plexiglass Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com