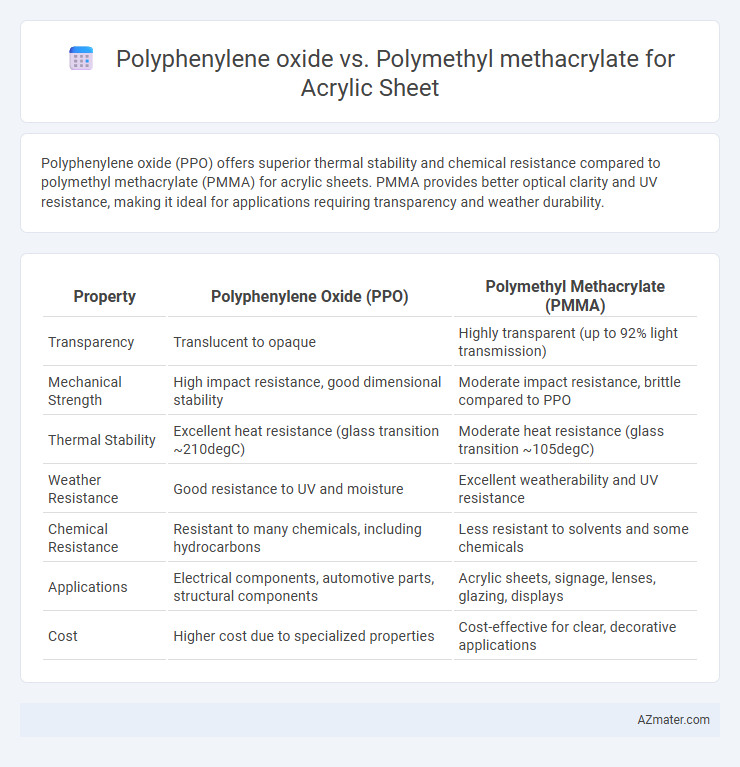
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) for acrylic sheets. PMMA provides better optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and weather durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Translucent to opaque | Highly transparent (up to 92% light transmission) |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact resistance, good dimensional stability | Moderate impact resistance, brittle compared to PPO |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent heat resistance (glass transition ~210degC) | Moderate heat resistance (glass transition ~105degC) |
| Weather Resistance | Good resistance to UV and moisture | Excellent weatherability and UV resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to many chemicals, including hydrocarbons | Less resistant to solvents and some chemicals |
| Applications | Electrical components, automotive parts, structural components | Acrylic sheets, signage, lenses, glazing, displays |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties | Cost-effective for clear, decorative applications |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide and Polymethyl Methacrylate
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for excellent dimensional stability, high heat resistance up to 150degC, and superior electrical insulating properties, making it suitable for demanding applications in automotive and electronics industries. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly referred to as acrylic or acrylic glass, offers outstanding optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, often utilized in glazing, signage, and display panels. When comparing acrylic sheets, PPO provides enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, whereas PMMA excels in transparency and ease of fabrication.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a backbone of alternating oxygen and phenylene groups, providing high thermal stability and excellent dimensional stability for acrylic sheets. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) possesses a linear structure with methyl methacrylate units, offering superior optical clarity and UV resistance but lower heat resistance compared to PPO. The aromatic rings in PPO's structure enhance mechanical strength and chemical resistance, while PMMA's ester groups contribute to its transparency and ease of fabrication.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability. PMMA offers excellent rigidity and surface hardness but is more prone to cracking under stress, limiting its long-term structural performance. PPO's higher tensile strength and better thermal stability contribute to greater durability in demanding environments, while PMMA remains favored for its clarity and weather resistance in less mechanically intensive uses.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent dimensional stability and heat resistance but has lower optical clarity compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which is renowned for its superior transparency and light transmittance of up to 92%. PMMA acrylic sheets provide exceptional optical clarity with minimal haze, making them ideal for applications requiring clear visibility, while PPO sheets tend to have a slightly cloudy appearance due to their molecular structure. For projects prioritizing maximum transparency and aesthetic appeal, PMMA is the preferred choice over PPO.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in acrylic sheet applications, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 190degC. PMMA typically softens around 100degC to 120degC, limiting its use in high-heat environments. PPO's enhanced dimensional stability and lower thermal expansion coefficient make it ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures.
Weatherability and UV Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior weatherability and UV resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in acrylic sheet applications due to its aromatic backbone structure that minimizes degradation under prolonged sunlight exposure. PMMA provides excellent initial clarity and UV resistance but tends to yellow and degrade faster under continuous UV radiation, limiting its long-term outdoor performance. PPO's enhanced stability ensures better retention of mechanical properties and optical clarity, making it more suitable for demanding exterior environments.
Chemical and Water Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior chemical resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for applications involving exposure to solvents, acids, and alkalis. PPO exhibits excellent water resistance with minimal moisture absorption, whereas PMMA tends to absorb more water, potentially compromising its mechanical properties over time. Consequently, PPO is preferred for environments demanding high chemical and water durability in acrylic sheet materials.
Ease of Fabrication and Processing
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and dimensional accuracy during fabrication, making it ideal for precision applications in acrylic sheets. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) excels with its excellent clarity and ease of thermoforming, enabling efficient processing using standard plastic fabrication techniques. While PPO requires controlled processing conditions due to its higher melting point, PMMA's lower processing temperatures reduce energy consumption and simplify manufacturing workflows.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), but PMMA acrylic sheets are generally more cost-efficient due to lower raw material and processing expenses. PMMA dominates market availability with widespread production and extensive use in glazing, signage, and displays, whereas PPO remains niche with limited suppliers and higher price points. Choosing PMMA acrylic sheets maximizes cost efficiency and accessibility for large-scale commercial and industrial applications.
Applications: Choosing the Right Material for Acrylic Sheets
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for acrylic sheet applications requiring durability in harsh environments such as automotive components and electrical housings. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) excels in optical clarity and weather resistance, preferred for transparent signs, displays, and skylights where light transmission and UV stability are critical. Selecting between PPO and PMMA depends on the balance of mechanical strength, environmental exposure, and optical requirements specific to the intended acrylic sheet application.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Acrylic Sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com